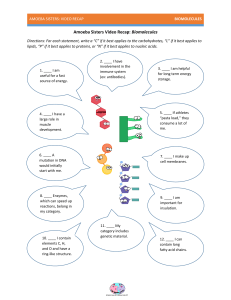
AMOEBA SISTERS: VIDEO RECAP MITOSIS: THE AMAZING CELL PROCESS THAT USES DIVISION TO MULTIPLY Summative assessments: Visualisation or model of meiosis/mitosis EVOLUTION Test - Evolution and Genetics Lab report – How can evolution be modeled? AND GENETICS How does the environment interact with genes to show variation in organisms and what are the consequences when genes and/or the environment changes? “Man selects only for his own good: Nature only for that of the being which she tends.” ― Charles Darwin, The Origin of Species 0 AMOEBA SISTERS: VIDEO RECAP MITOSIS: THE AMAZING CELL PROCESS THAT USES DIVISION TO MULTIPLY Table of Contents Introduction ..............................................................................................2 Part 1 - Evolution ........................................................................................3 Formative assessment – Beak adaptation lab (peer reviewed) ....................................6 Criterion B+C – design your own experiment ...................................................... 10 Part 2 – Meiosis / mitosis ............................................................................. 13 Amoeba Sisters Video Recap of Mitosis .......................................................... 13 Amoeba Sisters Video Recap of Meiosis ............................................................. 15 Part 3 – Genetics ....................................................................................... 17 Monohybrid crossings ............................................................................... 18 Practice monohybrid punnet squares ............................................................ 18 Practice crosses and ratios ........................................................................ 19 Monohybrid Crosses Practice ...................................................................... 21 Codominance and Incomplete Dominance (intermediate) .................................... 25 Practice Problems – Sex Linkage .................................................................. 29 Dihybrid cross........................................................................................ 33 Beyond Mendel – Codominance, Multiple Alleles, and Polygenic Traits ................. 37 Pedigree .............................................................................................. 39 1 AMOEBA SISTERS: VIDEO RECAP MITOSIS: THE AMAZING CELL PROCESS THAT USES DIVISION TO MULTIPLY Introduction In the following weeks we are going to explore the evolution theory and genetics to understand the inquiry; “How did we evolve into the species we are now”. In order for us to answer this question we need understanding in evolution and genetics and the mechanisms involved. Part one will consist of several experiments and other investigations to understand the concept natural selection, the driving force behind evolution. You will investigate Darwin and his theory and how it changed to the widely accepted theory we are using today. Part two will give a brief introduction into meiosis (and mitosis) as this is important in understanding how DNA is passed on to our offspring and how meiosis accounts for variation. Part three will zoom in on genetics. You will understand how the variations occurring through natural selection are passed on to offspring and how they find a way in the population. 2 MITOSIS: THE AMAZING CELL PROCESS THAT USES DIVISION TO MULTIPLY AMOEBA SISTERS: VIDEO RECAP Part 1 - Evolution 1. What is meant by the term adaptation? 2. Name one animal and one plant with which you are familiar, and describe how each is adapted to its environment. 3. Using only the following information, answer questions A to D. Cepaea is a type of snail which shows considerable variation in its shell colour. The basic colour can be yellow, brown, fawn, pink, orange or red. Over the top of this basic colour up to five bands of a darker colour may occur, around the shell. Colour of shell provides camouflage for the snail because some colours are more difficult to see than others against the background. Cepaea is an important part of the diet of thrushes. These birds collect snails and break open their shells by banging them on a stone. Thrushes tend to use the same stone, called an ‘anvil’ , whenever feeding in a particular area. It is possible to collect the remains of the shells and count the number of each shell type. It is also possible to collect the live snails in the same area and count the numbers of each shell type. Collections of both live snails and broken shells were made in an area where the ground layer plants gave a fairly evenly coloured background. The results are shown in the table. Live snails Shell remains Banded 264 486 Number Unbanded 296 377 of snails Total 560 863 % Banded 47.0 56.0 a) How many more live, unbanded Cepeae were collected than banded? b) Suggest an explanation for thrushes taking more banded snails even where there appear to be more unbanded snails in the live populations. c) Which type of shell, banded or unbanded, would you expect to occur most frequently in a live snail population i. Amongst dead leaves in a wood? ii. Amongst grasses growing on a sand dune? d) The main points of the theory of evolution by natural selection are listed below A The number of offspring is far greater than the number surviving to adult stage B Variations exist among the offspring C Some variations are useful and help the organisms to survive D Competition occurs between the offspring E Only those surviving can breed Natural selection can change the proportions of the different colours in a snail population. Use the five points A to E above to describe how this change might come about. 3 MITOSIS: THE AMAZING CELL PROCESS THAT USES DIVISION TO MULTIPLY AMOEBA SISTERS: VIDEO RECAP Amoeba Sisters Video Recap: Natural Selection 1. Populations can have variety, despite being made up of the same species. If a population has different expressed traits, this can be due to different inherited alleles. The frogs below are the same species, but they have different shades of green based on their inherited alleles. In a particular environment, lighter green frogs are easier to see by predators. Explain how natural selection could lead to a change in allele frequency. 2. Natural selection is an example of a mechanism of evolution. Does this mechanism produce a change in individuals or populations? Explain! 3. A major point of understanding natural selection is that not all organisms in a population get to reproduce. Consider the term fitness as used in biology. How does this term relate to natural selection? 4. Based on your answer above, do organisms with higher fitness mean that they have survived to an advanced age? Why or why not? 4 AMOEBA SISTERS: VIDEO RECAP MITOSIS: THE AMAZING CELL PROCESS THAT USES DIVISION TO MULTIPLY 5. Does fitness (as used in biology) and survival have the same meaning? Why or why not? 6. If an organism has high biological fitness in one environment, does that mean that it would also have high biological fitness in another environment? Why or why not? 7. Two students are discussing natural selection in bacteria and how it can relate to antibiotic resistance in bacteria. Bernadette states that when antibiotics are used, bacteria can respond by developing traits to help them defeat the antibiotic, which then may increase their fitness. Dominique states that there is already a variety of traits among the bacteria. Bacteria that have traits that allow them to survive the antibiotic and reproduce may have higher fitness. Which individual's reasoning do you agree with more and why? 8. A major misconception about natural selection is that this mechanism “gives organisms what they want or need so they can adapt to an environment.” Explain why this is not correct. 9. Consider a major environmental change. If there are not organisms in a population that have traits that allow them to still continue to survive to reproduce, what would likely happen to that population? 5 MITOSIS: THE AMAZING CELL PROCESS THAT USES DIVISION TO MULTIPLY AMOEBA SISTERS: VIDEO RECAP Formative assessment – Beak adaptation lab (peer reviewed) Problem statement: you are going to mimic how the variations of Darwin’s finches compete for the same food sources. Pretend that the brown coloured beans are seeds for the birds. Natural selection happens when a population changes in response to their environment. Hypothesis: If I had the ___________________ adaptation, then I would be the most fit for survival in the grass environment. Materials and procedure: explained by teacher Data: Beans brown Knife Spoon 1st generation Fork Taped Hand Total -100= Beans brown Knife Spoon 2nd generation Fork Taped Hand Total -100= Beans brown Knife Spoon 3rd generation Fork Taped Hand Total -100= Beans brown Knife Spoon 4th generation Fork Taped Hand Total -100= Graphing: Create one line graph with the generation on the x-axis and the total number of beans on the y-axis. Use a legend and colored pencils to graph all five of the five-beaked adaptations Analysis: 1) Independent variable:_________________________________________________ Dependent variable: _________________________________________________ Controlled variables: _________________________________________________ 2) Which finch became extinct first and explain why it was not the best adapted for survival? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 3) Which finch was best adapted for survival? ___________________________________ 6 AMOEBA SISTERS: VIDEO RECAP MITOSIS: THE AMAZING CELL PROCESS THAT USES DIVISION TO MULTIPLY 4) Why was the brown beans (seeds) well adapted in the grass environment? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 5) If white or red beans (seeds) were introduced into the grass, which seeds would you think would be eaten the most?____________________ Explain why? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 6) Would the length of the grass affect which adaptation was better suited for the collecting beans? If so, explain which adaptation would most be affected for short or long grass. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 7) In this lab we had only one environment, the ___________________. Four adaptations became extinct in that environment, but on the Galapagos islands, there were many surviving species of finches. How might the finches in this lab avoid extinction due to competition? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 8) Conclusion: explain about how natural selection leads to adaptation of populations using the following terms: population, environment, competition, fittest, adaptation and selection. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 7 AMOEBA SISTERS: VIDEO RECAP MITOSIS: THE AMAZING CELL PROCESS THAT USES DIVISION TO MULTIPLY Peer review You will grade each other’s work in pairs according to the following procedure 1. You form a group of 3 2. You will check each other’s work in a rotation set up and you will award points to each question, use the table below to see how many points you can award each question Question # points to be awarded Graph 1 point for a correct title (1/2 point also possible for a title) 1 point for labelling both y AND x-axis (1/2 point for 1) 1 point for correct values (scale) 1 point for a completed graph with all 5 lines 1 point for a correct legend Q1 2 points (-1 for each mistake, 0 points with only 1 correct answer) Q2 2 points (depending on explanation) Q3 1 point Q4 2 points (depending on explanation) Q5 2 points (depending on explanation) Q6 2 points (depending on explanation) Q7 2 points (depending on explanation) Q8 6 points, check if all mentioned words are used in the correct way. Each correctly used/explained word in relation to the question will count as 1 point 3. You will use a premade format (next page) to fill in the points given to your peers, after you have checked both you will discuss in your group a final decision on how many points may be awarded for each answer. This is called standardizing and it ensures that a fair grade can be given. 4. The given grade will appear on managebac as a formative grade, teacher will randomly select a couple graded papers to standardize further. 8 AMOEBA SISTERS: VIDEO RECAP MITOSIS: THE AMAZING CELL PROCESS THAT USES DIVISION TO MULTIPLY Peer review format Name of person who is being graded:_____________________________ Peer review 1 done by: _______________________________ Peer review 2 done by: _______________________________ Question #points given by peer reviewer 1 #points given by peer reviewer 2 Final decision #points Graph Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q5 Q6 Q7 Q8 Total Comments by peer reviewer 1: ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ Comments by peer reviewer 2: ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 9 AMOEBA SISTERS: VIDEO RECAP MITOSIS: THE AMAZING CELL PROCESS THAT USES DIVISION TO MULTIPLY Criterion B+C – design your own experiment In the Finch adaptions lab we have seen how natural selection works in regards with food sources and how natural selection in turn leads to adaptation of populations. This one was about the beak of the birds. You are now going to design your own experiment about natural selection specified on the importance of coloration. How did evolution give certain animals their specific colour? And how can you show with an experiment that certain coloured animals would have a really hard time surviving? - Individual assignment Include ALL parts of a lab report Experiment will be conducted! 10 MITOSIS: THE AMAZING CELL PROCESS THAT USES DIVISION TO MULTIPLY AMOEBA SISTERS: VIDEO RECAP Achievement level 0 1-2 Level descriptor B The student does not reach a standard described by any of the descriptors below. The student is able to: 3-4 The student is able to: 5-6 outline a problem or question to be tested by a scientific investigation formulate a testable hypothesis using scientific reasoning outline how to manipulate the variables, and outline how relevant data will be collected design a safe method in which he/she selects material and equipment The student is able to: 7-8 state a problem or question to be tested by a scientific investigation outline a testable hypothesis outline the variables design a method, with limited success describe a problem or question to be tested by a scientific investigation formulate and explain a testable hypothesis using scientific reasoning describe how to manipulate the variables, and describe how sufficient, relevant data will be collected design a complete and safe method in which he/she selects appropriate material and equipment The student is able to: explain a problem or question to be tested by a scientific investigation formulate and explain a testable hypothesis using correct scientific reasoning explain how to manipulate the variables, and explain how sufficient, relevant data will be collected design a logical, complete and safe method in which he/she selects appropriate material and equipment 11 MITOSIS: THE AMAZING CELL PROCESS THAT USES DIVISION TO MULTIPLY AMOEBA SISTERS: VIDEO RECAP Achievement level 0 1-2 Level descriptor C The student does not reach a standard described by any of the descriptors below. The student is able to: 3-4 The student is able to: 5-6 correctly collect and present data in numerical and/or visual forms accurately interpret data and explain results outline the validity of a hypothesis based on the outcome of a scientific investigation outline the validity of the method based on the outcome of a scientific investigation outline improvements or extensions to the method The student is able to: 7-8 collect and present data in numerical and/or visual forms interpret data state the validity of a hypothesis based on the outcome of a scientific investigation state the validity of the method based on the outcome of a scientific investigation state improvements or extensions to the method correctly collect, organize and present data in numerical and/or visual forms accurately interpret data and explain results using scientific reasoning discuss the validity of a hypothesis based on the outcome of a scientific investigation discuss the validity of the method based on the outcome of a scientific investigation describe improvements or extensions to the method that would benefit the scientific investigation The student is able to: correctly collect, organize, transform and present data in numerical and/or visual forms accurately interpret data and explain results using correct scientific reasoning evaluate the validity of a hypothesis based on the outcome of a scientific investigation evaluate the validity of the method based on the outcome of a scientific investigation explain improvements or extensions to the method that would benefit the scientific investigation 12 MITOSIS: THE AMAZING CELL PROCESS THAT USES DIVISION TO MULTIPLY AMOEBA SISTERS: VIDEO RECAP Part 2 – Meiosis / mitosis Amoeba Sisters Video Recap of Mitosis: The Amazing Cell Process That Uses Division to Multiply 1. Mitosis is done by your body cells. What types of cells do not undergo mitosis? 2. Describe 2 ways that mitosis is important for your body. 3. This illustration is trying to demonstrate something that mitosis is not. In mitosis, the cells that are created are 4. Mitosis is just one small part of the cell cycle! Describe what would occur if cells were in mitosis more than they were in interphase. 5. When cells are dividing, it is important to understand that they have to move chromosomes equally to both cells. Based on this illustration, describe what a chromosome is made of. 6. Mitosis starts and ends with diploid cells. That means they have two sets of chromosomes (both parents each contribute a set). In humans, how many chromosomes should be in each of these diploid cells after mitosis? 13 AMOEBA SISTERS: VIDEO RECAP MITOSIS: THE AMAZING CELL PROCESS THAT USES DIVISION TO MULTIPLY Sketch the Mitotic Stages Directions: We encourage you to be creative with a cartoon illustration of your own for each phase. Label the chromosomes, spindles, and nucleus (if applicable). Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase 14 AMOEBA SISTERS: VIDEO RECAP MITOSIS: THE AMAZING CELL PROCESS THAT USES DIVISION TO MULTIPLY Amoeba Sisters Video Recap of Meiosis 1. The purpose of meiosis is to make gametes, also known as sperm and egg cells. In humans, your body cells have 46 chromosomes. How many chromosomes are in a sperm or egg cell if, when they come together to form a fertilized zygote, there are 46 chromosomes? Write the correct number of chromosomes next to the sperm and egg. 2. Interphase must occur once before meiosis can happen. (Same thing for mitosis). What would happen if interphase didn’t occur first? 3. A cell that begins meiosis has 23 chromosomes inherited from the mother (shown in green in the cartoon below) and 23 chromosomes inherited from the father (shown in blue in the cartoon below). In the process of meiosis, chromosomes begin to match up in homologous pairs. How would you know if two chromosomes were homologous? 4. Crossing over is a very important event in Prophase I of meiosis! What happens during crossing over and what is the significance? 5. Meiosis does PMAT twice! That means there is a prophase I and a prophase II. There is a metaphase I and a metaphase II. Etc… If the cartoon below has chromosomes in the middle of the cell, how would you know whether it was in metaphase I or metaphase II? 6. Meiosis does not always occur without any difficulties. Describe what occurs during nondisjunction and the effect on the resulting cells. 15 MITOSIS: THE AMAZING CELL PROCESS THAT USES DIVISION TO MULTIPLY AMOEBA SISTERS: VIDEO RECAP Can you finish the meiosis chain? Write the correct stage that comes next in each circle. Don’t forget the number that comes after the stage name! Then write any details about what this stage looks like next to it. Now let’s play, “Which Clip Would That Be Said In?” Keeping mitosis and meiosis separate in your mind can be a bit tricky. Read the following speech bubbles. Determine whether they would be correctly placed in the mitosis clip, the meiosis clip, or both by drawing a line to the correct place in the Venn diagram. Interphase occurs once before the process begins. Process ends with identical cells. Produces gametes Produces 4 cells that each have 23 chromosomes. Crossing over occurs Process is important for growth and repair 16 AMOEBA SISTERS: VIDEO RECAP MITOSIS: THE AMAZING CELL PROCESS THAT USES DIVISION TO MULTIPLY Part 3 – Genetics 1. Use examples to explain the difference between continuous and discontinuous variation ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 2. a) Explain the term mutation _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ b) State two examples of mutation in humans _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ c) Explain why genetic variation is important _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 3. Explain the difference between genotype and phenotype ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 4. Explain the difference between gene and allele ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 17 MITOSIS: THE AMAZING CELL PROCESS THAT USES DIVISION TO MULTIPLY AMOEBA SISTERS: VIDEO RECAP Monohybrid crossings Practice monohybrid punnet squares Use your knowledge of genes and inheritance to determine the probability of any offspring of these superheroes having their powers (mutated genes). Write down the ratios and the percentage of chances of having the specific ability. h = allele for the power to heal f = allele ability to fly m = allele for mind reading powers s = allele for super strength l =allele for laser eyes o = allele for the ability to control the weather w = allele for the ability to climb up walls Remember: Mutated genes are recessive For each match and each superpower figure out the probability of inheriting that superpower Jean Grey Hh ff Wolverine X hh Ff mm MM Ss ss Rogue ff Ss LL Superman ff X Storm ss ll ff Cyclops FF LL ll oo X OO 18 MITOSIS: THE AMAZING CELL PROCESS THAT USES DIVISION TO MULTIPLY AMOEBA SISTERS: VIDEO RECAP Practice crosses and ratios 1. a) Brown eye colour is dominant. If a woman is homozygous for brown eyes, what is her genotype going to be? (BB, Bb or bb) b) Blue eye colour is recessive on the same Allele as Brown eyes. If a man has blue eyes, he must be homozygous. What is his genotype? (BB, Bb or bb) c) The woman from part a, and the man from part b have a child. Fill in this punnett square. In the grey squares you should put the Alleles of the mother and father. Mother Father d) What is the fraction ( __/4) of Brown eyed children? e) What is the ratio? ___________ 2. A flower arranger is growing some flowers in a garden. He has seeds for red, and seeds for pink plants. Both colours are found on the same allele as each other. Red is the dominant colour, while pink is recessive. a) Using the letter R, what are the possible Genotypes for the red coloured flower? ____________________________________ b) What is the genotype for the pink flower? _________________ 19 AMOEBA SISTERS: VIDEO RECAP MITOSIS: THE AMAZING CELL PROCESS THAT USES DIVISION TO MULTIPLY c) Because homozygous dominant and heterozygous are both red, the farmer wants to know which one he has. He crosses the red and the pink seeds and lets them grow. Half of them are pink and half are red. Were the red seeds homozygous dominant, or heterozygous? 3. A man is a carrier for sickle cell disease. He does not suffer from the disease. This disease means that blood cells do not form in the proper shape. The disease affects only in the heterozygous recessive state. a) Using the letter S, what is the genotype for the male carrier? b) The man has a child with a woman who is also a carrier for the disease. Draw a punnett square in the space below for the possibilities of offspring genotypes. c) What is the ratio of children that have the disease? ________ d) What is the ration of children that are carriers of the disease? ________ e) Is there a chance that they could have a child that is neither a carrier nor a sufferer? __________ 20 AMOEBA SISTERS: VIDEO RECAP MITOSIS: THE AMAZING CELL PROCESS THAT USES DIVISION TO MULTIPLY Monohybrid Crosses Practice For all of the following questions, use these facts: the trait is fur color (f). Black fur is dominant over gray fur. a) Write the letter of the dominant allele. _________ b) Write the letter of the recessive allele. _________ c) Write out the homozygous dominant genotype (2 alleles). _________ d) Write out the heterozygous genotype (2 alleles). _________ e) Write out the homozygous recessive genotype. _________ f) Write the genotype for gray fur. _________ g) Write the genotype for Black fur. _________ or _________ h) Write the phenotype for #3. _________________________ i) Write the phenotype for #4. _________________________ j) Write the phenotype for #5. _________________________ Still using fur color, do the following monohybrid cross problems. (Remember: Black fur is dominant over gray) If the mother is homozygous recessive and the father is homozygous dominant. a) Write the genotype probabilities. b) Write the phenotype probabilities. If the mother is heterozygous, and the father is heterozygous. a) Write the genotype probabilities. b) Write the phenotype probabilities. If the mother is heterozygous, and the father is homozygous dominant. a)Write the genotype probabilities. b) Write the phenotype probabilities. 21 MITOSIS: THE AMAZING CELL PROCESS THAT USES DIVISION TO MULTIPLY AMOEBA SISTERS: VIDEO RECAP If the mother is homozygous recessive, and the father is heterozygous. a) Write the genotype probabilities. b) Write the phenotype probabilities. Word Problems using Monohybrid Crosses 1. Purple flowers (P) are dominant to white flowers (p). Perform the following crosses. For each cross, give the phenotype and genotype of all offspring. A. PP x pp B. Pp x Pp C. PP x Pp 2. In pea plants, yellow seed color is dominant to green seed color. If a heterozygous pea plant is crossed with a plant that is homozygous recessive for seed color, what is the probability that the offspring will have green seeds? 3. If all of the offspring of a particular cross have the genotype Gg, what must the genotype of the parents be? 22 AMOEBA SISTERS: VIDEO RECAP MITOSIS: THE AMAZING CELL PROCESS THAT USES DIVISION TO MULTIPLY 4. In fruit flies normal wings (W) is dominant over vestigial wings (w). The results of a cross, of two fruit flies, give the following results: Normal wing 793 Vestigial wing 811 What are the genotypes of the parents of the F1 generation offspring? Use a Punnett square to prove your answer. 5. Red eyes (R) in fruit flies are dominant over white eyes (r). Using Punnett squares, find the possible eye colors of the F1 generation for each of the following crosses. A. Rr x rr B. rr x RR C. Rr x Rr 6. The result of a cross is 3 purple flowers and 1 white flower. Using a cross, determine whether a plant with purple flowers is heterozygous (Pp) or homozygous dominant (PP). 23 AMOEBA SISTERS: VIDEO RECAP MITOSIS: THE AMAZING CELL PROCESS THAT USES DIVISION TO MULTIPLY Practice with Crosses. Show all work! 5. A TT (tall) plant is crossed with a tt (short plant). What percentage of the offspring will be tall? ___________ 6. A Tt plant is crossed with a Tt plant. What percentage of the offspring will be short? ______ 7. A heterozygous round seeded plant (Rr) is crossed with a homozygous round seeded plant (RR). What percentage of the offspring will be homozygous (RR)? ____________ 8. A homozygous round seeded plant is crossed with a homozygous wrinkled seeded plant. What are the genotypes of the parents? __________ x __________ What percentage of the offspring will also be homozygous? ______________ 9. In pea plants purple flowers are dominant to white flowers. If two white flowered plants are cross, what percentage of their offspring will be white flowered? ______________ 10. A white flowered plant is crossed with a plant that is heterozygous for the trait. What percentage of the offspring will have purple flowers? _____________ 11. Two plants, both heterozygous for the gene that controls flower color are crossed. What percentage of their offspring will have purple flowers? ______________ What percentage will have white flowers? ___________ 12. In guinea pigs, the allele for short hair is dominant. What genotype would a heterozygous short haired guinea pig have? _______ What genotype would a purebreeding short haired guinea pig have? _______ What genotype would a long haired guinea pig have? ________ 13. Show the cross for a pure breeding short haired guinea pig and a long haired guinea pig. What percentage of the offspring will have short hair? __________ 14. Show the cross for two heterozygous guinea pigs. What percentage of the offspring will have short hair? ________ What percentage of the offspring will have long hair? _______ 24 AMOEBA SISTERS: VIDEO RECAP MITOSIS: THE AMAZING CELL PROCESS THAT USES DIVISION TO MULTIPLY Codominance and Incomplete Dominance (intermediate) 1. Practice setting up keys for the phenotypes listed in each set. Remember that the "medium" trait must always be heterozygous. a) Birds can be blue, white, or white with bluetipped feathers. b) Flowers can be white, pink, or red. c) A Hoo can have curly hair, spiked hair, or a mix of both curly and spiked. d) A Sneech can be tall, medium, or short. e) A Bleexo can be spotted, black, or white. 2. Now, can you figure out in the above list, which of the letters represent codominant traits and which are incomplete. Codominant _____________ Incompletely Dominant ________________ 3. In Smileys, eye shape can be starred, circular, or a circle with a star. Write the genotypes for the pictured phenotypes 4. Show the cross between a star-eyed and a circle eyed. What are the phenotypes of the offspring? ____________ What are the genotypes? __________ 25 AMOEBA SISTERS: VIDEO RECAP MITOSIS: THE AMAZING CELL PROCESS THAT USES DIVISION TO MULTIPLY 5. Show the cross between a circle-star eyed, and a circle eyed. How many of the offspring are circle-eyed? ____________ How many of the offspring are circle-star eyed? ____________ 6. Show the cross between two circle-star eyed. How many of the offspring are circle-eyed? ____________ How many of the offspring are circle-star eyed? ____________ How many are star eyed? ____________ 26 AMOEBA SISTERS: VIDEO RECAP MITOSIS: THE AMAZING CELL PROCESS THAT USES DIVISION TO MULTIPLY Incomplete dominance 1. In snapdragons, flower color is controlled by incomplete dominance. The two alleles are red (R) and white (W). The heterozygous genotype is expressed as pink (RW) a. What is the phenotype of a plant with the genotype RR? ___________ b. What is the phenotype of a plant with the genotype WW? ___________ c. What is the phenotype of a plant with the genotype RW? __________ 2. Predict the offspring when two pink Four o’clock flowers (RW) are crossed. a. What is the predicted genotypic ratio for the offspring? b. What is the predicted phenotypic ratio for the offspring? 3. A pink-flowered plant is crossed with a white-flowered plant. What is the probability of producing a. A pink-flowered plant? ______________ b. A red flowered plant? _______________ c. A white flowered plant? ________________ D . What cross will produce the most pink-flowered plants? Show a punnett square to support your answer. 4. A homozygous black bird is crossed with a homozygous white bird. The offspring are all bluish-gray. Cross a black bird and a bluish gray bird. What are the genotypic ratios and percent chance of each phenotype? 4. What results if a white individual is crossed with a bluish-gray individual? (SHOW YOUR WORK) 6. If two bluish-gray individuals were crossed, what would be the ratios for both phenotype and genotype of the offspring? 27 AMOEBA SISTERS: VIDEO RECAP MITOSIS: THE AMAZING CELL PROCESS THAT USES DIVISION TO MULTIPLY Codominance 1. In a certain fish, blue scales and red scales are codominant. What happens if you breed a patchwork fish with a fish that only has blue scales? Step 1: determine the genotypes of the parents Step 2: set up the punnet square Step 3: count the number of each phenotype 2. What is the phenotypic and genotypic ratio when you cross two patchwork fish? 3. In some chickens, the gene for feather color is controlled by codominance. The allele for black is B and the allele for white is W. The heterozygous phenotype is known as erminette (black and white spotted). a) What is the genotype for black chickens? ___________ b) What is the genotype for white chickens? ____________ c) What is the genotype for erminette chickens? __________ 4. Two erminette chickens were crossed. Show the punnet square a) What is the probability they would have a black chick? b) What is the probability they would have a white chick? 28 AMOEBA SISTERS: VIDEO RECAP MITOSIS: THE AMAZING CELL PROCESS THAT USES DIVISION TO MULTIPLY Practice Problems – Sex Linkage 1. Coat color in cats is a codominant trait and is also located on the X chromosome. Cats can be black, orange or calico. A calico cat has black and orange splotches. In order to be calico, the cat must have an allele for the black color and an allele for the orange color. Use a Punnett square to show why there are no male calico cats. 2. A female calico cat is crossed with a male black cat. What are the phenotypes of the offspring and in what proportion? 3. In humans, Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is a disease where muscles become weaker over time. The gene is located on the X chromosome and is recessive. Those afflicted with this disease usually die in childhood. If a female is a carrier for DMD, what percentage of her sons will inherit the disease? What percentage of her daughters will inherit the disease. 4. Eye color in fruit flies is sex linked, with the recessive allele causing white eyes. Show the cross for a white eyed female and a red-eyed male. How many offspring will have white eyes and what is their sex? 5. Show the reciprocal cross: A red eyed female (homozygous) and white eyed male. How many offspring will have white eyes and what is their sex? 29 AMOEBA SISTERS: VIDEO RECAP MITOSIS: THE AMAZING CELL PROCESS THAT USES DIVISION TO MULTIPLY 5. In humans, color blindness is sex linked and recessive. If a woman is colorblind, what percentage of her sons will also be colorblind? Sex linkage – fruit flies 30 AMOEBA SISTERS: VIDEO RECAP MITOSIS: THE AMAZING CELL PROCESS THAT USES DIVISION TO MULTIPLY 31 AMOEBA SISTERS: VIDEO RECAP MITOSIS: THE AMAZING CELL PROCESS THAT USES DIVISION TO MULTIPLY 32 AMOEBA SISTERS: VIDEO RECAP MITOSIS: THE AMAZING CELL PROCESS THAT USES DIVISION TO MULTIPLY Dihybrid cross In rabbits, grey hair is dominant to white hair. Also in rabbits, black eyes are dominant to red eyes. GG = gray hair Gg = gray hair gg = white hair BB = black eyes Bb = black eyes bb = red eyes 1. What are the phenotypes (descriptions) of rabbits that have the following genotypes: Ggbb ____________________ ggBB ________________________ ggbb ____________________ GgBb _________________________ 2. A male rabbit with the genotype GGbb is crossed with a female rabbit with the genotype ggBb The square is set up below. Fill it out and determine the phenotypes and proportions in the offspring. How many out of 16 have grey fur and black eyes? ______ How many out of 16 have grey fur and red eyes? ________ How many out of 16 have white fur and black eyes? ______ How many out of 16 have white fur and red eyes? _______ 33 AMOEBA SISTERS: VIDEO RECAP MITOSIS: THE AMAZING CELL PROCESS THAT USES DIVISION TO MULTIPLY 3. A male rabbit with the genotype GgBb . Determine the gametes produced by this rabbit (the sperm would have these combinations of alleles) Hint there are 4 combinations. 4. Use the gametes from #3 to set up the punnet square below. Put the male's gametes on the top and the female's gametes down the side. Then fill out the square and determine what kind of offspring would be produced from this cross and in what proportion. Use a blank page for more room. 5. An aquatic arthropod called a Cyclops has antennae that are either smooth or barbed. The allele for barbs is dominant. In the same organism, resistance to pesticides is a recessive trait. Make a "key" to show all the possible genotypes (and phenotypes) of this organism. Use the rabbit key to help you if you're lost. 6. A Cyclops that is resistant to pesticides and has smooth antennae is crossed with one that is heterozygous for both traits. Show the genotypes of the parents. ______________ x _______________ 7. Set up a punnet square for the cross and show the phenotypic ratios. 34 AMOEBA SISTERS: VIDEO RECAP MITOSIS: THE AMAZING CELL PROCESS THAT USES DIVISION TO MULTIPLY 35 AMOEBA SISTERS: VIDEO RECAP MITOSIS: THE AMAZING CELL PROCESS THAT USES DIVISION TO MULTIPLY 36 AMOEBA SISTERS: VIDEO RECAP MITOSIS: THE AMAZING CELL PROCESS THAT USES DIVISION TO MULTIPLY Beyond Mendel – Codominance, Multiple Alleles, and Polygenic Traits 1. In a certain cactus, prickly spines can be two pronged or one pronged. If a true breeding one-pronged cactus is crossed with a true breeding twopronged cactus, the F1 generation has a mixture of spines, some are twopronged, some are one-pronged. a. Is this an example of codominance or incomplete dominance? b. Show the F2 generation (a cross between the two F1's). What are the phenotypes of the offspring and in what proportion? 2. In this same cactus, if you cross a plant that has red flowers to one that has yellow flowers, you produce a plant that has orange flowers. Is this codominance or incomplete dominance? Show the cross of an orange flowered plant to a red flowered plant. 3. A red flowered, two-pronged cactus is crossed with a yellow flowered one-pronged cactus. What are the resulting offspring and in what proportion? 4. Show the cross of a cactus that is heterozygous for both traits crossed with one that has red flowers and one-pronged spikes. 37 AMOEBA SISTERS: VIDEO RECAP MITOSIS: THE AMAZING CELL PROCESS THAT USES DIVISION TO MULTIPLY 5. A man with type A blood is married to a woman with type O blood. What are ALL of the possible blood types of their children. 6. A man with type AB blood is married to a woman with type O blood. What are all the possible blood types of their children? 7. A man with type A blood whose mother was type O is married to a woman with type AB blood. What are the blood types of their children and in what proportion? 8. In Snarlymonsters, the number of teeth is polygenic. The recessive condition (aabbcc) results in a toothless Snarlymonster, and the dominant condition (AABBCC) results in a Snarlymonster with 6 teeth. There are 5 other possible variations. How many teeth would a AaBbCc Snarlymonster have? ______ How many would a AABBcc Snarlymonster have? ______ How many would a aaBbcc Snarlymonster have? ______ 9. List the phenotypic ratios (how many teeth) of all the potential offspring for the cross AABBCc x AAbbcc . 10. List the phenotypic ratios (how many teeth) of all the potential offspring for the cross aaBbCc x AAbbcc . 38 AMOEBA SISTERS: VIDEO RECAP MITOSIS: THE AMAZING CELL PROCESS THAT USES DIVISION TO MULTIPLY Pedigree 1. Susan is a carrier of sickle cell disease. She is married to Ivan who is also a carrier. Susan’s father, Stewart, was also a carrier of the disease, but her mother, Ruth, did not. Susan has a brother called James who is not a carrier. Ivan has two sisters who are also carriers. His mother Rachel suffers from the disease but his father Richard does not. Susan and Ivan have two sons. Jack has sickle cell disease, but his brother, Robert, does not. Put the names of the family onto the pedigree chart below. 39 AMOEBA SISTERS: VIDEO RECAP MITOSIS: THE AMAZING CELL PROCESS THAT USES DIVISION TO MULTIPLY 40 AMOEBA SISTERS: VIDEO RECAP MITOSIS: THE AMAZING CELL PROCESS THAT USES DIVISION TO MULTIPLY 41 AMOEBA SISTERS: VIDEO RECAP MITOSIS: THE AMAZING CELL PROCESS THAT USES DIVISION TO MULTIPLY 42