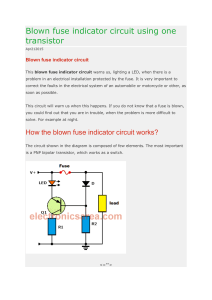
Blown fuse indicator circuit using one transistor Apr212015 Blown fuse indicator circuit This blown fuse indicator circuit warns us, lighting a LED, when there is a problem in an electrical installation protected by the fuse. It is very important to correct the faults in the electrical system of an automobile or motorcycle or other, as soon as possible. This circuit will warn us when this happens. If you do not know that a fuse is blown, you could find out that you are in trouble, when the problem is more difficult to solve. For example at night. How the blown fuse indicator circuit works? The circuit shown in the diagram is composed of few elements. The most important is a PNP bipolar transistor, which works as a switch. <=""> If V+ is present and the fuse is in good condition, the transistor will be in the cut off region and it will not conduct. (see that the voltage at the base of the transistor is V+ – 0.7 volts) and consequently the LED does not light up. When the fuse blows, no current flows through it and the voltage level at the base of transistor decreases to zero volts. The transistor enters the saturation region (there is an electrical current that flows through the emitter and collector), LED lights up, warning that there is a problem. There are many fuses in the electrical system of a car. To have a general control of all fuses, you can implement a parallel arrangement of this circuit. This circuit can also be used in toys, car radios, and in almost any DC or battery powered circuit. List of components for the Blown fuse indicator circuit 1 PNP bipolar transistor or BJT, BC558, NTE159 (Q1) 1 1N4001 or 1N4148 semiconductor diode (D1) 1 red LED 1 510 ohms resistor (R1) 1 510 K resistor (R2) The circuit is powered from the same DC source, the load use.