ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
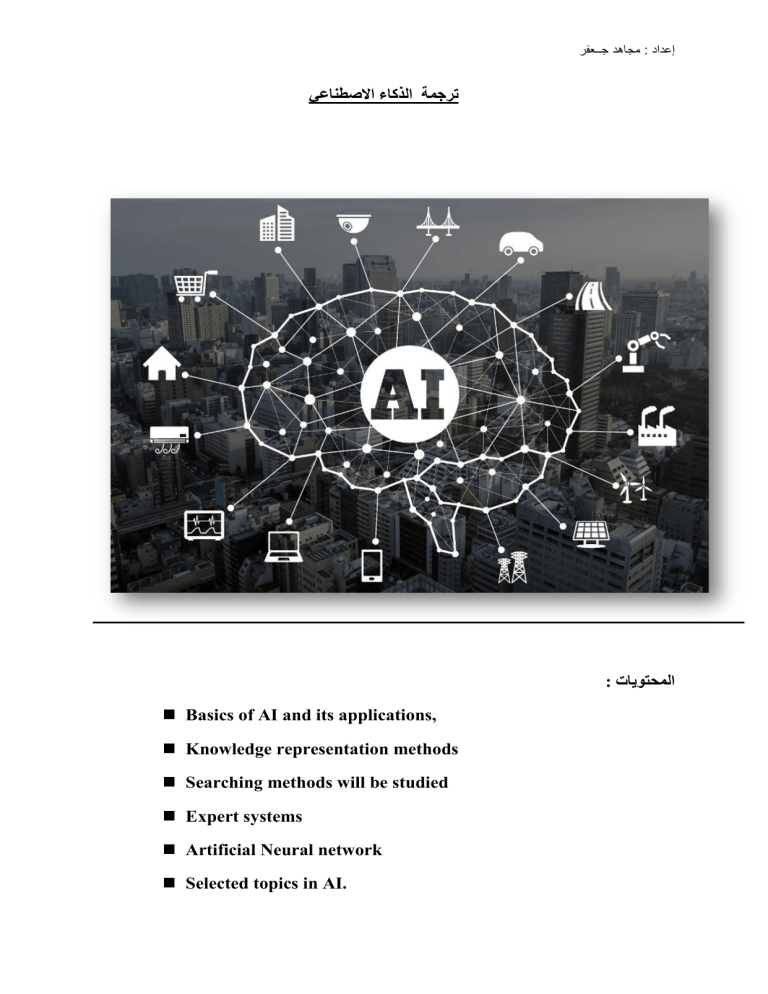
ﺗﺮﺟﻤﺔ ﺍﻟﺬﻛﺎء ﺍﻻﺻﻄﻨﺎﻋﻲ
: ﺍﻟﻤﺤﺘﻮﻳﺎﺕ
Basics of AI and its applications,
Knowledge representation methods
Searching methods will be studied
Expert systems
Artificial Neural network
Selected topics in AI.
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
LECTURE 1 & 2: Basics of AI and its applications
U
()ﺃﺳﺎﺳﻴﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺬﻛﺎء ﺍﻻﺻﻄﻨﺎﻋﻲ ﻭﺗﻄﺒﻴﻘﺎﺗﻪ
U
1-what is intelligence? ()ﻣﺎ ﻫﻮ ﺍﻟﺬﻛﺎء
1. The capacity to acquire and apply knowledge.
()ﺍﻟﻘﺪﺭﺓ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻛﺘﺴﺎﺏ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﺔ ﻭﺗﻄﺒﻴﻘﻬﺎ
2. The faculty of thought and reason.
()ﻭﺣﺪﺓ ﺍﻟﻔﻜﺮ ﻭﺍﻻﺳﺘﻨﺘﺎﺝ
3. It is the abilities to learn, understand natural language, to recognize the realworld environment, and to think.
()ﻫﻮ ﺍﻟﻘﺪﺭﺓ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻟﺘﻌﻠﻢ ﻭﻓﻬﻢ ﺍﻟﻄﺒﻴﻌﺔ ﻭﺍﻟﺘﻌﺮﻑ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺌﺔ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﻌﺎﻟﻢ ﺍﻟﺤﻘﻴﻘﻲ ﻭﺍﻟﺘﻔﻜﻴﺮ
2-what is the intelligence composed of? ( )ﻣﻤﺎ ﻳﺘﻜﻮﻥ ﺍﻟﺬﻛﺎء
1. Reasoning
()ﺍﻻﺳﺘﻨﺘﺎﺝ
2. Learning
()ﺍﻟﺘﻌﻠﻢ
3. Problem Solving
()ﺣﻞ ﺍﻟﻤﺸﻜﻼﺕ
4. Perception
()ﺍﻟﺘﺼﻮﺭ
5.
Linguistic Intelligence
()ﺍﻟﺬﻛﺎء ﺍﻟﻠﻐﻮﻱ
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
3-what is artificial intelligence? ( )ﻣﺎ ﻫﻮ ﺍﻟﺬﻛﺎء ﺍﻻﺻﻄﻨﺎﻋﻲ
Artificial intelligence is the study of systems that act in a way that to any observer
would appear to be intelligent.
(.)ﺍﻟﺬﻛﺎء ﺍﻻﺻﻄﻨﺎﻋﻲ ﻫﻮ ﺩﺭﺍﺳﺔ ﺍﻷﻧﻈﻤﺔ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺗﺘﺼﺮﻑ ﺑﻄﺮﻳﻘﺔ ﺗﺒﺪﻭ ﺫﻛﻴﺔ
Artificial Intelligence involves using methods based on the intelligent behavior of
humans and other animals to solve complex problems.
(.`)ﺍﻟﺬﻛﺎء ﺍﻻﺻﻄﻨﺎﻋﻲ ﻳﺘﻀﻤﻦ ﺍﺳﺘﺨﺪﺍﻡ ﺃﺳﺎﻟﻴﺐ ﺗﻘﻮﻡ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻟﺴﻠﻮﻙ ﺍﻟﺬﻛﻲ ﻟﻺﻧﺴﺎﻥ ﻭﺍﻟﺤﻴﻮﺍﻧﺎﺕ ﺍﻷﺧﺮﻯ ﻟﺤﻞ ﺍﻟﻤﺸﺎﻛﻞ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﻘﺪﺓ
AI is concerned with real-world problems (difficult tasks), which require complex and
sophisticated reasoning processes and knowledge.
ﻭﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺗﺘﻄﻠﺐ ﻋﻤﻠﻴﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺘﻔﻜﻴﺮ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﻘﺪﺓ،()ﺍﻟﺬﻛﺎء ﺍﻻﺻﻄﻨﺎﻋﻲ ﻫﻲ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﻨﻴﺔ ﻣﻊ ﺍﻟﻤﺸﺎﻛﻞ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﻌﺎﻟﻢ ﺍﻟﺤﻘﻴﻘﻲ )ﺍﻟﻤﻬﺎﻡ ﺍﻟﺼﻌﺒﺔ
(ﻭﺍﻟﻤﺘﻄﻮﺭﺓ ﻭﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﺔ
OR :
Artificial Intelligence is a way of making a computer, a computer-controlled robot, or a
software think intelligently, in the similar manner the intelligent humans think. )ﺍﻟﺬﻛﺎء
ﺃﻭ ﺍﻟﺒﺮﻣﺠﻴﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺗﻔﻜﺮ ﺑﺬﻛﺎء ﺑﻄﺮﻳﻘﺔ ﻣﺸﺎﺑﻬﺔ ﻟﺬﻛﺎء، ﺭﻭﺑﻮﺕ ﻣﺘﺤﻜﻢ،ﺍﻻﺻﻄﻨﺎﻋﻲ ﻫﻮ ﻭﺳﻴﻠﺔ ﻟﺠﻌﻞ ﺟﻬﺎﺯ ﺍﻟﻜﻤﺒﻴﻮﺗﺮ
( ﺍﻟﻔﻜﺮ ﺍﻹﻧﺴﺎﻧﻲ
OR:
“AI is the study of ideas that enable computers to be intelligent.” [P. Winston]
“It is the science and engineering of making intelligent machines, especially
intelligent computer programs. It is related to the similar tasks of using computers to
understand human intelligence, but AI does not have to confine itself to methods that
are biologically observable.”
John McCarthy, Stanford University, computer Science Department
(")ﺍﻟﺬﻛﺎء ﺍﻻﺻﻄﻨﺎﻋﻲ ﻫﻮ ﺩﺭﺍﺳﺔ ﺍﻷﻓﻜﺎﺭ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺗﻤﻜﻦ ﺃﺟﻬﺰﺓ ﺍﻟﻜﻤﺒﻴﻮﺗﺮ ﻟﺘﻜﻮﻥ ﺫﻛﻴﺔ.
[]ﻭﻧﺴﺘﻮﻥ
ﻭﻫﻮ ﻣﺮﺗﺒﻂ ﺑﻤﻬﺎﻡ ﻣﻤﺎﺛﻠﺔ ﻻﺳﺘﺨﺪﺍﻡ ﺃﺟﻬﺰﺓ. ﻭﺧﺎﺻﺔ ﺑﺮﺍﻣﺞ ﺍﻟﻜﻤﺒﻴﻮﺗﺮ ﺍﻟﺬﻛﻴﺔ،)ﻫﻮ ﻋﻠﻢ ﻭﻫﻨﺪﺳﺔ ﺻﻨﻊ ﺁﻟﻴﺎﺕ ﺫﻛﻴﺔ
ﻭﻟﻜﻦ ﺍﻟﺬﻛﺎء ﺍﻻﺻﻄﻨﺎﻋﻲ ﻻ ﺗﻘﺘﺼﺮ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻷﺳﺎﻟﻴﺐ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﻳﻤﻜﻦ ﻣﻼﺣﻈﺘﻬﺎ ﺑﻴﻮﻟﻮﺟﻴﺎ،ﺍﻟﻜﻤﺒﻴﻮﺗﺮ ﻟﻔﻬﻢ ﺍﻟﺬﻛﺎء ﺍﻟﺒﺸﺮﻱ. "
[.] ﺟﻮﻥ ﻣﻜﺎﺭﺛﻲ
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
4-what are the goals of Ai? ()ﻣﺎ ﻫﻲ ﺃﻫﺪﺍﻑ ﺍﻟﺬﻛﺎء ﺍﻻﺻﻄﻨﺎﻋﻲ
To understand the principles that makes intelligence possible.
()ﻓﻬﻢ ﺍﻟﻤﺒﺎﺩﺉ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺗﺠﻌﻞ ﺍﻟﺬﻛﺎء ﻣﻤﻜﻨﺔ
To make computer more useful.
(.) ﻟﺠﻌﻞ ﺍﻟﻜﻤﺒﻴﻮﺗﺮ ﺃﻛﺜﺮ ﻓﺎﺋﺪﺓ
To develop useful, powerful applications.
(ﻟﺘﻄﻮﻳﺮ ﺗﻄﺒﻴﻘﺎﺕ ﻣﻔﻴﺪﺓ ﻭﻗﻮﻳﺔ.)
To Create Expert Systems: The systems which exhibit intelligent behavior, learn, demonstrate, explain, and
advice its users.
( ﻭﺗﻘﺪﻳﻢ ﺍﻟﻤﺸﻮﺭﺓ ﻟﻠﻤﺴﺘﺨﺪﻣﻴﻦ، ﻭﺷﺮﺡ، ﻭﺍﻟﺘﻌﻠﻢ ﻭﺇﺛﺒﺎﺕ، ﻫﻲ ﺍﻷﻧﻈﻤﺔ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺗﻈﻬﺮ ﺍﻟﺴﻠﻮﻙ ﺍﻟﺬﻛﻲ:))ﻹﻧﺸﺎء ﻧﻈﻢ ﺧﺒﻴﺮﺓ
To Implement Human Intelligence in Machines: Creating systems that
Understand, think, learn, and behave like humans.
( ﻭﺍﻟﺘﺼﺮﻑ ﻣﺜﻞ ﺍﻟﺒﺸﺮ، ﻭﺍﻟﺘﻌﻠﻢ، ﻭﺍﻟﺘﻔﻜﻴﺮ، ﺇﻧﺸﺎء ﺍﻟﻨﻈﻢ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﻳﻤﻜﻨﻬﺎ ﺍﻟﻔﻬﻢ:)ﻟﺘﻨﻔﻴﺬ ﺍﻟﺬﻛﺎء ﺍﻟﺒﺸﺮﻱ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻵﻻﺕ
5-What’s involved in Intelligence? ()ﻣﺎﺫﺍ ﻳﺘﻀﻤﻦ ﺍﻟﺬﻛﺎء ﺍﻻﺻﻄﻨﺎﻋﻲ
Ability to interact with the real world ()ﺍﻟﻘﺪﺭﺓ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻟﺘﻔﺎﻋﻞ ﻣﻊ ﺍﻟﻌﺎﻟﻢ ﺍﻟﺤﻘﻴﻘﻲ
to perceive, understand, and act
()ﺇﺩﺭﺍﻙ ﻭﻓﻬﻢ ﺍﻷﻓﻌﺎﻝ ﻭﺍﻟﺘﺼﺮﻓﺎﺕ
e.g., speech, image ( ﺍﻟﺼﻮﺭ ﻭﺍﻟﺘﺨﺎﻁﺐ: )ﻣﺜﺎﻝ
Reasoning and Planning ()ﺍﻟﺘﻔﻜﻴﺮ ﻭﺍﻟﺘﺨﻄﻴﻂ
solving new problems, planning, making decisions and ability to deal with unexpected
problems, uncertainties
( ﻭﺍﺗﺨﺎﺫ ﺍﻟﻘﺮﺍﺭﺍﺕ ﻭﺍﻟﻘﺪﺭﺓ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻟﺘﻌﺎﻣﻞ ﻣﻊ ﺍﻟﻤﺸﺎﻛﻞ ﻏﻴﺮ ﺍﻟﻤﺘﻮﻗﻌﺔ، ﻭﺍﻟﺘﺨﻄﻴﻂ،)ﺣﻞ ﺍﻟﻤﺸﺎﻛﻞ ﺍﻟﺠﺪﻳﺪﺓ
Learning and Adaptation ()ﺍﻟﺘﻌﻠﻢ ﻭﺍﻟﺘﻜﻴﻒ
we are continuously learning and adapting
()ﻧﺤﻦ ﻧﺘﻌﻠﻢ ﻭﻧﺘﻜﻴﻒ ﺑﺎﺳﺘﻤﺮﺍﺭ
e.g., a baby learning to categorize and recognize animals
( ﺗﻌﻠﻢ ﺍﻟﻄﻔﻞ ﻟﻜﻴﻔﻴﺔ ﺗﺼﻨﻴﻒ ﺍﻟﺤﻴﻮﺍﻧﺎﺕ ﻭﺍﻟﺘﺮﻑ ﻋﻠﻴﻬﺎ:)ﻣﺜﺎﻝ
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
6-What are the capabilities that, the computer would need to possess to make Ai? ﻣﺎ ﻫﻲ
()ﺍﻟﻘﺪﺭﺍﺕ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﻳﺤﺘﺎﺝ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﺳﻮﺏ ﻻﻣﺘﻼﻛﻬﺎ ﻟﺼﻨﻊ ﺍﻟﺬﻛﺎء ﺍﻻﺻﻄﻨﺎﻋﻲ
Natural language processing: To communicate successfully.
( ﻟﻠﺘﻮﺍﺻﻞ ﺑﻨﺠﺎﺡ:)ﻣﻌﺎﻟﺠﺔ ﺍﻟﻠﻐﺔ ﺍﻟﻄﺒﻴﻌﻴﺔ
Knowledge representation: To store what it knows or hears.
( ﻟﺘﺨﺰﻳﻦ ﻣﺎ ﻳﻌﺮﻓﻪ ﺃﻭ ﻳﺴﻤﻌﻪ:ﺗﻤﺜﻴﻞ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﺔ.)
Automated reasoning: to answer questions and draw conclusions using stored
information
( ﻟﻺﺟﺎﺑﺔ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻷﺳﺌﻠﺔ ﻭﺍﺳﺘﺨﻼﺹ ﺍﻟﻨﺘﺎﺋﺞ ﺑﺎﺳﺘﺨﺪﺍﻡ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﻠﻮﻣﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻤﺨﺰﻧﺔ:)ﺍﻟﺘﻔﻜﻴﺮ ﺍﻵﻟﻲ
Machine learning: To adapt to new circumstances and to detect and
extrapolate patterns.
( ﻟﻠﺘﻜﻴﻒ ﻣﻊ ﺍﻟﻈﺮﻭﻑ ﺍﻟﺠﺪﻳﺪﺓ ﻭﺍﻟﻜﺸﻒ ﻋﻦ ﺍﻷﻧﻤﺎﻁ ﻭﺍﺳﺘﻘﺮﺍءﻫﺎ:ﺗﻌﻠﻢ ﺍﻵﻟﺔ.)
Computer vision: To perceive objects.
( ﻟﺘﺼﻮﺭ ﺍﻟﻜﺎﺋﻨﺎﺕ:ﺭﺅﻳﺔ ﺍﻟﻜﻤﺒﻴﻮﺗﺮ.)
Robotics to manipulate objects and move.
( ﻟﻤﻌﺎﻟﺠﺔ ﺍﻟﻜﺎﺋﻨﺎﺕ ﻭﺗﺤﺮﻳﻜﻬﺎ: )ﺍﻟﺮﻭﺑﻮﺕ
7- What Contributes to Ai? () ﻓﻴﻤﺎ ﻳﺴﺎﻫﻢ ﺍﻟﺬﻛﺎء ﺍﻻﺻﻄﻨﺎﻋﻲ
Artificial intelligence is a science and technology based on disciplines such as Computer
Science, Biology, Psychology, Linguistics, Mathematics, and Engineering. A major thrust of
AI is in the development of computer functions associated with human intelligence, such as
reasoning, learning, and problem solving.
Out of the following areas, one or multiple areas can contribute to build an intelligent system.
، ﻭﻋﻠﻢ ﺍﻟﻨﻔﺲ، ﻭﻋﻠﻢ ﺍﻷﺣﻴﺎء،)ﺍﻟﺬﻛﺎء ﺍﻻﺻﻄﻨﺎﻋﻲ ﻫﻮ ﺍﻟﻌﻠﻢ ﻭﺍﻟﺘﻜﻨﻮﻟﻮﺟﻴﺎ ﺍﻟﻘﺎﺋﻤﺔ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻟﺘﺨﺼﺼﺎﺕ ﻣﺜﻞ ﺍﻟﻜﻤﺒﻴﻮﺗﺮ ﻭﺍﻟﻌﻠﻮﻡ
ﻣﺜﻞ، ﺍﻟﻬﺪﻑ ﺍﻷﺳﺎﺳﻲ ﻣﻨﻪ ﻫﻮ ﺗﻄﻮﻳﺮ ﻭﻅﺎﺋﻒ ﺍﻟﻜﻤﺒﻴﻮﺗﺮ ﺍﻟﻤﺮﺗﺒﻄﺔ ﺑﺎﻟﺬﻛﺎء ﺍﻟﺒﺸﺮﻱ. ﻭﺍﻟﻬﻨﺪﺳﺔ، ﻭﺍﻟﺮﻳﺎﺿﻴﺎﺕ،ﻭﻋﻠﻢ ﺍﻟﻠﻐﺔ
( ﺑﻌﻴﺪﺍ ﻋﻦ ﺍﻟﻤﻨﻄﻘﺔ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻟﻴﺔ ﻓﺎﻥ ﻣﺠﺎﻝ ﺃﻭ ﻋﺪﺓ ﻣﺠﺎﻻﺕ ﻳﻤﻜﻦ ﺃﻥ ﺗﺴﻬﻢ ﻓﻲ ﺑﻨﺎء ﻧﻈﺎﻡ ﺫﻛﻲ، ﻭﺣﻞ ﺍﻟﻤﺸﻜﻼﺕ، ﻭﺍﻟﺘﻌﻠﻢ،ﺍﻟﺘﻔﻜﻴﺮ
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
8-What is AI Technique? ( )ﻣﺎ ﻫﻲ ﺗﻘﻨﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﺬﻛﺎء ﺍﻻﺻﻄﻨﺎﻋﻲ
AI Technique is a manner to organize and use the knowledge efficiently in such a way that:
(: )ﺗﻘﻨﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﺬﻛﺎء ﺍﻻﺻﻄﻨﺎﻋﻲ ﻫﻲ ﻁﺮﻳﻘﺔ ﻟﺘﻨﻈﻴﻢ ﻭﺍﺳﺘﺨﺪﺍﻡ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﺔ ﺑﻜﻔﺎءﺓ ﻓﻲ ﻣﺜﻞ ﻫﺬﻩ ﺍﻟﻄﺮﻕ
It should be perceivable by the people who provide it.
.ﻳﻨﺒﻐﻲ ﺃﻥ ﻳﺪﺭﻛﻬﺎ ﺍﻟﻨﺎﺱ ﺍﻟﺬﻳﻦ ﻳﻘﺪﻣﻮﻧﻬﺎ
Itshould be easily modifiable to correct errors.
.ﻳﺠﺐ ﺃﻥ ﺗﻜﻮﻥ ﻗﺎﺑﻠﺔ ﻟﻠﺘﻌﺪﻳﻞ ﺑﺴﻬﻮﻟﺔ ﻟﺘﺼﺤﻴﺢ ﺍﻷﺧﻄﺎء
It should be useful in many situations though it is incomplete or inaccurate.
.ﻳﻨﺒﻐﻲ ﺃﻥ ﻳﻜﻮﻥ ﻣﻔﻴﺪﺍ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﻌﺪﻳﺪ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻻﺕ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻟﺮﻏﻢ ﻣﻦ ﺃﻧﻬﺎ ﻏﻴﺮ ﻛﺎﻣﻠﺔ ﺃﻭ ﻏﻴﺮ ﺩﻗﻴﻘﺔ
AI techniques elevate the speed of execution of the complex.
ﺗﻘﻨﻴﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺬﻛﺎء ﺍﻻﺻﻄﻨﺎﻋﻲ ﺗﺮﻓﻊ ﺳﺮﻋﺔ ﺗﻨﻔﻴﺬ ﺍﻟﺒﺮﻧﺎﻣﺞ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﻘﺪﺓ.
In the real world, the knowledge has some unwelcomed properties:
(ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﺔ ﻟﺪﻳﻬﺎ ﺑﻌﺾ ﺍﻟﺨﺼﺎﺋﺺ ﻏﻴﺮ ﺍﻟﻤﺮﻏﻮﺏ ﻓﻴﻬﺎ،)ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﻌﺎﻟﻢ ﺍﻟﺤﻘﻴﻘﻲ
Its volume is huge, next to unimaginable.
ﺑﺠﺎﻧﺐ ﻻ ﻳﻤﻜﻦ ﺗﺼﻮﺭﻫﺎ،ﺣﺠﻤﻪ ﺿﺨﻤﺔ
It is not well-organized or well-formatted.
.ﺃﻧﻬﺎ ﻟﻴﺴﺖ ﻣﻨﻈﻤﺔ ﺗﻨﻈﻴﻤﺎ ﺟﻴﺪﺍ ﺃﻭ ﺟﻴﺪﺓ ﺍﻟﺘﻨﺴﻴﻖ
It keeps changingconstantly.
ﺃﻧﻬﺎ ﺗﺘﻐﻴﺮ ﺑﺎﺳﺘﻤﺮﺍﺭ.
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
9-What are the applications of Ai? () ﻣﺎ ﻫﻲ ﺗﻄﺒﻴﻘﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺬﻛﺎء ﺍﻻﺻﻄﻨﺎﻋﻲ
Medicine ()ﺍﻟﻄﺐ
Image guided surgery
()ﺍﻟﺼﻮﺭ ﺍﻟﺠﺮﺍﺣﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﻮﺟﻬﻪ
Image analysis and enhancement
()ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺍﻟﺼﻮﺭﺓ ﻭﺗﻌﺰﻳﺰﻫﺎ
Transportation: ()ﺍﻟﻨــﻘﻞ
Autonomous vehicle control
()ﺍﻟﺴﻴﻄﺮﺓ ﺍﻟﺬﺍﺗﻴﺔ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻟﻤﺮﻛﺒﺎﺕ
Pedestrian detection
()ﻛﺸﻒ ﺍﻟﻤﺸﺎﺓ
Games.()ﺍﻷﻟﻌﺎﺏ
Ai plays crucial role in strategic games such as chess, poker, tic-tac-toe, etc., where
machine can think of large number of possible positions based on heuristic
knowledge.
ﻭﻣﺎ ﺇﻟﻰ، ﺗﻴﻚ ﺗﺎﻙ ﺗﻮ، ﻟﻌﺒﺔ ﺍﻟﺒﻮﻛﺮ،)ﺍﻟﺬﻛﺎء ﺍﻻﺻﻄﻨﺎﻋﻲ ﻳﻠﻌﺐ ﺩﻭﺭﺍ ﻣﻬﻤﺎ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻷﻟﻌﺎﺏ ﺍﻻﺳﺘﺮﺍﺗﻴﺠﻴﺔ ﻣﺜﻞ ﺍﻟﺸﻄﺮﻧﺞ
(. ﺣﻴﺚ ﻳﻤﻜﻦ ﻟﻶﻟﺔ ﻳﻤﻜﻦ ﺃﻥ ﻧﻔﻜﺮ ﻓﻲ ﻋﺪﺩ ﻛﺒﻴﺮ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﻤﻮﺍﻗﻒ ﺍﻟﻤﻤﻜﻨﺔ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺃﺳﺎﺱ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﺔ ﺍﻹﺭﺷﺎﺩﻳﺔ،ﺫﻟﻚ
Robotics.()ﺍﻟﺮﻭﺑﻮﺗﺎﺕ
Robots are able to perform the tasks given by a human. They have sensors to detect
physical data from the real world such as light, heat, temperature, movement, sound,
bump, and pressure. They have efficient processors, multiple sensors and huge
memory, to exhibit intelligence. In addition, they are capable of learning from their
mistakes and they can adapt to the new environment.
)ﺍﻟﺮﻭﺑﻮﺗﺎﺕ ﻗﺎﺩﺭﺓ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺃﺩﺍء ﺍﻟﻤﻬﺎﻡ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﻳﻌﻄﻴﻬﺎ ﻟﻬﺎ ﺍﻷﻧﺴﺎﻥ ﻟﺪﻳﻬﻢ ﺃﺟﻬﺰﺓ ﺍﺳﺘﺸﻌﺎﺭ ﻟﻜﺸﻒ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻧﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻤﺎﺩﻳﺔ ﻣﻦ
،ﻭ ﻟﺪﻳﻬﻢ ﻣﻌﺎﻟﺠﺎﺕ ﻓﻌﺎﻟﺔ. ﻭﺍﻟﻀﻐﻂ، ﻭﺍﻟﺼﻮﺕ، ﻭﺍﻟﺤﺮﻛﺔ،ﺍﻟﻌﺎﻟﻢ ﺍﻟﺤﻘﻴﻘﻲ ﻣﺜﻞ ﺍﻟﻀﻮء ﻭﺍﻟﺤﺮﺍﺭﺓ ﻭﺩﺭﺟﺔ ﺍﻟﺤﺮﺍﺭﺓ
ﻓﻬﻲ ﻗﺎﺩﺭﺓ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻟﺘﻌﻠﻢ ﻣﻦ، ﻭﺑﺎﻹﺿﺎﻓﺔ ﺇﻟﻰ ﺫﻟﻚ. ﻟﻌﺮﺽ ﺍﻟﺬﻛﺎء،ﻭﺃﺟﻬﺰﺓ ﺍﺳﺘﺸﻌﺎﺭ ﻣﺘﻌﺪﺩﺓ ﻭﺿﺨﻤﺔ ﺍﻟﺬﺍﻛﺮﺓ
( ﻭﻳﻤﻜﻨﻬﺎ ﺃﻥ ﺗﺘﻜﻴﻒ ﻣﻊ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺌﺔ ﺍﻟﺠﺪﻳﺪﺓ،ﺍﻷﺧﻄﺎء
Expert Systems ()ﺍﻟﻨﻈﻢ ﺍﻟﺨﺒﻴﺮﺓ
There are some applications which integrate machine, software, and special
Information to impart reasoning and advising. They provide explanation and advice to
The users.
ﻟﺘﻘﺪﻳﻢ ﺍﻟﺘﻔﺴﻴﺮ. ﻭﻣﻌﻠﻮﻣﺎﺕ ﺧﺎﺻﺔ ﻟﺼﻨﻊ ﺍﻟﺘﻔﻜﻴﺮ، ﻭﺍﻟﺒﺮﻣﺠﻴﺎﺕ،)ﻫﻨﺎﻙ ﺑﻌﺾ ﺍﻟﺘﻄﺒﻴﻘﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺗﺘﻜﺎﻣﻞ ﻓﻴﻪ ﺍﻵﻟﺔ
(ﻭﺍﻟﻤﺸﻮﺭﺓ ﻟﻠﻤﺴﺘﺨﺪﻣﻴﻦ
.
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
Speech Recognition()ﺍﻟﺘﻌﺮﻑ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻟﻜﻼﻡ
Some intelligent systems are capable of hearing and comprehending the language in
terms of sentences and their meanings while a human talks to it. It can handle different
accents, slang words, noise in the background, change in human’s noise due to cold, etc.
ﻭﺑﺎﻟﺘﺎﻟﻲ.)ﺑﻌﺾ ﺍﻷﻧﻈﻤﺔ ﺍﻟﺬﻛﻴﺔ ﻗﺎﺩﺭﺓ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺳﻤﺎﻉ ﻭﻓﻬﻢ ﺍﻟﻠﻐﺔ ﻣﻦ ﺣﻴﺚ ﺍﻟﺠﻤﻞ ﻭﻣﻌﺎﻧﻴﻬﺎ ﺃﺛﻨﺎء ﺗﺤﺪﺙ ﺍﻹﻧﺴﺎﻥ ﺇﻟﻴﻬﺎ
ﻭﻓﻬﻢ ﺍﻟﺘﻐﻴﺮ ﻓﻲ ﺿﻮﺿﺎء ﺍﻹﻧﺴﺎﻥ، ﻭﺍﻟﻀﻮﺿﺎء ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﺨﻠﻔﻴﺔ، ﻛﻠﻤﺎﺕ ﻋﺎﻣﻴﺔ،ﻳﻤﻜﻨﻬﺎ ﺍﻟﺘﻌﺎﻣﻞ ﻣﻊ ﻟﻬﺠﺎﺕ ﻣﺨﺘﻠﻔﺔ
( ﺍﻟﺦ، ﺑﺴﺒﺐ ﺍﻟﺒﺮﺩ ﻣﺜﻼ
Handwriting Recognition()ﺍﻟﺘﻌﺮﻑ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺧﻂ ﺍﻟﻴﺪ.
The handwriting recognition software reads the text written on paper by a pen or on
screen by a stylus. It can recognize the shapes of the letters and convert it into editable
text.
)ﻳﻘﻮﻡ ﺑﺮﻧﺎﻣﺞ ﺍﻟﺘﻌﺮﻑ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻟﻜﺘﺎﺑﺔ ﺍﻟﻴﺪﻭﻳﺔ ﺑﻘﺮﺍءﺓ ﺍﻟﻨﺺ ﺍﻟﻤﻜﺘﻮﺏ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻟﻮﺭﻕ ﺑﻮﺍﺳﻄﺔ ﻗﻠﻢ ﺃﻭ ﻋﻠﻰ
( ﻭﻳﻤﻜﻨﻪ ﺍﻟﺘﻌﺮﻑ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻷﺷﻜﺎﻝ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﺤﺮﻭﻑ ﻭﺗﺤﻮﻳﻠﻪ ﺇﻟﻰ ﻧﺺ ﻳﻤﻜﻦ ﺗﻌﺪﻳﻠﻪ.ﺍﻟﺸﺎﺷﺔ ﺑﻮﺍﺳﻄﺔ ﺍﻟﻘﻠﻢ
Bioinformatics()ﺍﻟﻤﻌﻠﻮﻣﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺤﻴﻮﻳﺔ
Gene data analysis
( )ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺑﻴﺎﻧﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺠﻴﻨﺎﺕ
Prediction of protein structure
()ﺍﻟﺘﻨﺒﺆ ﺑﺒﻨﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﺒﺮﻭﺗﻴﻦ
Text classification, document sorting()ﺗﺼﻨﻴﻒ ﺍﻟﻨﺼﻮﺹ ﻭﻓﺮﺯ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺘﻨﺪﺍﺕ
Web pages, e-mails
( ﺭﺳﺎﺋﻞ ﺍﻟﺒﺮﻳﺪ ﺍﻹﻟﻜﺘﺮﻭﻧﻲ،)ﺻﻔﺤﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻮﻳﺐ
Articles in the news
()ﻣﻘﺎﻻﺕ ﺍﻷﺧﺒﺎﺭ
Video, image classification
()ﺗﺼﻨﻴﻒ ﺍﻟﺼﻮﺭ ﻭﺍﻟﻔﻴﺪﻳﻮﻫﺎﺕ
Music composition, picture drawing
( ﺭﺳﻢ ﺍﻟﺼﻮﺭﺓ،)ﺗﻜﻮﻳﻦ ﺍﻟﻤﻮﺳﻴﻘﻰ
Natural Language Processing .
ﻓﻬﻢ ﻭﻣﻌﺎﻟﺠﺔ ﺍﻟﻠﻐﺔ ﺍﻟﻄﺒﻴﻌﻴﺔ ﻟﻺﻧﺴﺎﻥ
Perception.
()ﺍﻹﺩﺭﺍﻙ
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
10-what is the deference between AI programs Vs Traditional programs?
()ﺍﻟﻔﺮﻕ ﺑﻴﻦ ﺑﺮﺍﻣﺞ ﺍﻟﺬﻛﺎء ﺍﻻﺻﻄﻨﺎﻋﻲ ﻭﺍﻟﺒﺮﺍﻣﺞ ﺍﻟﺘﻘﻠﻴﺪﻳﺔ
AI programs contain on a range of ways to access of the solution through the paths
within the knowledge base.
)ﺗﺤﺘﻮﻱ ﺑﺮﺍﻣﺞ ﺍﻟﺬﻛﺎء ﺍﻻﺻﻄﻨﺎﻋﻲ ﻋﻠﻰ ﻣﺠﻤﻮﻋﺔ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﻄﺮﻕ ﻟﻠﻮﺻﻮﻝ ﺇﻟﻰ ﺍﻟﺤﻞ ﻣﻦ ﺧﻼﻝ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺎﺭﺍﺕ ﺩﺍﺧﻞ ﻗﺎﻋﺪﺓ
(ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﺔ
GUI in AI programs are smart and strength.
()ﻭﺍﺟﻬﺎﺕ ﺑﺮﺍﻣﺞ ﺍﻟﺬﻛﺎء ﺍﻻﺻﻄﻨﺎﻋﻲ ﺫﻛﻴﺔ ﻭﻗﻮﻳﺔ
Expert systems can deal with uncertain data and incomplete or contradictory data.
( )ﻳﻤﻜﻦ ﺃﻥ ﺗﺘﻌﺎﻣﻞ ﺍﻟﻨﻈﻢ ﺍﻟﺨﺒﻴﺮﺓ ﻣﻊ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻧﺎﺕ ﻏﻴﺮ ﺍﻟﻤﺆﻛﺪﺓ ﻭﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻧﺎﺕ ﻏﻴﺮ ﺍﻟﻤﻜﺘﻤﻠﺔ ﺃﻭ ﺍﻟﻤﺘﻨﺎﻗﻀﺔ.
Languages used in AI programs are closer to human languages.
()ﺍﻟﻠﻐﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺘﺨﺪﻣﺔ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﺬﻛﺎء ﺍﻻﺻﻄﻨﺎﻋﻲ ﺍﻗﺮﺏ ﻟﻠﻐﺔ ﺍﻻﻧﺴﺎﻥ
The knowledge base in expert systems is a combination of the properties and laws and
the results of experience acquired and accurate information and probability. the
databases in the traditional programs is a store of facts and only facts fixed and
known.
)ﻗﺎﻋﺪﺓ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﺔ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﻨﻈﻢ ﺍﻟﺨﺒﻴﺮﺓ ﻫﻲ ﻣﺰﻳﺞ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﺨﺼﺎﺋﺺ ﻭﺍﻟﻘﻮﺍﻧﻴﻦ ﻭﻧﺘﺎﺋﺞ ﺍﻟﺨﺒﺮﺓ ﺍﻟﻤﻜﺘﺴﺒﺔ ﻭﺍﻟﻤﻌﻠﻮﻣﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺪﻗﻴﻘﺔ ﻭﺍﻻﺩﺭﺍﻙ
(ﺍﻣﺎ ﻗﻮﺍﻋﺪ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻧﺎﺕ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﺒﺮﺍﻣﺞ ﺍﻟﺘﻘﻠﻴﺪﻳﺔ ﻫﻲ ﻣﺨﺰﻥ ﺍﻟﺤﻘﺎﺋﻖ ﻭﻓﻘﻂ ﺍﻟﺤﻘﺎﺋﻖ ﺍﻟﺜﺎﺑﺘﺔ ﻭﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻭﻓﺔ
11-what is the Difference between Human and Machine Intelligence?
() ﻣﺎﻫﻮ ﺍﻟﻔﺮﻕ ﺑﻴﻦ ﺍﻟﺬﻛﺎء ﺍﻟﺒﺸﺮﻱ ﻭﺫﻛﺎء ﺍﻻًﻟﻪ
Humans perceive by patterns whereas the machines perceive by set of rules and data.
(ﻳﺪﺭﻙ ﺍﻟﺒﺸﺮ ﻣﻦ ﺧﻼﻝ ﺍﻷﻧﻤﺎﻁ ﻓﻲ ﺣﻴﻦ ﺃﻥ ﺍﻵﻻﺕ ﺗﺪﺭﻙ ﻣﻦ ﺧﻼﻝ ﻣﺠﻤﻮﻋﺔ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﻘﻮﺍﻋﺪ ﻭﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻧﺎﺕ.)
Humans store and recall information by patterns, machines do it by searching
Algorithms. For example, the number 40404040 is easy to remember, store and recall
as its pattern is simple.
( ﺍﻟﺮﻗﻢ:ﺍﻟﺒﺸﺮ ﻳﺨﺰﻥ ﻭﻳﺴﺘﺪﻋﻲ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﻠﻮﻣﺎﺕ ﺑﺎﺳﺘﺨﺪﺍﻡ ﺍﻻﻧﻤﺎﻁ ﺍﻣﺎ ﺍﻻﻻﺕ ﺗﻔﻌﻞ ﺫﻟﻚ ﻋﻦ ﻁﺮﻳﻖ ﺧﻮﺍﺭﺯﻣﻴﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺚ ﻓﻤﺜﻼ
ﺳﻬﻞ ﺍﻟﺘﺬﻛﺮ ﻭﺍﻟﺘﺨﺰﻳﻦ ﻭﺍﻻﺳﺘﺮﺟﺎﻉ ﻭﺍﻳﻀﺎ ﺫﺍﺕ ﻧﻤﻂ ﺳﻬﻞ40404040)
Humans can figure out the complete object even if some part of it is missing or
Distorted; whereas the machines cannot correctly.
( ﻳﻤﻜﻦ ﻟﻠﺒﺸﺮ ﻣﻌﺮﻓﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﻮﺿﻮﻉ ﺑﺸﻜﻞ ﻛﺎﻣﻞ ﺣﺘﻰ ﻟﻮ ﻛﺎﻥ ﺟﺰء ﻣﻨﻪ ﻣﻔﻘﻮﺩ ﻓﻲ ﺣﻴﻦ ﺃﻥ ﺍﻵﻻﺕ ﻻ ﻳﻤﻜﻨﻬﺎ ﻓﻌﻞ ﺫﻟﻚ ﺑﺸﻜﻞ
ﺻﺤﻴﺢ.)
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
12-What are the Academic Disciplines relevant to AI?
()ﻣﺎ ﻫﻲ ﺍﻟﺘﺨﺼﺼﺎﺕ ﺍﻷﻛﺎﺩﻳﻤﻴﺔ ﺫﺍﺕ ﺍﻟﺼﻠﺔ ﺑﺎﻟﺬﻛﺎء ﺍﻻﺻﻄﻨﺎﻋﻲ
. Philosophy ()ﻓﻠﺴﻔﺔ
Logic, methods of reasoning, mind as physical system, foundations of learning,
language, rationality.
( ﻭﺃﺳﺲ ﺍﻟﺘﻌﻠﻢ ﻭﺍﻟﻠﻐﺔ ﻭﺍﻟﻌﻘﻼﻧﻴﺔ، ﻭﺍﻟﻌﻘﻞ ﻛﻨﻈﺎﻡ ﻣﺎﺩﻱ، ﻭﻁﺮﻕ ﺍﻟﺘﻔﻜﻴﺮ،)ﺍﻟﻤﻨﻄﻖ
Mathematics ()ﺍﻟﺮﻳﺎﺿﻴﺎﺕ
Formal representation and proof, algorithms, computation.
(، ﻭﺍﻟﺤﺴﺎﺏ، ﻭﺍﻟﺨﻮﺍﺭﺯﻣﻴﺎﺕ،)ﺍﻟﺘﻤﺜﻴﻞ ﺍﻟﺮﺳﻤﻲ ﻭﺍﻹﺛﺒﺎﺕ
Probability/Statistics ()ﺍﻹﺣﺼﺎء ﻭﺍﻻﺣﺘﻤﺎﻻﺕ
Modeling and learning from data ()ﺍﻟﻨﻤﺬﺟﺔ ﻭﺍﻟﺘﻌﻠﻢ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻧﺎﺕ
Economics()ﺍﻻﻗﺘﺼﺎﺩ
Decision theory, rational economic agents ( ﺍﻟﻌﻮﺍﻣﻞ ﺍﻻﻗﺘﺼﺎﺩﻳﺔ ﺍﻟﻌﻘﻼﻧﻴﺔ،)ﻧﻈﺮﻳﺔ ﺍﻟﻘﺮﺍﺭ
Neuroscience()ﻋﻠﻢ ﺍﻷﻋﺼﺎﺏ
Neurons as information processing units.
(ﺍﻟﺨﻼﻳﺎ ﺍﻟﻌﺼﺒﻴﺔ ﻭﻭﺣﺪﺍﺕ ﻣﻌﺎﻟﺠﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﻠﻮﻣﺎﺕ.)
Psychology/Cognitive Science()ﺍﻟﻌﻠﻮﻡ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﻴﺔ ﻭﺍﻟﻨﻔﺴﻴﺔ
How do people behave, perceive, process cognitive information, represent
knowledge.
( ﻳﻤﺜﻠﻮﻥ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﺔ، ﻳﻌﺎﻟﺠﻮﻥ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﻠﻮﻣﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﻴﺔ، ﻳﺪﺭﻛﻮﻥ،)ﻛﻴﻒ ﻳﺘﺼﺮﻑ ﺍﻟﻨﺎﺱ
Computer engineering ()ﻫﻨﺪﺳﺔ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﺳﻮﺏ
Building fast computers ()ﺑﻨﺎء ﺣﻮﺍﺳﻴﺐ ﺳﺮﻳﻌﺔ
Control theory ()ﻧﻈﺮﻳﺔ ﺍﻟﺘﺤﻜﻢ
Design systems that maximize an objective function over time
()ﺑﻨﺎء ﺍﻧﻈﻤﺔ ﺗﺴﻌﻰ ﺍﻟﻲ ﺗﻌﻈﻴﻢ ﺍﻟﻤﻬﺎﻡ ﻭﺍﻟﻮﻅﺎﺋﻒ ﺑﻤﺮﻭﺭ ﺍﻟﻮﻗﺖ
Linguistics ()ﺍﻟﻠﻐﻮﻳﺎﺕ
Knowledge representation, grammars ()ﺗﻤﺜﻴﻞ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﺔ ﻭﺍﻟﻘﻮﺍﻋﺪ
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
13-What can Ai system do? () ﻣﺎﺫﺍ ﺑﺈﻣﻜﺎﻥ ﻧﻈﺎﻡ ﺍﻟﺬﻛﺎء ﺍﻻﺻﻄﻨﺎﻋﻲ ﻓﻌﻠﻪ
Today’s AI systems have been able to achieve limited success in some of these tasks.
(ﺍﻟﻴﻮﻡ ﺗﻤﻜﻨﺖ ﻧﻈﻢ ﺍﻟﺬﻛﺎء ﺍﻻﺻﻄﻨﺎﻋﻲ ﻣﺴﻦ ﺗﺤﻘﻴﻖ ﻧﺠﺎﺡ ﻣﺤﺪﻭﺩ ﻓﻰ ﺑﻌﺾ ﻫﺬﻩ ﺍﻟﻤﻬﺎﻡ.)
• In Computer vision, the systems are capable of face recognition
(• ﺍﻟﻨﻈﻢ ﻗﺎﺩﺭﺓ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻟﺘﻌﺮﻑ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻟﻮﺟﻮﻩ،)ﻓﻲ ﺭﺅﻳﺔ ﺍﻟﻜﻤﺒﻴﻮﺗﺮ
• In Robotics, we have been able to make vehicles that are mostly autonomous.
()ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﺮﻭﺑﻮﺗﺎﺕ ﺃﺻﺒﺤﻨﺎ ﻗﺎﺩﺭﻳﻦ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺟﻌﻞ ﺍﻟﻤﺮﻛﺒﺎﺕ ﻣﺴﺘﻘﻠﺔ
In Natural language processing, we have systems that are capable of simple machine
translation.
( ﻟﺪﻳﻨﺎ ﺃﻧﻈﻤﺔ ﻗﺎﺩﺭﺓ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻟﺘﺮﺟﻤﺔ ﺍﻵﻟﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﺒﺴﻴﻄﺔ،ﻓﻲ ﻣﻌﺎﻟﺠﺔ ﺍﻟﻠﻐﺔ ﺍﻟﻄﺒﻴﻌﻴﺔ.)
• Today’s Expert systems can carry out medical diagnosis in a narrow domain
()ﺍﻟﻴﻮﻡ ﺍﻟﻨﻈﻢ ﺍﻟﺨﺒﻴﺮﻡ ﺑﺎﻣﻜﺎﻧﻬﺎ ﺍﺟﺮﺍء ﺍﻟﺘﺸﺨﻴﺼﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻄﺒﻴﻪ ﻓﻲ ﻣﺠﺎﺍﻻﺕ ﻣﺘﺨﺼﺼﻪ ﻭﺿﻴﻘﻪ
• Speech understanding systems are capable of recognizing several thousand words
continuous speech
(• )ﺃﻧﻈﻤﺔ ﻓﻬﻢ ﺍﻟﻜﻼﻡ ﻗﺎﺩﺭﺓ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻟﺘﻌﺮﻑ ﻋﻠﻰ ﻋﺪﺓ ﺁﻻﻑ ﻛﻠﻤﺔ ﻓﻲ ﺧﻼﻝ ﻛﻼﻡ ﻣﺴﺘﻤﺮ
• Planning and scheduling systems had been employed in scheduling experiments
with the Hubble Telescope.
(• ﺗﻢ ﺍﺳﺘﺨﺪﺍﻡ ﻧﻈﻢ ﺍﻟﺘﺨﻄﻴﻂ ﻭﺍﻟﺠﺪﻭﻟﺔ ﻓﻲ ﺟﺪﻭﻟﺔ ﺍﻟﺘﺠﺎﺭﺏ ﻣﻊ ﺗﻠﺴﻜﻮﺏ ﻫﺎﺑﻞ.)
• The Learning systems are capable of doing text categorization into about a 1000
topics
(• ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﻤﻮﺿﻮﻋﺎﺕ1000 )ﺃﻧﻈﻤﺔ ﺍﻟﺘﻌﻠﻢ ﻗﺎﺩﺭﺓ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻟﻘﻴﺎﻡ ﺗﺼﻨﻴﻒ ﺍﻟﻨﺺ ﺇﻟﻰ ﺣﻮﺍﻟﻲ
• In Games, AI systems can play at the Grand Master level in chess (world
champion),etc.
( ﺍﻧﻈﻤﺔ ﺍﻟﺬﻛﺎء ﺍﻻﺻﻨﺎﻋﻲ ﻗﺎﺩﺭﺓ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻟﻠﻌﺐ ﻋﻠﻰ ﻣﺴﺘﻮﻯ ﺑﻄﻞ ﺍﻟﻌﺎﻟﻢ ﻓﻲ ﻟﻌﺒﺔ ﺍﻟﺸﻄﺮﻧﺞ ﻭﻏﻴﺮﻩ ﻣﻦ,ﻓﻲ ﺍﻻﻟﻌﺎﺏ
)ﺍﻻﻟﻌﺎﺏ
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
14-What can Ai system not to do yet?
() ﻣﺎﺫ ﻳﺴﺘﻌﺼﻲ ﻋﻠﻲ ﺍﻧﻈﻤﺔ ﺍﻟﺬﻛﺎء ﺍﻻﺻﻄﻨﺎﻋﻲ ﻓﻌﻠﻪ ﺣﺘﻰ ﺍﻻﻥ
Understand natural language robustly (e.g., read and understand articles in a
newspaper)
( )ﻓﻬﻢ ﺍﻟﻠﻐﺔ ﺍﻟﻄﺒﻴﻌﻴﺔ ﺑﻘﻮﺓ ﻣﺜﻞ ﻗﺮﺍءﺓ ﻭﻓﻬﻢ ﺍﻟﻤﻘﺎﻻﺕ ﻓﻲ ﺻﺤﻴﻔﺔ
Interpret an arbitrary visual scene
()ﺗﻔﺴﻴﺮ ﺍﻟﻤﺸﻬﺪ ﺍﻟﺒﺼﺮﻱ ﺍﻟﺘﻌﺴﻔﻲ
Learn a natural language
()ﺗﻌﻠﻢ ﻟﻐﺔ ﻁﺒﻴﻌﻴﺔ
Construct plans in dynamic real-time domains
()ﺍﻧﺸﺎء ﺧﻄﻂ ﻓﻲ ﻣﺠﺎﻻﺕ ﺩﻳﻨﺎﻣﻴﻜﺔ ﺍﻟﻮﻗﺖ ﺍﻟﺤﻘﻴﻘﻲ
14-What are the Characteristics of AI ?( )ﻣﺎ ﻫﻲ ﺧﺼﺎﺋﺺ ﺍﻟﺬﻛﺎء ﺍﻻﺻﻄﻨﺎﻋﻲ
Symbolic Representation
()ﺍﻟﺘﻤﺜﻴﻞ ﺍﻟﺮﻣﺰﻱ
Heuristics
()ﺍﻻﺳﺘﺪﻻﻝ
Knowledge Representation
()ﺗﻤﺜﻴﻞ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﺔ
Incomplete data
()ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻧﺎﺕ ﻏﻴﺮ ﺍﻟﻤﻜﺘﻤﻠﺔ
Conflicting data
()ﺗﻀﺎﺭﺏ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻧﺎﺕ
Ability to learn
()ﻗﺎﺑﻠﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﺘﻌﻠﻢ
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
15-What are the Ai technique Characteristics?( )ﻣﺎ ﻫﻲ ﺧﺼﺎﺋﺺ ﺗﻘﻨﻴﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺬﻛﺎء ﺍﻻﺻﻄﻨﺎﻋﻲ
They capture generalizations
()ﺍﻟﺘﻘﺎﻁ ﺍﻟﺘﻌﻤﻴﻤﺎﺕ
Can be understood by domain expert
()ﻳﻤﻜﻦ ﻓﻬﻤﻬﺎ ﻣﻦ ﻗﺒﻞ ﺍﻟﺨﺒﺮﺍء ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﻤﺠﺎﻝ
Easily modified to correct errors or reflect changes in the world view
()ﺳﻬﻮﻟﺔ ﺗﻌﺪﻳﻞ ﻭﺗﺼﺤﻴﺢ ﻻﺧﻄﺎء ﻭﻋﻜﺲ ﺍﻟﺘﻐﻴﻴﺮﺍﺕ ﻓﻲ ﻧﻈﺮﺓ ﺍﻟﻌﺎﻟﻢ
Used in lots of different situations
()ﺗﺴﺘﺨﺪﻡ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﻜﺜﻴﺮ ﻣﻦ ﻣﺨﺘﻠﻒ ﺍﻟﻤﺠﺎﻻﺕ
Reduce its own size/bulk by narrowing the range of possibilities it must consider at
any given time
()ﺗﻀﻴﻴﻖ ﻧﻄﺎﻗﻬﺎ ﻋﻦ ﻁﺮﻳﻖ ﺗﻀﻴﻴﻖ ﻧﻄﺎﻕ ﺍﻻﺣﺘﻤﺎﻻﺕ ﺍﻟﻮﺍﺟﺐ ﺍﻋﺘﺒﺎﺭﻫﺎ ﻓﻲ ﺃﻱ ﻟﺤﻈﺔ
16-discuss A Brief History of AI?( )ﻧﺎﻗﺶ ﺍﻟﺘﺎﺭﻳﺦ ﺍﻟﻤﻮﺟﺰ ﻟﻠﺬﻛﺎء ﺍﻻﺻﻄﻨﺎﻋﻲ
In 1940, attempts began to build a system of thinking, these attempts ended in creating neural
networks to try to simulate the shape and arrangement and functioning of cells in the nervous
system of humans.
In 1956, a conference at the Faculty of Dartmouth for Research in Artificial Intelligence. The
computer can solve problems in algebra and prove logical theorems and speaking English.
In the early eighties, there have been expert systems. And is one of artificial intelligence
programs that simulate the knowledge and analytical skills of one or more of the expert
human.
ﻭﺍﻧﺘﻬﺖ ﻫﺬﻩ ﺍﻟﻤﺤﺎﻭﻻﺕ ﻓﻲ ﺧﻠﻖ ﺍﻟﺸﺒﻜﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻌﺼﺒﻴﺔ ﻓﻲ ﻣﺤﺎﻭﻟﺔ ﻟﻤﺤﺎﻛﺎﺓ، ﺑﺪﺃﺕ ﻣﺤﺎﻭﻻﺕ ﻟﺒﻨﺎء ﻧﻈﺎﻡ ﺍﻟﺘﻔﻜﻴﺮ،1940 )ﻓﻲ ﻋﺎﻡ
ﺷﻜﻞ ﻭﺗﺮﺗﻴﺐ ﻭﻋﻤﻞ ﺍﻟﺨﻼﻳﺎ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﺠﻬﺎﺯ ﺍﻟﻌﺼﺒﻲ ﻟﻠﺒﺸﺮ.
ﻟﺠﻌﻞ ﺍﻟﻜﻤﺒﻴﻮﺗﺮ ﻗﺎﺩﺭ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺣﻞ ﺍﻟﻤﺸﺎﻛﻞ ﻓﻲ. ﻋﻘﺪ ﻣﺆﺗﻤﺮ ﻓﻲ ﻛﻠﻴﺔ ﺩﺍﺭﺗﻤﻮﺙ ﻟﻠﺒﺤﻮﺙ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﺬﻛﺎء ﺍﻻﺻﻄﻨﺎﻋﻲ،1956 ﻓﻲ ﻋﺎﻡ
ﺍﻟﺠﺒﺮ ﻭﺇﺛﺒﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻨﻈﺮﻳﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻤﻨﻄﻘﻴﺔ ﻭﺍﻟﺘﺤﺪﺙ ﺑﺎﻟﻠﻐﺔ ﺍﻹﻧﺠﻠﻴﺰﻳﺔ.
ﻛﺎﻧﺖ ﻫﻨﺎﻙ ﺍﻟﻨﻈﻢ ﺍﻟﺨﺒﻴﺮﺓ ﻭﻫﻲ ﻭﺍﺣﺪﺓ ﻣﻦ ﺑﺮﺍﻣﺞ ﺍﻟﺬﻛﺎء ﺍﻻﺻﻄﻨﺎﻋﻲ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺗﺤﺎﻛﻲ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﺔ ﻭﺍﻟﻤﻬﺎﺭﺍﺕ،ﻓﻲ ﺃﻭﺍﺋﻞ ﺍﻟﺜﻤﺎﻧﻴﻨﺎﺕ
(ﺍﻟﺘﺤﻠﻴﻠﻴﺔ ﻣﻦ ﻭﺍﺣﺪ ﺃﻭ ﺃﻛﺜﺮ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﺨﺒﺮﺍء
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
17-what are the advantages of AI?( )ﻣﺎ ﻫﻲ ﻣﺤﺎﺳﻦ ﺍﻟﺬﻛﺎء ﺍﻻﺻﻄﻨﺎﻋﻲ
more powerful and more useful computers
()ﺟﻌﻞ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﺳﻮﺏ ﺍﻛﺜﺮ ﻓﺎﺋﺪﺓ ﻭﻗﻮﻩ
new and improved interfaces
()ﻭﺍﺟﻬﺎﺕ ﺟﺪﻳﺪﻩ ﻭﻣﺤﺴﻨﺔ
solving new problems
()ﺣﻞ ﺍﻟﻤﺸﺎﻛﻞ ﺍﻟﺠﺪﻳﺪﻩ
better handling of information
( )ﺗﻌﺎﻣﻞ ﺍﺣﺴﻦ ﻣﻊ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﻠﻮﻣﺎﺕ
relieves information overload
()ﺗﺨﻔﻴﻒ ﺍﻟﺘﺤﻤﻴﻞ ﺍﻟﺰﺍﺋﺪ ﻟﻠﻤﻌﻠﻮﻣﺎﺕ
conversion of information into knowledge
()ﺗﺤﻮﻳﻞ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﻠﻮﻣﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻰ ﻣﻌﺮﻓﺔ
18-what are the disadvantages of AI?( )ﻣﺎ ﻫﻲ ﻋﻴﻮﺏ ﺍﻟﺬﻛﺎء ﺍﻻﺻﻄﻨﺎﻋﻲ
increased costs
()ﺯﻳﺎﺩﺓ ﺍﻟﺘﻜﺎﻟﻴﻒ
difficulty with software development - slow and expensive
()ﺻﻌﻮﺑﺔ ﻓﻲ ﺗﻄﻮﻳﺮ ﺍﻟﺒﺮﻣﺠﻴﺎﺕ ﺑﻄﻴﺌﺔ ﻭﻣﻜﻠﻔﺔ
few experienced programmers
()ﻗﻠﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﺨﺘﺼﻴﻦ ﻓﻲ ﺑﺮﻣﺠﺘﻪ
few practical products have reached the market as yet.
()ﻗﻠﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﻨﺘﺠﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻌﻤﻠﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﻭﺻﻠﺖ ﻟﺴﻮﻕ ﺍﻟﻌﻤﻞ ﻟﺤﺪ ﺍﻻﻥ
AI is a very fascinating field. It can help us solve difficult, real-world problems, creating new
opportunities in business, engineering, and many other application areas.
ﻭﺧﻠﻖ ﻓﺮﺹ ﺟﺪﻳﺪﺓ ﻓﻲ ﻣﺠﺎﻝ ﺍﻷﻋﻤﺎﻝ، ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﻌﺎﻟﻢ ﺍﻟﺤﻘﻴﻘﻲ، ﻭﻳﻤﻜﻦ ﺃﻥ ﺗﺴﺎﻋﺪﻧﺎ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺣﻞ ﺍﻟﻤﺸﺎﻛﻞ ﺍﻟﺼﻌﺒﺔ.)ﺍﻟﺬﻛﺎء ﺍﻻﺻﻄﻨﺎﻋﻲ ﻫﻮ ﺣﻘﻞ ﺭﺍﺋﻊ ﺟﺪﺍ
(. ﻭﺍﻟﻌﺪﻳﺪ ﻣﻦ ﻣﺠﺎﻻﺕ ﺍﻟﺘﻄﺒﻴﻖ ﺍﻷﺧﺮﻯ، ﻭﺍﻟﻬﻨﺪﺳﺔ،ﺍﻟﺘﺠﺎﺭﻳﺔ
Even though AI technology is integrated into the fabric of everyday life. The ultimate promises of
AI are still decades away and the necessary advances in knowledge and technology will require a
sustained fundamental research effort.
, ﻭﺍﻟﻮﻋﻮﺩ ﺍﻟﻨﻬﺎﺋﻴﺔ ﻟﻠﺬﻛﺎء ﺍﻻﺻﻄﻨﺎﻋﻲ ﺍﻟﺪﻭﻟﻴﺔ ﻻ ﺗﺰﺍﻝ ﺑﻌﻴﺪﻩ.)ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻟﺮﻏﻢ ﻣﻦ ﺃﻥ ﺗﻜﻨﻮﻟﻮﺟﻴﺎ ﺍﻟﺬﻛﺎء ﺍﻻﺻﻄﻨﺎﻋﻲ ﻳﺘﻢ ﺩﻣﺠﻬﺎ ﻓﻲ ﻧﺴﻴﺞ ﺍﻟﺤﻴﺎﺓ ﺍﻟﻴﻮﻣﻴﺔ
(.ﻭﺍﻟﺘﻘﺪﻡ ﺍﻟﻀﺮﻭﺭﻱ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﺔ ﻭﺍﻟﺘﻜﻨﻮﻟﻮﺟﻴﺎ ﺗﺘﻄﻠﺐ ﺟﻬﺪﺍ ﺑﺤﺜﻴﺎ ﺃﺳﺎﺳﻴﺎ ﻣﺴﺘﻤﺮﺍ
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
LECTURE 3 & 4: Knowledge representation methods
U
()ﻁﺮﻕ ﺗﻤﺜﻴﻞ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﺔ
1-what is data? ()ﻣﺎ ﻫﻲ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻧﺎﺕ
Data is raw. It simply exists and has no significance beyond its existence (in and of
itself). It can exist in any form, usable or not. It does not have meaning of itself. In
computer parlance, a spreadsheet generally starts out by holding data.
ﻭﻳﻤﻜﻦ ﺃﻥ ﺗﻮﺟﺪ.( ﺇﻧﻬﺎ ﻣﻮﺟﻮﺩﺓ ﺑﺒﺴﺎﻁﺔ ﻭﻟﻜﻦ ﻟﻴﺲ ﻟﻬﺎ ﺃﻫﻤﻴﺔ ﺗﺘﺠﺎﻭﺯ ﻭﺟﻮﺩﻫﺎ )ﻓﻲ ﺣﺪ ﺫﺍﺗﻪ.)ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻧﺎﺕ ﻫﻲ ﺍﻟﺨﺎﻡ
ﺟﺪﻭﻝ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻧﺎﺕ ﻳﺒﺪﺃ، ﻓﻲ ﻟﻐﺔ ﺍﻟﻜﻤﺒﻴﻮﺗﺮ. ﻟﻴﺲ ﻟﻬﺎ ﻣﻌﻨﻰ ﻓﻲ ﺣﺪ ﺫﺍﺗﻬﺎ. ﺻﺎﻟﺤﺔ ﻟﻼﺳﺘﻌﻤﺎﻝ ﻛﺎﻧﺖ ﺃﻡ ﻻ،ﻓﻲ ﺃﻱ ﺷﻜﻞ
(ﻋﺎﺩﺓ ﻣﻦ ﺧﻼﻝ ﻋﻘﺪ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻧﺎﺕ.
2-what is information? ()ﻣﺎ ﻫﻲ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﻠﻮﻣﺎﺕ
Information is data that has been given meaning by way of relational connection.
. (ﺍﻟﻤﻌﻠﻮﻣﺎﺕ ﻫﻲ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻧﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺃﻋﻄﺖ ﻣﻌﻨﻰ ﻋﻦ ﻁﺮﻳﻖ ﺍﺗﺼﺎﻝ ﺃﻟﻌﻼﺋﻘﻲ ﺑﻴﻦ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻧﺎﺕ.)
3-what is knowledge? ()ﻣﺎ ﻫﻲ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﺔ
is the appropriate collection of information, such that it's intent is to be useful.
()ﻫﻲ ﻣﺠﻤﻮﻋﺔ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﻠﻮﻣﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻘﺼﺪ ﻣﻨﻬﺎ ﺍﻥ ﺗﻜﻮﻥ ﻣﻔﻴﺪﻩ
Knowledge is a familiarity with someone or something, which can include information,
facts, descriptions, and/or skills acquired through experience or education
Example, knowledge of, the "times table".
ﺃﻭ/ ﻭﺍﻟﺬﻱ ﻳﻤﻜﻦ ﺃﻥ ﻳﺘﻀﻤﻦ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﻠﻮﻣﺎﺕ ﻭﺍﻟﺤﻘﺎﺋﻖ ﻭﺍﻷﻭﺻﺎﻑ ﻭ،)ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﺔ ﻫﻲ ﺍﻹﻟﻤﺎﻡ ﺑﺸﺨﺺ ﻣﺎ ﺃﻭ ﺷﻲء ﻣﺎ
( ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﺔ ﺑﺠﺪﻭﻝ ﺍﻷﻭﻗﺎﺕ: ﻣﺜﺎﻝ,ﺍﻟﻤﻬﺎﺭﺍﺕ ﺍﻟﻤﻜﺘﺴﺒﺔ ﻣﻦ ﺧﻼﻝ ﺍﻟﺨﺒﺮﺓ ﺃﻭ ﺍﻟﺘﻌﻠﻴﻢ
4-what is the Knowledge Representation? ()ﻣﺎ ﻫﻮ ﺗﻤﺜﻴﻞ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﺔ
Knowledge representation and reasoning is the field of artificial intelligence dedicated to
representing information about the world in a form that a computer system can utilize to
solve complex tasks
)ﺗﻤﺜﻴﻞ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﺔ ﻭﺍﻻﺳﺘﻨﺘﺎﺝ ﻫﻮ ﻣﺠﺎﻝ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﺬﻛﺎء ﺍﻻﺻﻄﻨﺎﻋﻲ ﻣﺨﺼﺺ ﻟﺘﻤﺜﻴﻞ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﻠﻮﻣﺎﺕ ﺣﻮﻝ ﺍﻟﻌﺎﻟﻢ ﻓﻲ ﺷﻜﻞ ﺃﻥ ﻧﻈﺎﻡ
(ﺍﻟﻜﻤﺒﻴﻮﺗﺮ ﻳﻤﻜﻦ ﺍﻻﺳﺘﻔﺎﺩﺓ ﻣﻨﻬﺎ ﻓﻲ ﺣﻞ ﺍﻟﻤﻬﺎﻡ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﻘﺪﺓ
5-what is the aim of Knowledge Representation? ()ﻣﺎ ﻫﻮ ﺍﻟﻬﺪﻑ ﻣﻦ ﺗﻤﺜﻴﻞ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﺔ
The aim of the representation is to make the language clear and precise and unambiguous
()ﺍﻟﻬﺪﻑ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﺘﻤﺜﻴﻞ ﻫﻮ ﺟﻌﻞ ﺍﻟﻠﻐﺔ ﻭﺍﺿﺤﺔ ﻭﺩﻗﻴﻘﺔ ﻭﻻ ﻟﺒﺲ ﻓﻴﻬﺎ
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
It is a common language between human beings and machines; this language
should enable the computer to think and generates new facts from this data then
solving problems.
ﻭﻳﻧﺑﻐﻲ ﻟﻬﺫﻩ ﺍﻟﻠﻐﺔ ﺗﻣﻛﻳﻥ ﺍﻟﻛﻣﺑﻳﻭﺗﺭ ﻣﻥ ﺍﻟﺗﻔﻛﻳﺭ ﻭﺗﻭﻟﻳﺩ ﺣﻘﺎﺋﻕ ﺟﺩﻳﺩﺓ ﻣﻥ ﻫﺫﻩ،)ﻫﻲ ﻟﻐﺔ ﻣﺷﺗﺭﻛﺔ ﺑﻳﻥ ﺍﻟﺑﺷﺭ ﻭﺍﻵﻻﺕ
(ﺍﻟﺑﻳﺎﻧﺎﺕ ﺛﻡ ﺣﻝ ﺍﻟﻣﺷﺎﻛﻝ
The aim of the Knowledge Representation in the area of artificial
intelligence is to find a way to represent the facts and knowledge through
symbols.
)ﻭﺍﻟﻬﺩﻑ ﻣﻥ ﺗﻣﺛﻳﻝ ﺍﻟﻣﻌﺭﻓﺔ ﻓﻲ ﻣﺟﺎﻝ ﺍﻟﺫﻛﺎء ﺍﻻﺻﻁﻧﺎﻋﻲ ﻫﻭ ﺇﻳﺟﺎﺩ ﻭﺳﻳﻠﺔ ﻟﺗﻣﺛﻳﻝ ﺍﻟﺣﻘﺎﺋﻕ ﻭﺍﻟﻣﻌﺭﻓﺔ
(ﻣﻥ ﺧﻼﻝ ﺍﻟﺭﻣﻭﺯ
Representation of knowledge means finding a uniform method enables the
computer to simulate the human way of thinking.
(. ﺗﻣﺛﻳﻝ ﺍﻟﻣﻌﺭﻓﺔ ﻳﻌﻧﻲ ﺇﻳﺟﺎﺩ ﻁﺭﻳﻘﺔ ﻣﻭﺣﺩﺓ ﺗﻣﻛﻥ ﺍﻟﻛﻣﺑﻳﻭﺗﺭ ﻟﻣﺣﺎﻛﺎﺓ ﻁﺭﻳﻘﺔ ﺍﻟﺗﻔﻛﻳﺭ ﺍﻟﺑﺷﺭﻱ.)
The process of transforming the problem into a simpler language include a
set of rules synthetic (Syntactic Rules) and the rules of meaning (Semantic
Rules).
(ﺗﺗﺿﻣﻥ ﻋﻣﻠﻳﺔ ﺗﺣﻭﻳﻝ ﺍﻟﻣﺷﻛﻠﺔ ﺇﻟﻰ ﻟﻐﺔ ﺃﺑﺳﻁ ﻣﺟﻣﻭﻋﺔ ﻣﻥ ﺍﻟﻘﻭﺍﻋﺩ ﺍﻟﺗﺭﻛﻳﺑﻳﺔ )ﺍﻟﻘﻭﺍﻋﺩ ﺍﻟﻧﺣﻭﻳﺔ
(ﻭﻗﻭﺍﻋﺩ ﺍﻟﻣﻌﺎﻧﻲ )ﺍﻟﻘﻭﺍﻋﺩ ﺍﻟﺩﻻﻟﻳﺔ.
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
6-what are the Representation Characteristics? ()ﻣﺎ ﻫﻲ ﺧﺼﺎﺋﺺ ﺍﻟﺘﻤﺜﻴﻞ
Natural Constraint
()ﺍﻟﻘﻴﻮﺩ ﺍﻟﻄﺒﻴﻌﻴﺔ
Complete
()ﺍﻻﻛﺘﻤﺎﻝ
Concise
()ﺍﻻﺧﺘﺼﺎﺭ
Transparent
()ﺍﻟﺸﻔﺎﻓﻴﺔ
Details elimination
()ﺍﺯﺍﻟﺔ ﺍﻟﺘﻔﺎﺻﻴﻞ
Computation Efficient
()ﻛﻔﺎءﺓ ﺍﻟﺤﺴﺎﺑﺎﺕ
7-what are the Knowledge Representation methods? ()ﻣﺎ ﻫﻲ ﺃﺳﺎﻟﻴﺐ ﺗﻤﺜﻴﻞ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﺔ
First Order Logics
(fol )ﻣﻨﻄﻖ ﺍﻝ
Production Rules Systems
()ﺃﻧﻈﻤﺔ ﻗﻮﺍﻋﺪ ﺍﻹﻧﺘﺎﺝ
Semantic Network
()ﺷﺒﻜﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺎﻧﻲ
Frames
()ﺍﻻﻁﺎﺭﺍﺕ
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
First Order Logic / Predicate Logic
•Problem of Propositional Logic
•FOL Syntax
•Universal Quantifiers
•Existential Quantifiers
•Quantifiers Scope
•Connections between ∀and ∃
•Thinking in FOL “Representing Knowledge in FOL”
8-what are the types of logic? ()ﻣﺎ ﻫﻲ ﺃﻧﻮﺍﻉ ﺍﻟﻤﻨﻄﻖ
Logics are characterized by what they commit to as "primitives".
ﺗﺼﻨﻒ ﺃﻧﻮﺍﻉ ﺍﻟﻤﻨﻄﻖ ﺑﻨﺎءﺍ ﻋﻠﻰ ﻣﺎ ﺗﺘﺨﺬﻩ ﻛﺄﻭﻟﻮﻳﺎﺕ
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
9-what is the Propositional Logic? ()ﻣﺎ ﻫﻮ ﺍﻟﻤﻨﻄﻖ ﺃﻻﻗﺘﺮﺍﺣﻲ
A proposition logic is a sentence, written in a language, that has a truth value (i.e., it is true or
false) in a world. A proposition is built from atomic propositions using logical connectives. ...
A direct connection exists to Boolean variables, which are variables with domain {true ,
false}.
ﺗﻢ ﺑﻨﺎء ﺍﻗﺘﺮﺍﺡ ﻣﻦ.)ﺍﻟﻤﻨﻄﻖ ﺍﻻﻗﺘﺮﺍﺣﻲ ﻫﻮ ﺟﻤﻠﺔ ﻣﻜﺘﻮﺑﺔ ﺑﻠﻐﺔ ﻟﻬﺎ ﻗﻴﻤﺔ ﺣﻘﻴﻘﺔ )ﺃﻱ ﺃﻧﻬﺎ ﺻﺤﻴﺤﺔ ﺃﻭ ﺧﺎﻁﺌﺔ( ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﻌﺎﻟﻢ
ﻭﻫﻲ ﻣﺘﻐﻴﺮﺍﺕ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﻤﺠﺎﻝ، ﻳﻮﺟﺪ ﺍﺗﺼﺎﻝ ﻣﺒﺎﺷﺮ ﻟﻠﻤﺘﻐﻴﺮﺍﺕ ﺍﻟﻤﻨﻄﻘﻴﺔ... .ﺍﻟﻤﻘﺘﺮﺣﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺬﺭﻳﺔ ﺑﺎﺳﺘﺨﺪﺍﻡ ﺍﻟﺮﺑﻂ ﺍﻟﻤﻨﻄﻘﻲ
( (ﺧﺎﻁﺊ,)ﺻﺤﻴﺢ.
10-what is the first order Logic?
It is reasoning in which each sentence, or statement, is broken down into a subject and a
predicate. The predicate modifies or defines the properties of the subject. ... First-order logic
is also known as first-order predicate calculus or first-order functional calculus..
ﻳﻘﻮﻡ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﻨﺪ ﺑﺘﻌﺪﻳﻞ ﺃﻭ ﺗﻌﺮﻳﻒ ﺧﺼﺎﺋﺺ. ﺇﻟﻰ ﻣﻮﺿﻮﻉ ﻭﻣﺴﻨﺪ، ﺃﻭ ﺑﻴﺎﻥ،)ﻫﻮ ﺍﻟﻤﻨﻄﻖ ﺍﻟﺬﻱ ﻳﺘﻢ ﻓﻴﻪ ﺗﻘﺴﻴﻢ ﻛﻞ ﺟﻤﻠﺔ
ﻭﻳﻌﺮﻑ ﺍﻟﻤﻨﻄﻖ ﺍﻷﻭﻝ ﺃﻳﻀﺎ ﺑﺎﺳﻢ ﺣﺴﺎﺏ ﺍﻟﺘﻔﺎﺿﻞ ﻭﺍﻟﺘﻜﺎﻣﻞ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﻨﺪ ﺍﻷﻭﻝ ﺃﻭ ﺣﺴﺎﺏ ﺍﻟﺘﻔﺎﺿﻞ ﻭﺍﻟﺘﻜﺎﻣﻞ... .ﺍﻟﻤﻮﺿﻮﻉ
(ﺍﻟﻮﻅﻴﻔﻲ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﺪﺭﺟﺔ ﺍﻷﻭﻟﻰ
11-what are the Problems of Propositional Logic? ()ﻣﺎ ﻫﻲ ﻣﺸﺎﻛﻞ ﺍﻟﻤﻨﻄﻖ ﺍﻻﻗﺘﺮﺍﺣﻲ
Propositional logic has very limited expressive power
Can’t have one proposition to represent a group of objects
e.g.: if we want to say “Every student is happy”
In Propositional Logic ⇒“Ali is happy”, “Ahmed is happy”, “Mohamed is happy”…
e.g., cannot say "pits cause breezes in adjacent squares“except by writing one sentence
for each square.
We want to be able to say this in one single sentence: “for all squares and pits, pits
cause breezes in adjacent squares.
First order logic will provide this flexibility by using ∀, ∃.
i.e ∀x At(x,sust) ⇒Happy(x)
So, FOL fixes the problems of PL:
PL doesn’t have variables BUT FOL does.
PL can't directly express properties of individuals or relations between individuals,
But FOL can do that.
Inference in PL is fairly easy But In FOL it is more complex
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
10-what first order Logic depend on?( FOL) ﻋﻠﻰ ﻣﺎﺫﺍ ﻳﻌﺘﻤﺪ ﻣﻨﻄﻖ ﺍﻝ
P-Logic assumes the world contains facts that are either true or false.
�First-Order Logic models the world in terms of:
�Objects: which are things with individual identities?
�e.g. people, houses, numbers, colors, baseball games, wars, computers,
�Variable: Represents object, X, Y, Z…
�Predicate/relation: Gives relation between objects, variables, i.e. brother of, bigger than,
part of, comes between, Person (Ahmed), Likes (Ali, Yasser), Equilateral Triangle(X,Y,Z)
�Function: a relation where there is only one “value” for any given “input”
MotherOf (Yasser), OldestSonOf (Wailed, Aymen) …
� Properties: Describe specific aspects of objects, used to distinguish between objects
Green, heavy, visible,
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
Syntax of FOL: Basic Elements
( ﺍﻟﻌﻧﺎﺻﺭ ﺍﻷﺳﺎﺳﻳﺔ:)ﺑﻧﺎء ﺍﻟﺟﻣﻠﺔ ﻓﻲ ﻣﻧﻁﻕ ﺍﻟﻁﻠﺏ ﺍﻷﻭﻝ
� Constants ()ﺛﻭﺍﺑﺕ: Ahmed, 2, sust...
�Predicates ()ﻣﺳﻧﺩﺍﺕ: Brother, Greater than,...
�Functions ()ﺩﻭﺍﻝ: Sqrt, LeftLegOf...
�Variables ()ﻣﺗﻐﻳﺭﺍﺕ: x, y, a, b,...
�Connectives ()ﻭﺻﻼﺕ ﻣﻧﻁﻘﻳﺔ:¬, ⇒, ∧, ∨, ⇔
�Equality ()ﺍﻟﻣﺳﺎﻭﺍﺓ:=
�Quantifiers ()ﺍﻟﻣﺣﺩﺩﺍﺕ:∀, ∃
Examples of Objects, Relations, ( ، ﻭﺍﻟﻌﻼﻗﺎﺕ، ﺃﻣﺛﻠﺔ ﻋﻥ ﺍﻟﻛﺎﺋﻧﺎﺕ...)
�“The smell homeless occupies square [1, 3]”
Objects: homeless, square1, 3, Property: smell, Relation: occupies
�“Two plus two equals four”
Objects: two, four, Relation: equals, Function: plus
�Function (Term1… Termn):e.g.Sqrt (9), Distance (Damam, Khober)…
�Is a relation for which there is one answer
�Maps one or more objects to another single object
�Represents a user defined functional relation
�Cannot be used with logical connectives
�A term denotes an object in the world.
�A ground term is a term with no variables.
�A free variable is a variable that isn't bound by a quantifier.
�∃y Likes(x,y) xi s free, y is bound
�A well-formed formula (wff)is a sentence containing no “free” variables. i.e., all variables
are “bound” by universal or existential quantifiers.
�∀x R(x,y) has x bound as a universally quantified variable, but y is free.
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
Atomic & Complex Sentence ()ﺍﻟﺟﻣﻝ ﺍﻟﺫﺭﻳﺔ ﻭﺍﻟﻣﺭﻛﺑﺔ
�A sentence represents a fact in the world that is assigned a truth value.
()ﺍﻟﺟﻣﻠﺔ ﺍﻟﺗﻲ ﺗﻣﺛﻝ ﺣﻘﻳﻘﺔ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﻌﺎﻟﻡ ﺗﺣﻣﻝ ﻗﻳﻣﺔ ﺣﻘﻳﻘﻳﺔ
�Atomic sentence= predicate (term1,...,term n) or term1= term2
�Father(Ahmed, Mohamed), Mother(Asmaa, Ahmed),
Sister(Dena, Ahmed)
�Married(Ahmed, Asmaa)
�Married(Father-Of(Ahmed), Mother-Of(Ahmed))
�Complex sentences are made from atomic sentences using connectives:
¬S, S1 ∧S2, S1 ∨S2, S1 ⇒S2, S1 ⇔S2,
�Sibling(Ahmed,Ali) ⇒Sibling(Ali,Ahmed)
�Friend(Ali,Ahmed) ⇒Friend(Ahmed,Ali)
�Father(Ahmed, Yasser) ∧Mother(Asmaa, Yasser) ∧Sister(Yara,
Yasser) ¬Sister(Yasser, Yara)
�Parents(Ahmed, Dena, Ali, Yara) ∧ ¬ Married(Ahmed, Dena)
�Parents(Yasser, Yaraa) ⇒ ¬ Married(Yasser, Yara)
Constants
�Constant symbols, which represent individuals in the world
�Yasser
�3
�Green
�Function symbols, which map individuals to individuals
�father-of(Yara) = Yasser
�color-of(Sky) = Blue
�Predicate symbols, which map individuals to truth values
�greater(5,3)
�green(Grass)
�color(Grass, Green)
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
Universal Quantifiers (∀):)(")ﻋﻼﻣﺔ "ﻟﻛﻝ
�Used to express properties of collections of objects and eliminates the need to explicitly enumerate all
objects as in PL.
�Universal quantifier : ∀<variables> <sentence>
�Means the sentence holds true for all values in the domain of variable x.
�Everyone at SUST is smart: ∀x At(x,SUST) ⇒Smart(x)
�∀x P is true in a model m iff P is true with x being each possible object in the model.
�All humans are mammals.
�∀x Human(x) ⇒Mammal(x): for all x if x is a human then x is a mammal
�All birds can fly
�∀x Bird(x) ⇒Can-Fly(x)
�Main connective typically ⇒forming if-then rules
�Mammals must have hair
�∀x Mammal(x) ⇒HasHair(x): for all x if x is a mammal then x has hair
�Equivalent to the conjunction of P instantiations: At(Ahmed,SUST) ⇒Smart(Ahmed) ∧At(Aymen, SUST)
⇒Smart(Aymen) ∧ ...
Universal Quantifiers (∀): A Common Mistake:
�Common mistakes with the use of ∧as main connective with ∀:
�Examples
�∀x At(x,SUST) ∧Smart(x): means “ Everyone is at SUST and everyone is smart”.
�∀x Human(x) ∧Mammal(x) means? Everything is human and a mammal
(Human(Ali) ∧Mammal(Ali)) ∧
(Human(Yasser)∧Mammal(Yasser)) ∧
(Human(Y) ∧Mammal(Y) ) ∧…
�∀x student(x)^smart(x) means “Everyone in the world is a student and is smart”
�Universal quantification should be rarely used to make blanket statements about every individual in the
world
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
Existential Quantifiers ( ∃)(")ﻋﻼﻣﺔ "ﻟﺑﻌﺽ
Existential quantifier: ∃<variables> <sentence>
�Means the sentence holds true for some value/s of x in the domain of x.
�Existential quantifiers (∃)are usually used with “∧”to specify a list of properties about an
individual:
�∃x student(x) ^smart(x) means “There is a student who is smart”
�Mammals may have arms. ∃x Mammal(x) ∧HasArms(x), this interpreted as there exist an x such
that x is a mammal and x has arms
�“Some humans are computer scientists”: ∃x Human(x) ∧Computer-Scientist(x)
�“Ahmed has a sister who is a computer scientist”: ∃x Sister(x, Ahmed) ∧Computer-Scientist(x).
�“Some birds can’t fly”: ∃x Bird(x) ∧¬Can-Fly(x)
�Common mistake :using ⇒as the main connective with ∃Results in a weak statement: examples:
�∃x At(x,SUST) ⇒Smart(x): is true if there is anyone who is not at SUST!
Example: Family Relationships:
�Objects: People
�Properties: Gender, …
�Expressed as un array predicates Male(x), Female(y)
�Relations: parenthood, brotherhood, marriage
�Expressed through binary predicates Brother(x,y),…
�Functions: motherhood, fatherhood
�Mother(x), Father(y)
�Because every person has exactly one mother and one father
�There may also be a relation Mother-of(x,y), Father-of(x,y)
�Family Relationships
�∀w,h Husband(h,w) ⇔Male(h) ∧Spouse(h,w)
�∀x Male(x) ⇔¬Female(x)
�∀g,c Grandparent(g,c) ⇔∃p Parent(g,p) ∧Parent(p,c)
�∀x,y Sibling(x,y) ⇔¬(x=y) ∧∃p Parents(p,x) ∧Parents(p,y)
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
Quantifiers Scope:
�The order of quantification:
�∀x ∀y Likes(x,y)
Everyone likes everyone. It’s the active voice.
�∀y ∀x Likes(x,y) Everyone is liked by everyone. It’s the passive voice.
�Switching the order of universal quantifiers does not change the meaning.
�∀x ∀y is the same as ∀y ∀x
�Similarly, you can switch the order of existential quantifiers.
�∃x ∃y is the same as ∃y ∃x
�note: ∃x ∃y can be written as ∃x,y, likewise with ∀
�Switching the order of universals and existential does change meaning:
�Everyone likes someone: ∀x ∃y likes(x,y)
�Someone is liked by everyone: ∃y ∀x likes(x,y)
Connections between ∀and ∃:)(")ﺍﻟﺮﺑﻂ ﺑﻴﻦ ﻋﻼﻣﺘﻲ "ﻟﻜﻞ" ﻭ"ﻟﺒﻌﺾ
�∀x Likes(x,IceCream)
is what in English?
Everyone likes ice cream.
�What is the logical negation of this sentence?
Not everyone likes ice cream.which is the same as…
∃x ¬Likes(x,IceCream)is what in English?
Someone doesn't like ice cream.
�Properties of quantifiers:
�∀x P(x) when negated is ∃x ¬P(x)
�∃x P(x) when negated is ∀x ¬P(x)
� All statements made with one quantifier can be converted into equivalent statements with the other quantifier
by using negation.
�∀is a conjunction over all objects under discussion
�∃is a disjunction over all objects under discussion
�De Morgan’s rules apply to quantified sentences
∀x ¬P(x) ≡¬∃x P(x),
∀x P(x) ≡¬∃x ¬P(x),
¬∀x P(x) ≡∃x ¬P(x)
¬∀x ¬P(x) ≡∃x P(x)
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
Knowledge Engineering in FOL(fol) ﻫﻧﺩﺳﺔ ﺍﻟﻣﻌﺭﻓﺔ ﻓﻲ ﻣﻧﻁﻕ ﺍﻝ
1. Identify the task ()ﺗﺣﺩﻳﺩ ﺍﻟﻣﻬﺎﻡ
2. Assemble the relevant knowledge ()ﺗﺟﻣﻳﻊ ﺍﻟﻣﻌﺎﺭﻑ ﺫﺍﺕ ﺍﻟﺻﻠﺔ
3. Decide on a vocabulary of predicates, functions, and constants
( ﻭﺍﻟﺛﻭﺍﺑﺕ، ﺍﻟﺩﻭﺍﻝ،)ﺍﺗﺧﺎﺫ ﻗﺭﺍﺭ ﺑﺷﺄﻥ ﺍﻟﻣﻔﺭﺩﺍﺕ ﻣﻥ ﺍﻟﻣﺳﻧﺩﺍﺕ
4. Encode general knowledge about the domain()ﺗﺭﻣﻳﺯ ﺍﻟﻣﻌﺎﺭﻑ ﺍﻟﻌﺎﻣﺔ ﺣﻭﻝ ﺍﻟﻣﺟﺎﻝ
5. Encode a description of the specific problem instance()ﺗﺭﻣﻳﺯ ﻟﺗﻭﺻﻳﻑ ﺍﻟﻣﺷﻛﻠﺔ ﺍﻟﻣﺣﺩﺩﺓ
6. Create queries to the inference procedure and get answers
()ﺇﻧﺷﺎء ﺍﺳﺗﻌﻼﻣﺎﺕ ﻹﺟﺭﺍء ﺍﻻﺳﺗﺩﻻﻝ ﻭﺍﻟﺣﺻﻭﻝ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺇﺟﺎﺑﺎﺕ
7. Debug the knowledge base()ﺗﺻﺣﻳﺢ ﻗﺎﻋﺩﺓ ﺍﻟﻣﻌﺭﻓﺔ
Semantic Networks:()ﺷﺒﻜﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺎﻧﻲ
U
.ﺍﻟﺸﺒﻜﺔ ﺍﻟﺪﻻﻟﻴﺔ ﻫﻲ ﻣﺨﻄﻂ ﺗﻤﺜﻴﻞ ﺑﺴﻴﻂ ﺗﺴﺘﺨﺪﻡ ﺍﻟﺮﺳﻢ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻧﻲ ﻟﻠﻌﻘﺪ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﻤﻰ ﻭﺍﻷﻗﻮﺍﺱ ﺍﻟﻤﻮﺟﻬﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﻤﻴﺔ ﻟﺘﺮﻣﻴﺰ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﺔ
Nodes – objects, concepts, events
ﺍﻷﺷﻴﺎء ﻭﺍﻟﻤﻔﺎﻫﻴﻢ ﻭﺍﻷﺣﺪﺍﺙ- ﺍﻟﻌﻘﺪ
Arcs – relationships between nodes
ﺍﻟﻌﻼﻗﺎﺕ ﺑﻴﻦ ﺍﻟﻌﻘﺪ- ﺃﻗﻮﺍﺱ
Conceptual Graphs):(ﺍﻟﺮﺳﻮﻡ ﺍﻟﻤﻔﺎﻫﻴﻤﻴﺔ
U
U
Conceptual graphs are semantic nets representing the meaning of (simple) sentences
in natural language
ﺍﻟﺮﺳﻮﻡ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻧﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﻔﺎﻫﻴﻤﻴﺔ ﻫﻲ ﺷﺒﻜﺎﺕ ﺩﻻﻟﻴﺔ ﺗﻤﺜﻞ ﻣﻌﻨﻰ ﺍﻟﺠﻤﻞ )ﺍﻟﺒﺴﻴﻄﺔ( ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﻠﻐﺔ ﺍﻟﻄﺒﻴﻌﻴﺔ
Two types of nodes()ﻳﻮﺟﺪ ﻧﻮﻋﻴﻦ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﻌﻘﺪ:
Concept nodes; there are two types of concepts, individual concepts and generic concepts
( ﺍﻟﻤﻔﺎﻫﻴﻢ ﺍﻟﻔﺮﺩﻳﺔ ﻭﺍﻟﻤﻔﺎﻫﻴﻢ ﺍﻟﻌﺎﻣﺔ،)ﻋﻘﺪ ﺍﻟﻤﻔﻬﻮﻡ؛ ﻫﻨﺎﻙ ﻧﻮﻋﺎﻥ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﻤﻔﺎﻫﻴﻢ
Relation nodes(binary relations between concepts)
(()ﻋﻘﺪ ﺍﻟﻌﻼﺋﻘﻴﺔ )ﺍﻟﻌﻼﻗﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺜﻨﺎﺋﻴﺔ ﺑﻴﻦ ﺍﻟﻤﻔﺎﻫﻴﻢ
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
Nodes and Arcs)()ﺍﻟﻌﻘﺪ ﻭﺍﻷﻗﻮﺍﺱ:
U
Arcs define binary relations which hold between objects denoted by the nodes.
(.)ﺃﻗﻮﺍﺱ ﺗﻘﻮﻡ ﺑﺘﻌﺮﻳﻒ ﺍﻟﻌﻼﻗﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺜﻨﺎﺋﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺗﻌﻘﺪ ﺑﻴﻦ ﺍﻟﻜﺎﺋﻨﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺗﺸﻴﺮ ﺇﻟﻴﻬﺎ ﺍﻟﻌﻘﺪ
mother (sue, john)
age (john, 5)
wife (sue, max)
age (max, 34)
Non-binary relations()ﺍﻟﻌﻼﻗﺔ ﻏﻴﺮ ﺍﻟﺜﻨﺎﺋﻴﺔ
…
U
We can represent the generic give event as a relation involving three things:
A giver()ﺍﻟﻤﻌﻄﻲ ﺃﻭ ﺍﻟﻤﺮﺳﻞ
A recipient()ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺘﻘﺒﻞ
An object()ﺍﻟﻜﺎﺋﻦ
Inheritance()ﺍﻟﻮﺭﺍﺛﺔ
U
Inheritance is one of the main kind of reasoning done in semantic nets
()ﺍﻟﻮﺭﺍﺛﺔ ﻫﻲ ﻭﺍﺣﺪﺓ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻷﻧﻮﺍﻉ ﺍﻷﺳﺎﺳﻴﺔ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻻﺳﺘﻨﺘﺎﺝ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺘﺨﺪﻣﺔ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﺸﺒﻜﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺪﻻﻟﻴﺔ
The ISA (is a) relation is often used to link a class and its super class.
Some links (e.g. haspart) are inherited along ISA paths
The semantics of a semantic net can be relatively informal or very formal
Often defined at the implementation level
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
Disadvantages of Semantic nets::()ﻣﺴﺎﻭﺉ ﺷﺒﻜﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺎﻧﻲ
U
Inheritance (particularly from multiple sources and when exceptions in inheritance are
wanted) can cause problems.
(.)ﻳﻤﻜﻦ ﻟﻠﻮﺭﺍﺛﺔ)ﺧﺎﺻﺔ ﻣﻦ ﻣﺼﺎﺩﺭ ﻣﺘﻌﺪﺩﺓ ﻭﻋﻨﺪﻣﺎ ﺗﻜﻮﻥ ﺍﻻﺳﺘﺜﻨﺎءﺍﺕ ﻣﻄﻠﻮﺑﺔ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﻮﺭﺍﺛﺔ(ﺃﻥ ﺗﺴﺒﺐ ﻣﺸﻜﻠﺔ
Facts placed in appropriately cause problems.
No standards about node and arc values
Frames:
U
Frames – semantic net with properties()ﺷﺒﻜﺔ ﻣﻌﺎﻧﻲ ﺫﺍﺕ ﺧﺼﺎﺋﺺ
A frame represents an entity as a set of slots (attributes) and associated values
()ﻳﻤﺜﻞ ﺍﻹﻁﺎﺭ ﻛﻴﺎﻧﺎ ﻛﻤﺠﻤﻮﻋﺔ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﻔﻮﺍﺻﻞ )ﺍﻟﺴﻤﺎﺕ( ﻭﺍﻟﻘﻴﻢ ﺍﻟﻤﺮﺗﺒﻄﺔ ﺑﻬﺎ
A frame can represent a specific entry, or a general concept
()ﻳﻤﻜﻦ ﺃﻥ ﻳﻤﺜﻞ ﺍﻹﻁﺎﺭ ﺇﺩﺧﺎﻻ ﻣﺤﺪﺩﺍ ﺃﻭ ﻣﻔﻬﻮﻣﺎ ﻋﺎﻣﺎ
Frames are implicitly associated with one another because the value of a attributes can
be another frame
()ﺗﺮﺗﺒﻂ ﺍﻹﻁﺎﺭﺍﺕ ﺿﻤﻨﺎ ﺑﺒﻌﻀﻬﺎ ﺍﻟﺒﻌﺾ ﻷﻥ ﻗﻴﻤﺔ ﺍﻟﺨﺎﺻﻴﺔ ﻳﻤﻜﻦ ﺃﻥ ﺗﻜﻮﻥ ﺇﻁﺎﺭﺍ ﺁﺧﺮ
3 components of a frame
()ﺍﻟﻣﻛﻭﻧﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺛﻼﺛﺔ ﻟﻼﻁﺎﺭ
•
frame name
()ﺍﺳﻡ ﺍﻻﻁﺎﺭ
•
attributes
(slots)
()ﺍﻟﺧﺻﺎﺋﺹ
•
values (fillers:
list of values,
range, string,
etc.)
()ﺍﻟﻘﻳﻡ
Book Frame
Slot Filler
AI. A modern Approach
•
Title
•
Author Russell & Norvig
•
Year 2003
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
Features of Frame Representation:()ﻣﻤﻴﺰﺍﺕ ﺍﺳﺘﺨﺪﺍﻡ ﺗﻤﺜﻴﻞ ﺍﻹﻁﺎﺭ
More natural support of values than semantic nets (each slots has constraints
describing legal values that a slot can take)
)ﺩﻋﻢ ﺃﻛﺜﺮ ﻁﺒﻴﻌﻴﺔ ﻟﻠﻘﻴﻢ ﻣﻘﺎﺭﻧﺔ ﺑﺎﻟﺸﺒﻜﺔ ﺍﻟﺪﻻﻟﻴﺔ )ﻛﻞ ﺣﻴﺰ ﺃﻭ ﻓﺘﺤﺔ ﻟﺪﻳﻪ ﻗﻴﻮﺩ ﺗﺼﻒ ﺍﻟﻘﻴﻢ ﺍﻟﻘﺎﻧﻮﻧﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﻳﻤﻜﻦ ﺃﻥ ﺗﺄﺧﺬﻫﺎ
((ﺍﻟﻔﺘﺤﺔ
Can be easily implemented using object-oriented programming techniques
()ﻳﻤﻜﻦ ﺗﻨﻔﻴﺬﻫﺎ ﺑﺴﻬﻮﻟﺔ ﺑﺎﺳﺘﺨﺪﺍﻡ ﺗﻘﻨﻴﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺒﺮﻣﺠﺔ ﻛﺎﺋﻨﻴﻪ ﺍﻟﺘﻮﺟﻪ
Inheritance is easily controlled
()ﻳﺘﻢ ﺍﻟﺘﺤﻜﻢ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﻮﺭﺍﺛﺔ ﺑﺴﻬﻮﻟﺔ
Benefits of Frames:()ﻓﻮﺍﺋﺪ ﺍﻹﻁﺎﺭﺍﺕ
U
Makes programming easier by grouping related knowledge
()ﻳﺠﻌﻞ ﺍﻟﺒﺮﻣﺠﺔ ﺃﺳﻬﻞ ﻣﻦ ﺧﻼﻝ ﺗﺠﻤﻴﻊ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺎﺭﻑ ﺫﺍﺕ ﺍﻟﺼﻠﺔ
Easily understood by non-developers
()ﺳﻬﻮﻟﺔ ﻓﻬﻤﻬﺎ ﺣﺘﻰ ﻣﻦ ﻗﺒﻞ ﻏﻴﺮ ﺍﻟﻤﻄﻮﺭﻳﻦ
Expressive power()ﻗﻮﺓ ﺍﻟﺘﻌﺒﻴﺮ
Easy to set up slots for new properties and relations
()ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﺴﻬﻞ ﺇﺿﺎﻓﺔ ﻓﺘﺤﺎﺕ ﻟﺨﺼﺎﺋﺺ ﺟﺪﻳﺪﺓ ﺃﻭ ﻋﻼﻗﺎﺕ
Easy to include default information and detect missing values
()ﺳﻬﻠﺔ ﻟﺘﺸﻤﻞ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﻠﻮﻣﺎﺕ ﺍﻻﻓﺘﺮﺍﺿﻴﺔ ﻭﺍﻟﻜﺸﻒ ﻋﻦ ﺍﻟﻘﻴﻢ ﺍﻟﻤﻔﻘﻮﺩﺓ
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
Drawbacks of Frames()ﻋﻴﻮﺏ ﺍﻹﻁﺎﺭﺍﺕ
U
No standards (slot-filler values)(()ﻻ ﺗﻮﺟﺪ ﻣﻌﺎﻳﻴﺮ )ﻗﻴﻢ ﻣﻠﺊ ﺍﻟﻔﺮﺍﻏﺎﺕ
More of a general methodology than a specific representation:
(:)ﺃﻛﺜﺮ ﻣﻦ ﻣﻨﻬﺠﻴﺔ ﻋﺎﻣﺔ ﻣﻦ ﺗﻤﺜﻴﻞ ﻣﻌﻴﻦ
Frame for a class-room will be different for a professor and for a maintenance
worker
()ﺳﻴﻜﻮﻥ ﺇﻁﺎﺭ ﻏﺮﻓﺔ ﺍﻟﺼﻒ ﻣﺨﺘﻠﻔﺔ ﻋﻦ ﺃﺳﺘﺎﺫ ﻭﻋﺎﻣﻞ ﺍﻟﺼﻴﺎﻧﺔ
No associated reasoning/inference mechanisms
()ﻻ ﻳﻮﺟﺪ ﺍﺭﺗﺒﺎﻁ ﺑﻴﻦ ﺁﻟﻴﺎﺕ ﺍﻻﺳﺘﻨﺘﺎﺝ ﻭﺍﻻﺳﺘﺪﻻﻝ
Knowledge base: production System( ﻧﻈﺎﻡ ﺍﻹﻧﺘﺎﺝ:)ﻗﺎﻋﺪﺓ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﺔ
U
Knowledge is represented using rules of the form :
(:)ﻳﺘﻢ ﺗﻤﺜﻴﻞ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﺔ ﺑﺎﺳﺘﺨﺪﺍﻡ ﻗﻮﺍﻋﺪ ﺍﻟﻨﻤﻮﺫﺝ
Rule: if Conditions then Conclusions
or
Rule: if Premises then Actions
or
Rule: if if-part then then-Part
A rule as described above is often referred to as a production rule
()ﻏﺎﻟﺒﺎ ﻣﺎ ﻳﺸﺎﺭ ﺇﻟﻰ ﻗﺎﻋﺪﺓ ﻛﻤﺎ ﻫﻮ ﻣﻮﺿﺢ ﺃﻋﻼﻩ ﺑﻘﺎﻋﺪﺓ ﺍﻹﻧﺘﺎﺝ
Example: if symptom1 and symptom2 and symptom3 then disease1
(1 ﺛﻢ ﺍﻟﻤﺮﺽ3 ﻭ ﺃﻋﺮﺍﺽ2 ﻭ ﺃﻋﺮﺍﺽ1 ﺇﺫﺍ ﺃﻋﺮﺍﺽ:)ﻣﺜﺎﻝ
Other examples
if - the leaves are dry, brittle and discoloured then - the plant has been attacked by red
spider mite
( ﻫﺸﺔ ﻭﻣﺸﻮﻫﻪ ﺇ ًﺫﺍ – ﺍﻟﺰﺭﻉ ﻗﺪ ﺗﻌﺮﺽ ﻟﻬﺠﻮﻡ ﻣﻦ ﻗﺒﻞ ﺳﻮﺱ ﺍﻟﻌﻨﻜﺒﻮﺕ ﺍﻷﺣﻤﺮ،)ﺇﺫﺍ ﻛﺎﻧﺖ ﺍﻷﻭﺭﺍﻕ ﺟﺎﻓﺔ
If – it is raining then – you should take an umbrella ()ﺇﺫﺍ ﻛﺎﻧﺖ ﺗﻤﻄﺮ ﺍﺫﺍً ﻓﻌﻠﻴﻚ ﺣﻤﻞ ﺍﻟﻤﻈﻠﺔ
if - the customer closes the account then - delete the customer from the database
()ﺇﺫﺍ ﺍﻟﻐﻲ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺘﺨﺪﻡ ﺣﺴﺎﺑﻪ ﺇﺫﺍً ﻗﻢ ﺑﻤﺴﺤﻪ ﻣﻦ ﻗﺎﻋﺪﺓ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻧﺎﺕ
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
Rule-based reasoning:()ﺍﻻﺳﺘﻨﺘﺎﺝ ﺍﻟﻘﺎﺋﻢ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻟﻘﻮﺍﻋﺪ
U
•
The essence of a rule-based reasoning system is that it goes through a series of
cycles.
(.)ﺟﻮﻫﺮ ﻧﻈﺎﻡ ﺍﻟﻤﻨﻄﻖ ﺍﻟﻘﺎﺋﻢ ﻋﻠﻰ ﻗﻮﺍﻋﺪ ﻫﻮ ﺃﻧﻪ ﻳﻤﺮ ﻣﻦ ﺧﻼﻝ ﺳﻠﺴﻠﺔ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﺪﻭﺭﺍﺕ
In each cycle, it attempts to pick an appropriate rule from its collection of rules,
depending on the present circumstances, and to use it.
(. ﻭﺍﺳﺘﺨﺪﺍﻣﻬﺎ، ﺍﻋﺘﻤﺎﺩﺍ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻟﻈﺮﻭﻑ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻟﻴﺔ، ﻓﺈﻧﻪ ﻳﺤﺎﻭﻝ ﺍﺧﺘﻴﺎﺭ ﻗﺎﻋﺪﺓ ﻣﻨﺎﺳﺒﺔ ﻣﻦ ﻣﺠﻤﻮﻋﺔ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﻘﻮﺍﻋﺪ،)ﻓﻲ ﻛﻞ ﺩﻭﺭﺓ
•
Because using a rule produces new information, it's possible for each new
cycle to take the reasoning process further than the cycle before. This is rather
like a human following a chain of ideas in order to come to a conclusion.
ﻣﺜﻞ. ﻓﻤﻦ ﺍﻟﻤﻤﻜﻦ ﻟﻜﻞ ﺩﻭﺭﺓ ﺟﺪﻳﺪﺓ ﺍﻟﻘﻴﺎﻡ ﺑﻌﻤﻠﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﺘﻔﻜﻴﺮ ﺃﻛﺜﺮ ﻣﻦ ﺩﻭﺭﺓ ﻣﻦ ﻗﺒﻞ،)ﻷﻥ ﺍﺳﺘﺨﺪﺍﻡ ﻗﺎﻋﺪﺓ ﻳﻨﺘﺞ ﻣﻌﻠﻮﻣﺎﺕ ﺟﺪﻳﺪﺓ
(.ﺍﻹﻧﺴﺎﻥ ﺣﻴﺚ ﻳﻘﻮﻡ ﺑﺴﻠﺴﻠﺔ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻷﻓﻜﺎﺭ ﻣﻦ ﺃﺟﻞ ﺍﻟﺘﻮﺻﻞ ﺇﻟﻰ ﻧﺘﻴﺠﺔ
Forward Chaining:()ﺍﻟﺘﺴﻠﺴﻞ ﺍﻷﻣﺎﻣﻲ
U
Forward Chaining is based on Modules Ponens inference rule:
(A, A⇒B ) / B
In other words, if A is true and we have A -->B then we can deduce that B is true
In the context of Expert System, it is used as follows:
(: ﻳﺴﺘﺨﺪﻡ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻟﻨﺤﻮ ﺍﻟﺘﺎﻟﻲ،)ﻭﻓﻲ ﺳﻴﺎﻕ ﺍﻟﻨﻈﻢ ﺍﻟﺨﺒﻴﺮﺓ
if A is in WM and we have a rule in KB of the form if A then B then we can
deduce B (add B to WM as new information)
Do until problem is solved or no antecedents match
Collect the rules whose antecedents are found in WM.
If more than one rule matches
use conflict resolution strategy to eliminate all but one
Do actions indicated in by rule “fired”
ﺇﺫﺍ ﺗﻄﺎﺑﻘﺖ ﺃﻛﺜﺮ ﻣﻦ,, WM ﺍﺟﻤﻊ ﺍﻟﻘﻮﺍﻋﺪ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﻭﺟﺪﺕ ﺃﺳﻼﻓﻬﺎ ﻓﻲ,, )ﺣﺘﻰ ﻳﺘﻢ ﺣﻞ ﺍﻟﻤﺸﻜﻠﺔ ﺃﻭ ﻻ ﺗﻄﺎﺑﻖ ﺍﻟﺴﻮﺍﺑﻖ
ﻫﻞ ﺍﻹﺟﺮﺍءﺍﺕ ﺍﻟﻤﺸﺎﺭ ﺇﻟﻴﻬﺎ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﻘﺎﻋﺪﺓ,, ﺍﺳﺘﺨﺪﺍﻡ ﺇﺳﺘﺮﺍﺗﻴﺠﻴﺔ ﺣﻞ ﺍﻟﻨﺰﺍﻋﺎﺕ ﻟﻠﻘﻀﺎء ﻋﻠﻰ ﻛﻞ ﻭﺍﺣﺪ ﻓﻘﻂ,, ﻗﺎﻋﺪﺓ ﻭﺍﺣﺪﺓ
(""ﺃﻁﻠﻖ
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
Algorithm:
U
1. Match WM with KB to select production rules
( ﻟﺘﺤﺪﻳﺪ ﻗﻮﺍﻋﺪ ﺍﻹﻧﺘﺎﺝKB ﻣﻊWM )ﻗﺎﺭﻥ
2. Eliminate already applied rules()ﺍﻟﻘﻀﺎء ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻟﻘﻮﺍﻋﺪ ﺍﻟﻤﻄﺒﻘﺔ ﺑﺎﻟﻔﻌﻞ
3. If many rules select one which has the smallest number
()ﺇﺫﺍ ﻛﺎﻥ ﻫﻨﺎﻙ ﺍﻟﻌﺪﻳﺪ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﻘﻮﺍﻋﺪ ﺍﺧﺘﺎﺭ ﻭﺍﺣﺪ ﻭﻫﻮ ﺍﻟﺬﻱ ﻟﺪﻳﻪ ﺃﺻﻐﺮ ﻋﺪﺩ
4. Apply selected rule by adding its conclusion to WM
(WM)ﺗﻄﺒﻴﻖ ﻗﺎﻋﺪﺓ ﻣﺨﺘﺎﺭﺓ ﺑﺈﺿﺎﻓﺔ ﺍﺳﺘﻨﺘﺎﺟﻬﺎ ﺇﻟﻰ
5. If the problem is solved or no new information added then stop otherwise go to step 1
(1 )ﺇﺫﺍ ﺗﻢ ﺣﻞ ﺍﻟﻤﺸﻜﻠﺔ ﺃﻭ ﻟﻢ ﻳﺘﻢ ﺇﺿﺎﻓﺔ ﺃﻱ ﻣﻌﻠﻮﻣﺎﺕ ﺟﺪﻳﺪﺓ ﺇﺫﺍ ﺗﻮﻗﻒ ﺧﻼﻑ ﺫﻟﻚ ﺍﻧﺘﻘﻞ ﺇﻟﻰ ﺍﻟﺨﻄﻮﺓ
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
Backward Chaining()ﺍﻟﺘﺴﻠﺴﻞ ﺍﻟﺨﻠﻔﻲ
U
Backward Chaining is based on Modus Tollens inference rule:
(Tollens) ﻳﺴﺘﻨﺪ ﺍﻟﺘﺴﻠﺴﻞ ﺍﻟﺨﻠﻔﻲ ﺇﻟﻰ ﻗﺎﻋﺪﺓ ﺍﺳﺘﺪﻻﻝ
( B, A⇒B ) / A
If A implies B , and B is false, then A is false
In other words, if we have A⇒B then proving B is equivalent of proving A
In the context of Expert System, it is used as follows:
To prove a goal B which is not in WM and if we have a rule in KB of the form
if A then B then we have just to prove A (A is either present in WM or it
exists a rule with A as a conclusion)
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
U
LECTURE 5 & 6: Solving Problems by Searching
U
()ﺣﻞ ﺍﻟﻤﺸﻜﻼﺕ ﻋﻦ ﻁﺮﻳﻖ ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺚ
A problem solving agent: is a kind of goal-based agents that decide what to do by
finding sequences of actions that lead to desirable goal.
ﻫﻮ ﻧﻮﻉ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﻌﻮﺍﻣﻞ ﺍﻟﻘﺎﺋﻤﺔ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻟﻬﺪﻑ ﻭﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺗﻘﺮﺭ ﻣﺎ ﻳﺠﺐ ﺍﻟﻘﻴﺎﻡ ﺑﻪ ﻣﻦ ﺧﻼﻝ ﺇﻳﺠﺎﺩ ﺳﻠﺴﻠﺔ ﻣﻦ:)ﻋﺎﻣﻞ ﺣﻞ ﺍﻟﻤﺸﻜﻼﺕ
(.ﺍﻹﺟﺮﺍءﺍﺕ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺗﺆﺩﻱ ﺇﻟﻰ ﻫﺪﻑ ﻣﺮﻏﻮﺏ
Goal formulation : Limiting the objectives (we may have more than one objective)
( ﺗﻘﻠﻴﻞ ﺍﻷﻫﺪﺍﻑ )ﻗﺪ ﻳﻜﻮﻥ ﻟﺪﻳﻨﺎ ﺃﻛﺜﺮ ﻣﻦ ﻫﺪﻑ ﻭﺍﺣﺪ:)ﺻﻴﺎﻏﺔ ﺍﻷﻫﺪﺍﻑ
Problem formulation : Deciding what actions and states to consider
( ﺗﺤﺪﻳﺪ ﺍﻹﺟﺮﺍءﺍﺕ ﻭﺍﻟﺤﺎﻻﺕ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﻳﺠﺐ ﻣﺮﺍﻋﺎﺗﻬﺎ:)ﺻﻴﺎﻏﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﺸﻜﻠﺔ
The above two means searching for sequences of actions that lead to the goal
Examples:
)ﺍﻻﺛﻨﺎﻥ ﺃﻋﻼﻩ ﻳﻌﻨﻴﺎﻥ ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺚ ﻋﻦ ﺳﻼﺳﻞ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻹﺟﺮﺍءﺍﺕ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺗﺆﺩﻱ ﺇﻟﻰ ﺍﻟﻬﺪﻑ
(:ﺃﻣﺜﻠﺔ
Finding the shortest path between two cities in a given country.
(.)ﺍﻟﻌﺜﻮﺭ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺃﻗﺼﺮ ﺍﻟﻄﺮﻕ ﺑﻴﻦ ﻣﺪﻳﻨﺘﻴﻦ ﻓﻲ ﺑﻠﺪ ﻣﻌﻴﻦ
Find the shortest path for the salesman to travel, visiting each city once, and then
returning to the starting city.
(.)ﺍﺑﺤﺚ ﻋﻦ ﺃﻗﺼﺮ ﻣﺴﺎﺭ ﻳﺴﺎﻓﺮ ﺇﻟﻴﻪ ﺍﻟﺒﺎﺋﻊ ﻭﺯﻳﺎﺭﺓ ﻛﻞ ﻣﺪﻳﻨﺔ ﻣﺮﺓ ﻭﺍﺣﺪﺓ ﺛﻢ ﺍﻟﻌﻮﺩﺓ ﺇﻟﻰ ﺍﻟﻤﺪﻳﻨﺔ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺗﺒﺪﺃ ﻣﻨﻬﺎ
Problem Statement()ﻋﺮﺽ ﺍﻟﻤﺸﻜﻠﺔ
How do I get from initial state to goal?
()ﻛﻴﻒ ﻳﻤﻜﻨﻨﻲ ﺍﻟﻮﺻﻮﻝ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻟﺔ ﺍﻷﻭﻟﻴﺔ ﺇﻟﻰ ﺍﻟﻬﺪﻑ؟
Use a search algorithm (as we will see later).
(.()ﺍﺳﺘﺨﺪﻡ ﺧﻮﺍﺭﺯﻣﻴﺔ ﺑﺤﺚ )ﻛﻤﺎ ﺳﻨﺮﻯ ﻻﺣﻘًﺎ
From initial state, apply operators (actions) to the current state to generate new states:
expand
( ﻗﻢ ﺑﺎﻟﺘﻮﺳﻴﻊ: ﻗﻢ ﺑﺘﻄﺒﻴﻖ ﺍﻟﻌﻤﻠﻴﺎﺕ )ﺍﻷﺣﺪﺍﺙ( ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻟﺔ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻟﻴﺔ ﻹﻧﺸﺎء ﺣﺎﻻﺕ ﺟﺪﻳﺪﺓ، )ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻟﺔ ﺍﻷﻭﻟﻴﺔ
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
Find all adjacent cities in the shortest path
()ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺚ ﻋﻦ ﺟﻤﻴﻊ ﺍﻟﻤﺪﻥ ﺍﻟﻤﺠﺎﻭﺭﺓ ﻓﻲ ﺃﻗﺼﺮ ﺍﻟﻄﺮﻕ
Choose one of the adjacent states, and expand the state from there.
(. ﺛﻢ ﻭﺳّﻊ ﺍﻟﻮﻻﻳﺔ ﻣﻦ ﻫﻨﺎﻙ، )ﺍﺧﺘﺮ ﺇﺣﺪﻯ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻻﺕ ﺍﻟﻤﺘﺠﺎﻭﺭﺓ
Search strategy: Which states do you expand first?
( ﻣﺎ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻻﺕ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺗﻮﺳﻌﻬﺎ ﺃﻭﻻً؟:)ﺍﺳﺘﺮﺍﺗﻴﺠﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺚ
Continue until you find solution.
(.)ﺍﺳﺘﻤﺮ ﺣﺘﻰ ﺗﺠﺪ ﺍﻟﺤﻞ
Well Defined Problem and Solutions()ﻣﺸﻜﻠﺔ ﻭﺣﻠﻮﻝ ﻣﺤﺪﺩﺓ ﺟﻴﺪﺍ
U
The information needed to define a single state problem:
(:)ﺍﻟﻤﻌﻠﻮﻣﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻼﺯﻣﺔ ﻟﺘﺤﺪﻳﺪ ﻣﺸﻜﻠﺔ ﺣﺎﻟﺔ ﻭﺍﺣﺪﺓ
Initial state:The state the agent knows itself to be in. (e.g., initial chessboard, current
positions of objects in world, …)
ﺍﻟﻤﻮﺍﻗﻒ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻟﻴﺔ ﻟﻸﺷﻴﺎء ﻓﻲ، ﺭﻗﻌﺔ ﺍﻟﺸﻄﺮﻧﺞ ﺍﻷﻭﻟﻴﺔ، )ﻋﻠﻰ ﺳﺒﻴﻞ ﺍﻟﻤﺜﺎﻝ. ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻟﺔ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﻳﻌﺮﻓﻬﺎ ﺍﻟﻌﻤﻴﻞ ﻧﻔﺴﻪ:)ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻟﺔ ﺍﻷﻭﻟﻴﺔ
((... ، ﺍﻟﻌﺎﻟﻢ
Action/Operator:A set of actions that moves the problem from one state to another.
(e.g. chess move, robot action, simple change in location).
، ﺣﺮﻛﺔ ﺍﻟﺸﻄﺮﻧﺞ، )ﻋﻠﻰ ﺳﺒﻴﻞ ﺍﻟﻤﺜﺎﻝ. ﻣﺠﻤﻮﻋﺔ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻹﺟﺮﺍءﺍﺕ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺗﻨﻘﻞ ﺍﻟﻤﺸﻜﻠﺔ ﻣﻦ ﺣﺎﻟﺔ ﺇﻟﻰ ﺃﺧﺮﻯ: ﺍﻟﻌﻤﻠﻴﺔ/ )ﺍﻹﺟﺮﺍء
(.( ﺗﻐﻴﻴﺮ ﺑﺴﻴﻂ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﻤﻮﻗﻊ، ﺇﺟﺮﺍء ﺍﻟﺮﻭﺑﻮﺕ
Neighbourhood:The set of all possible states reachable from a given state
( ﻣﺠﻤﻮﻋﺔ ﺟﻤﻴﻊ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻻﺕ ﺍﻟﻤﻤﻜﻨﺔ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﻳﻤﻜﻦ ﺍﻟﻮﺻﻮﻝ ﺇﻟﻴﻬﺎ ﻣﻦ ﺩﻭﻟﺔ ﻣﻌﻴﻨﺔ:)ﺍﻟﺠﻴﺮﺍﻥ
State space:The set of all states reachable from the initial state by any sequence of
actions.
(. ﻣﺠﻤﻮﻋﺔ ﺟﻤﻴﻊ ﺍﻟﺪﻭﻝ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﻳﻤﻜﻦ ﺍﻟﻮﺻﻮﻝ ﺇﻟﻴﻬﺎ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻟﺔ ﺍﻷﻭﻟﻴﺔ ﺑﺄﻱ ﺳﻠﺴﻠﺔ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻹﺟﺮﺍءﺍﺕ:)ﻣﺴﺎﺣﺔ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻟﺔ
Path:Any sequence of actions leading from one state to another.
(. ﺃﻱ ﺗﺴﻠﺴﻞ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻹﺟﺮﺍءﺍﺕ ﻳﺆﺩﻱ ﻣﻦ ﺣﺎﻟﺔ ﺇﻟﻰ ﺃﺧﺮﻯ:)ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺎﺭ
Goal test:A test applicable to a single state problem to determine if it is the goal state. (e.g.,
winning chess position, target location)
ﺍﻟﻔﻮﺯ، )ﻋﻠﻰ ﺳﺒﻴﻞ ﺍﻟﻤﺜﺎﻝ. ﺍﺧﺘﺒﺎﺭ ﻣﻄﺒﻖ ﻋﻠﻰ ﻣﺸﻜﻠﺔ ﺣﺎﻟﺔ ﻭﺍﺣﺪﺓ ﻟﺘﺤﺪﻳﺪ ﻣﺎ ﺇﺫﺍ ﻛﺎﻧﺖ ﻫﻲ ﺣﺎﻟﺔ ﺍﻟﻬﺪﻑ:)ﺍﺧﺘﺒﺎﺭ ﺍﻟﻬﺪﻑ
(( ﺍﻟﻤﻮﻗﻊ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺘﻬﺪﻑ، ﺑﻤﺮﻛﺰ ﺍﻟﺸﻄﺮﻧﺞ
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
Path cost:The function that assigns a cost to the path; (e.g.How much it costs to take a
particular path).
(.( ﺍﻟﺘﻜﻠﻔﺔ ﺍﻟﻼﺯﻣﺔ ﻻﺗﺨﺎﺫ ﻣﺴﺎﺭ ﻣﻌﻴﻦ، ﺍﻟﻮﻅﻴﻔﺔ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺗﺴﻨﺪ ﺗﻜﻠﻔﺔ ﻟﻠﻤﺴﻴﺮ ؛ )ﻋﻠﻰ ﺳﺒﻴﻞ ﺍﻟﻤﺜﺎﻝ:)ﺗﻜﻠﻔﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺎﺭ
Problem Solving and Search()ﺣﻞ ﺍﻟﻤﺸﻜﻼﺕ ﻭﺍﻟﺒﺤﺚ
U
In solving problems, we sometimes have to search through many possible ways:
(: ﻳﺘﻌﻴﻦ ﻋﻠﻴﻨﺎ ﻓﻲ ﺑﻌﺾ ﺍﻷﺣﻴﺎﻥ ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺚ ﻋﺒﺮ ﺍﻟﻌﺪﻳﺪ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﻄﺮﻕ ﺍﻟﻤﻤﻜﻨﺔ، )ﻓﻲ ﺣﻞ ﺍﻟﻤﺸﻜﻼﺕ
We may know all the possible actions our robot can do, but we have to consider
various sequences to find a sequence of actions to achieve a goal
ﻭﻟﻜﻦ ﻋﻠﻴﻨﺎ ﺍﻟﻨﻈﺮ ﻓﻲ، )ﻗﺪ ﻧﻌﺮﻑ ﺟﻤﻴﻊ ﺍﻹﺟﺮﺍءﺍﺕ ﺍﻟﻤﻤﻜﻨﺔ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﻳﻤﻜﻦ ﺃﻥ ﻳﻘﻮﻡ ﺑﻬﺎ ﺍﻟﺮﻭﺑﻮﺕ ﺍﻟﺨﺎﺹ ﺑﻨﺎ
(ﺗﺴﻠﺴﻼﺕ ﻣﺨﺘﻠﻔﺔ ﻟﻠﻌﺜﻮﺭ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺳﻠﺴﻠﺔ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻹﺟﺮﺍءﺍﺕ ﻟﺘﺤﻘﻴﻖ ﻫﺪﻑ
We may know all the possible moves in a chess game, but we must consider many
possibilities to find a good move.
ﻟﻜﻦ ﻳﺠﺐ ﻋﻠﻴﻨﺎ ﺍﻟﺘﻔﻜﻴﺮ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﻌﺪﻳﺪ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻻﺣﺘﻤﺎﻻﺕ ﻟﻠﻌﺜﻮﺭ، )ﻗﺪ ﻧﻌﺮﻑ ﺟﻤﻴﻊ ﺍﻟﺘﺤﺮﻛﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻤﻤﻜﻨﺔ ﻓﻲ ﻟﻌﺒﺔ ﺍﻟﺸﻄﺮﻧﺞ
(.ﻋﻠﻰ ﺧﻄﻮﺓ ﺟﻴﺪﺓ
Many problems can be formalized in a general way as search problems.
(.)ﻳﻤﻜﻦ ﺇﺿﻔﺎء ﺍﻟﻄﺎﺑﻊ ﺍﻟﺮﺳﻤﻲ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻟﻌﺪﻳﺪ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﻤﺸﺎﻛﻞ ﺑﻄﺮﻳﻘﺔ ﻋﺎﻣﺔ ﻣﺜﻞ ﻣﺸﺎﻛﻞ ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺚ
Search problems described in terms of:
(:)ﻣﺸﺎﻛﻞ ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺚ ﺍﻟﻤﻮﺻﻮﻓﺔ ﻣﻦ ﺣﻴﺚ
An initial state: Current positions of objects in world, current location
( ﺍﻟﻤﻮﻗﻊ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻟﻲ، ﺍﻟﻤﻮﺍﻗﻒ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻟﻴﺔ ﻟﻠﻜﺎﺋﻨﺎﺕ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﻌﺎﻟﻢ:)ﺣﺎﻟﺔ ﺃﻭﻟﻴﺔ
A goal state: Target location( ﺍﻟﻤﻮﻗﻊ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺘﻬﺪﻑ:)ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻟﺔ ﺍﻟﻬﺪﻑ
Some possible actions: That gets you from one state to another.
(. ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺗﻨﻘﻠﻚ ﻣﻦ ﺣﺎﻟﺔ ﺇﻟﻰ ﺃﺧﺮﻯ:)ﺑﻌﺾ ﺍﻹﺟﺮﺍءﺍﺕ ﺍﻟﻤﺤﺘﻤﻠﺔ
The effectiveness of a search can be measured in at least three ways.
(.)ﻳﻤﻜﻦ ﻗﻴﺎﺱ ﻓﻌﺎﻟﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺚ ﺑﺜﻼﺙ ﻁﺮﻕ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻷﻗﻞ
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
1. Does it find a solution at all.
(.)ﻫﻞ ﻳﺠﺪ ﺣﻼ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻻﻁﻼﻕ
2. Is it an optimal solution (with low cost)?
()ﻫﻞ ﻫﻮ ﺍﻟﺤﻞ ﺍﻷﻣﺜﻞ )ﺑﺘﻜﻠﻔﺔ ﻣﻨﺨﻔﻀﺔ(؟
3. What is the search cost associated with the time and memory required to find a
solution?
()ﻣﺎ ﻫﻲ ﺗﻜﻠﻔﺔ ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺚ ﺍﻟﻤﺮﺗﺒﻄﺔ ﺑﺎﻟﻮﻗﺖ ﻭﺍﻟﺬﺍﻛﺮﺓ ﺍﻟﻤﻄﻠﻮﺑﺔ ﻹﻳﺠﺎﺩ ﺣﻞ؟
Example Toy Problems( ﻣﺸﻜﻠﺔ ﺍﻟﻠﻌﺒﺔ: )ﻣﺜﺎﻝ
U
There are two types of problems()ﻫﻨﺎﻙ ﻧﻮﻋﺎﻥ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﻤﺸﺎﻛﻞ
Toy problems, which intended to illustrate various problem solving methods.
(. ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺗﻬﺪﻑ ﺇﻟﻰ ﺗﻮﺿﻴﺢ ﻁﺮﻕ ﺣﻞ ﺍﻟﻤﺸﻜﻼﺕ ﺍﻟﻤﺨﺘﻠﻔﺔ، )ﻣﺸﺎﻛﻞ ﺍﻷﻟﻌﺎﺏ
State: The location of each of the eight tiles in one of the nine squares.
(. ﻣﻮﻗﻊ ﻛﻞ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﺒﻼﻁ ﺍﻟﺜﻤﺎﻧﻴﺔ ﻓﻲ ﻭﺍﺣﺪﺓ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﻤﺮﺑﻌﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺘﺴﻌﺔ:)ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻟﺔ
Operators: Blank moves left, right, up or down.
(. ﺗﺘﺤﺮﻙ ﺍﻟﻔﺮﺍﻏﺎﺕ ﻟﻠﻴﺴﺎﺭ ﺃﻭ ﺍﻟﻴﻤﻴﻦ ﺃﻭ ﻷﻋﻠﻰ ﺃﻭ ﻷﺳﻔﻞ:)ﺍﻟﻌﻤﻠﻴﺎﺕ
Goal test: State matches the goal configuration shown.
(. ﺗﺘﻄﺎﺑﻖ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻟﺔ ﻣﻊ ﺗﻬﻴﺌﺔ ﺍﻟﻬﺪﻑ ﺍﻟﻤﻮﺿﺤﺔ:)ﺍﺧﺘﺒﺎﺭ ﺍﻟﻬﺪﻑ
Path cost: Each step costs 1, so the path cost is just the length of the path.
( ﻭﺑﺎﻟﺘﺎﻟﻲ ﻓﺈﻥ ﺗﻜﻠﻔﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺎﺭ ﻫﻲ ﻓﻘﻂ ﻁﻮﻝ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺎﺭ، 1 ﻛﻞ ﺧﻄﻮﺓ ﺗﻜﻠﻒ:)ﺗﻜﻠﻔﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺎﺭ
Why search algorithms?
()ﻟﻣﺎﺫﺍ ﻧﺣﺗﺎﺝ ﺧﻭﺍﺭﺯﻣﻳﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺑﺣﺙ؟
So, we need a principled way to look for a solution in these huge search spaces
( ﻧﺣﻥ ﺑﺣﺎﺟﺔ ﺇﻟﻰ ﻁﺭﻳﻘﺔ ﻣﺑﺩﺋﻳﺔ ﻟﻠﺑﺣﺙ ﻋﻥ ﺣﻝ ﻓﻲ ﻣﺳﺎﺣﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺑﺣﺙ ﺍﻟﻬﺎﺋﻠﺔ ﻫﺫﻩ، )ﻟﺫﻟﻙ
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
Implementation: Distinction Between State and Node
U
( ﺍﻟﺘﻤﻴﻴﺰ ﺑﻴﻦ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻟﺔ ﻭﺍﻟﻌﻘﺪﺓ:)ﺍﻟﺘﻨﻔﻴﺬ
State-space: Configuration of the world
( ﺗﻜﻮﻳﻦ ﺍﻟﻌﺎﻟﻢ:)ﻓﻀﺎء ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻟﺔ
What city am I in?() ﻣﺎ ﺍﻟﻤﺪﻳﻨﺔ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺃﻧﺎ ﺑﻬﺎ؟
What is the arrangement of tiles in the puzzle?
()ﻣﺎ ﻫﻮ ﺗﺮﺗﻴﺐ ﺍﻟﺒﻼﻁ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﻠﻐﺰ؟
Node: Data structure within the search tree, It contains the following items:
(: ﺗﺤﺘﻮﻱ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻟﻌﻨﺎﺻﺮ ﺍﻟﺘﺎﻟﻴﺔ، ﺑﻨﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻧﺎﺕ ﺩﺍﺧﻞ ﺷﺠﺮﺓ ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺚ:)ﺍﻟﻌﻘﺪﺓ
State()ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻟﺔ
Parent node()ﺍﻟﻌﻘﺪﺓ ﺍﻷﻡ
Operator used to generate node()ﻋﻤﻠﻴﺔ ﺍﻭ ﺣﺮﻛﺔ ﺗﺴﺘﺨﺪﻡ ﻟﺘﻮﻟﻴﺪ ﻋﻘﺪﺓ
Depth of this node()ﻋﻤﻖ ﻫﺬﻩ ﺍﻟﻌﻘﺪﺓ
Path cost from root node to this node()ﺗﻜﻠﻔﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺎﺭ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﻌﻘﺪﺓ ﺍﻟﺠﺬﺭﻳﺔ ﻟﻬﺬﻩ ﺍﻟﻌﻘﺪﺓ
The River Problem()ﻣﺸﻜﻠﺔ ﺍﻟﻨﻬﺮ
U
F=Farmer ( )ﻣﺰﺍﺭﻉW=Wolf( )ﺫﺋﺐD=Duck ( )ﺑﻄﺔC=Corn )ﺣﺒﻮﺏ ﺫﺭﺓ
U
How can the farmer safely transport the wolf, the duck and the corn to the opposite shore?
()ﻛﻴﻒ ﻳﺴﺘﻄﻴﻊ ﺍﻟﻤﺰﺍﺭﻉ ﻧﻘﻞ ﺍﻟﺬﺋﺐ ﻭﺍﻟﺒﻂ ﻭﺍﻟﺬﺭﺓ ﺇﻟﻰ ﺍﻟﺸﺎﻁﺊ ﺍﻟﻤﻘﺎﺑﻞ ﺑﺄﻣﺎﻥ؟
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
State space: ()ﻓﻀﺎء ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻟﺔ
A problem is solved by moving from the initial state to the goal state by applying valid
operators in sequence. Thus the state space is the set of states reachable from a particular
initial state.
.)ﻳﺘﻢ ﺣﻞ ﺍﻟﻤﺸﻜﻠﺔ ﻋﻦ ﻁﺮﻳﻖ ﺍﻻﻧﺘﻘﺎﻝ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻟﺔ ﺍﻷﻭﻟﻴﺔ ﺇﻟﻰ ﺣﺎﻟﺔ ﺍﻟﻬﺪﻑ ﻋﻦ ﻁﺮﻳﻖ ﺗﻄﺒﻴﻖ ﻋﻮﺍﻣﻞ ﺍﻧﺘﻘﺎﻝ ﺻﺎﻟﺤﺔ ﺑﺎﻟﺘﺴﻠﺴﻞ
(.ﻭﺑﺎﻟﺘﺎﻟﻲ ﻓﺈﻥ ﻣﺴﺎﺣﺔ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻟﺔ ﻫﻲ ﻣﺠﻤﻮﻋﺔ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻻﺕ ﻳﻤﻜﻦ ﺍﻟﻮﺻﻮﻝ ﺇﻟﻴﻬﺎ ﻣﻦ ﺣﺎﻟﺔ ﺃﻭﻟﻴﺔ ﻣﻌﻴﻨﺔ
F WD C
WD C
D C
F
W
F W
F
F W
C
WD
D
F
C
C
F WD C
D
W
F
F
C
C
W
C
D
F
F WD
F W
C
F
D
WD
D C
F W
W
D
F WD
F W
F
C
D
C
F
F WD C
C
D C
W
F W
C
WD
F
C
F WD
D
W
F W
F WD
D C
C
D C
F W
D C
W
D
C
F W
C
D
C
F
D C
ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ :ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ
U
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
Search Strategies()ﺍﺳﺘﺮﺍﺗﻴﺠﻴﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺚ
U
1.Uninformed search (blind search)
(()ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺚ ﻏﻴﺮ ﺍﻟﺮﺳﻤﻲ ﺍﻭ ﻏﻴﺮ ﺍﻟﻤﻨﻈﻢ)ﺍﻟﺤﺚ ﺍﻷﻋﻤﻰ
Having no information about the number of steps from the current state to the goal.
(.)ﻋﺪﻡ ﻭﺟﻮﺩ ﻣﻌﻠﻮﻣﺎﺕ ﺣﻮﻝ ﻋﺪﺩ ﺍﻟﺨﻄﻮﺍﺕ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻟﺔ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻟﻴﺔ ﺇﻟﻰ ﺍﻟﻬﺪﻑ
2. Informed search (heuristic search)
(()ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺚ ﺍﻟﻤﻨﻈﻢ )ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺚ ﺍﻻﺟﺘﻬﺎﺩﻱ
More efficient than uninformed search. ()ﺃﻛﺜﺮ ﻓﻌﺎﻟﻴﺔ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺚ ﻏﻴﺮ ﺍﻟﻤﻨﻈﻢ
Uninformed search strategies()ﺍﺳﺘﺮﺍﺗﻴﺠﻴﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺚ ﻏﻴﺮ ﺍﻟﺮﺳﻤﻲ ﺍﻭ ﻏﻴﺮ ﺍﻟﻤﻨﻈﻢ
U
Uninformed search (blind search)
(()ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺚ ﻏﻴﺮ ﺍﻟﺮﺳﻤﻲ ﺍﻭ ﻏﻴﺮ ﺍﻟﻤﻨﻈﻢ)ﺍﻟﺤﺚ ﺍﻷﻋﻤﻰ
1. Breadth-first search(ً)ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺚ ﺑﺎﻟﺠﻮﺍﻧﺐ ﺃﻭﻻ
2. Depth-first search()ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺚ ﺑﺎﻟﺘﻌﻤﻖ ﺃﻭﻻ
3. Depth-limited search()ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺚ ﺑﺎﻟﺘﻌﻤﻖ ﺍﻟﻤﺤﺪﻭﺩ
4. Iterative deepening search()ﺑﺤﺚ ﺍﻟﺘﻌﻤﻖ ﺍﻟﻤﺘﻜﺮﺭ
Evaluating the Search Strategies()ﺗﻘﻴﻴﻢ ﺍﺳﺘﺮﺍﺗﻴﺠﻴﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺚ
U
Strategies are evaluated along the following dimensions:
(:)ﻳﺘﻢ ﺗﻘﻴﻴﻢ ﺍﻻﺳﺘﺮﺍﺗﻴﺠﻴﺎﺕ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺃﺳﺎﺱ ﺍﻷﺑﻌﺎﺩ ﺍﻟﺘﺎﻟﻴﺔ
Completeness: Does it always find a solution if one exists?
( ﻫﻞ ﻳﺠﺪ ﺍﻟﺤﻞ ﺩﺍﺋ ًﻤﺎ ﺇﺫﺍ ﻭﺟﺪ؟:)ﺍﻻﻛﺘﻤﺎﻝ
Time complexity: Number of nodes generated
( ﻋﺪﺩ ﺍﻟﻌﻘﺪ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺗﻢ ﺇﻧﺸﺎﺅﻫﺎ:)ﺗﻌﻘﻴﺪ ﺍﻟﻮﻗﺖ
Space complexity: Maximum number of nodes in memory
( ﺍﻟﺤﺪ ﺍﻷﻗﺼﻰ ﻟﻌﺪﺩ ﺍﻟﻌﻘﺪ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﺬﺍﻛﺮﺓ:)ﺗﻌﻘﻴﺪ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺎﺣﺔ
Optimality: Does it always find a least- cost solution?
( ﻫﻞ ﻳﺟﺩ ﺩﺍﺋﻣًﺎ ﺣﻼً ﺃﻗﻝ ﺗﮐﻟﻔﺔ؟:)ﺍﻷﻓﺿﻟﻳﺔ
Time and space complexity are measured in terms of
()ﻳﺘﻢ ﻗﻴﺎﺱ ﺗﻌﻘﻴﺪ ﺍﻟﺰﻣﺎﻥ ﻭﺍﻟﻤﻜﺎﻥ ﻣﻦ ﺣﻴﺚ
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
b:Maximum branching factor of the search tree
( ﻋﺎﻣﻞ ﺍﻟﺘﻔﺮﻉ ﺍﻷﻗﺼﻰ ﻟﺸﺠﺮﺓ ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺚ:b)
d: Depth of the least-cost solution
( ﻋﻤﻖ ﺍﻟﺤﻞ ﺍﻷﻗﻞ ﺗﻜﻠﻔﺔ:d)
m: Maximum depth of the state space (may be ∞ )
(∞ ﺃﻗﺼﻰ ﻋﻤﻖ ﻟﻤﺴﺎﺣﺔ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻟﺔ )ﻗﺪ ﻳﻜﻮﻥ:m
Blind Search()ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺚ ﺍﻷﻋﻤﻰ
U
Breadth-first search()ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺚ ﻋﻦ ﻁﺮﻳﻖ ﺍﻟﺠﻮﺍﻧﺐ
Expand all the nodes of one level first()ﺍﻟﺘﻮﺳﻊ ﻋﺒﺮ ﻛﻞ ﺍﻟﻌﻘﺪ ﻓﻲ ﻧﻔﺲ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺘﻮﻯ
Depth-first search()ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺚ ﺑﺎﻟﻌﻤﻖ
Expand one of the nodes at the deepest level()ﺍﻟﺘﻮﺳﻊ ﻣﻦ ﺧﻼﻝ ﻧﻔﺲ ﺍﻟﻌﻘﺪﺓ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺘﻮﻯ ﺍﻷﻋﻤﻖ
ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ :ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ
)ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺚ ﺑﺎﻟﺠﻮﺍﻧﺐ ﺍﻭ ﺑﺎﻟﻌﺮﺽ(Breadth-first search
U
)ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺚ ﺑﺎﻟﻌﻤﻖ(Depth-first search
U
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
Iterative deepening search
U
Open List()ﺍﻟﻘﺎﺋﻤﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﻐﻠﻘﺔ
All the states which are not processing()ﺗﺤﺘﻮﻯ ﻛﻞ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻻﺕ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﻟﻢ ﻳﺘﻢ ﻣﻌﺎﻟﺠﺘﻬﺎ
Close List()ﺍﻟﻘﺎﺋﻤﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﻐﻠﻘﺔ
All the states which are after processing()ﻛﻞ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻻﺕ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺗﻤﺖ ﻣﻌﺎﻟﺠﺘﻬﺎ
Describe the path to goal state()ﻭﺗﺼﻒ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺎﺭ ﻟﻠﻮﺻﻮﻝ ﺍﻟﻰ ﺍﻟﻬﺪﻑ
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
Depth-first search
U
Breadth-first search
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
Search Example
U
The Traveling Salesman
U
The Traveling Salesman
U
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
informed (Heuristic) search(()ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺚ ﺍﻟﻤﻨﻈﻢ )ﺍﻻﺟﺘﻬﺎﺩﻱ
U
Using problem specific knowledge to aid searching
()ﺍﺳﺘﺨﺪﺍﻡ ﻣﻌﺮﻓﺔ ﻣﺤﺪﺩﺓ ﻟﻤﺸﻜﻠﺔ ﻟﻠﻤﺴﺎﻋﺪﺓ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺚ
Without incorporating knowledge into searching, one can have no bias (i.e. a
preference) on the search space.
(. ﻻ ﻳﻤﻜﻦ ﺃﻥ ﻳﻜﻮﻥ ﻫﻨﺎﻙ ﺗﺤﻴﺰ )ﺃﻱ ﺗﻔﻀﻴﻞ( ﻓﻲ ﻣﺴﺎﺣﺔ ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺚ، )ﺑﺪﻭﻥ ﺩﻣﺞ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﺔ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺚ
Without a bias, one is forced to look everywhere to find the answer. Hence, the
complexity of uninformed search is intractable.
ﻓﺈﻥ ﺗﻌﻘﻴﺪ ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺚ ﻏﻴﺮ ﺍﻟﻤﻨﻈﻢ ﻣﺴﺘﻌﺺ، ﻭﻣﻦ ﺛﻢ. ﻳﻀﻄﺮ ﺍﻟﻤﺮء ﻟﻠﻨﻈﺮ ﻓﻲ ﻛﻞ ﻣﻜﺎﻥ ﻟﻠﻌﺜﻮﺭ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻟﺠﻮﺍﺏ، )ﺩﻭﻥ ﺍﻟﺘﺤﻴﺰ
(.ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻟﻌﺜﻮﺭ ﺍﻟﺤﻞ
Search everywhere!!
()ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺚ ﻓﻲ ﻛﻞ ﻣﻜﺎﻥ
With knowledge, one can search the state space as if he was given “hints” when
exploring a maze.
(. ﻳﻤﻜﻦ ﻟﻠﻤﺮء ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺚ ﻓﻲ ﻣﺴﺎﺣﺔ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻟﺔ ﻛﻤﺎ ﻟﻮ ﻛﺎﻥ ﺃﻋﻄﻰ "ﺗﻠﻤﻴﺤﺎﺕ" ﻋﻨﺪ ﺍﺳﺘﻜﺸﺎﻑ ﻣﺘﺎﻫﺔ، )ﻣﻊ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﺔ
Heuristic information in search = Hints
()ﻣﻌﻠﻮﻣﺎﺕ ﺇﺭﺷﺎﺩﻳﺔ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺚ = ﺗﻠﻤﻴﺤﺎﺕ
Leads to dramatic speed up in efficiency.
(.)ﻳﺆﺩﻱ ﺇﻟﻰ ﺗﺴﺮﻳﻊ ﻛﺒﻴﺮ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﻜﻔﺎءﺓ
Search only in this subtree!!
(!! ) ﺍﺑﺤﺚ ﻓﻘﻂ ﻓﻲ ﻫﺬﻩ ﺍﻟﺸﺠﺮﺓ ﺍﻟﻔﺮﻋﻴﺔ
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
More formally, how heuristic functions work?()ﺑﺸﻜﻞ ﺃﺩﻕ ﻛﻴﻒ ﺗﻌﻤﻞ ﺩﻭﺍﻝ ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺚ ﺍﻻﺟﺘﻬﺎﺩﻱ
In any search problem where there are at most b choices at each node and a depth of d at the
goal node, a naive search algorithm would have to, in the worst case, search around O(bd)
nodes before finding a solution (Exponential Time Complexity).
)ﻓﻲ ﺃﻱ ﻣﺸﻜﻠﺔ ﺑﺤﺚ ﺗﻮﺟﺪ ﻓﻴﻬﺎ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻷﻏﻠﺐ "ﺏ" ﺧﻴﺎﺭ ﻋﻨﺪ ﻛﻞ ﻋﻘﺪﺓ
ﺑﺎﻟﺒﺤﺚ ﺣﻮﻝ ﻋﻘﺪ، ﻓﻲ ﺃﺳﻮﺃ ﺍﻷﺣﻮﺍﻝ، ﻋﻤﻖ "ﺩ" ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻟﻌﻘﺪﺓ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﻳﻮﺟﺪ ﺑﻬﺎ ﺍﻟﻬﺪﻑ ﻳﺠﺐ ﺃﻥ ﺗﻘﻮﻡ ﺧﻮﺍﺭﺯﻣﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺚ ﺍﻟﺴﺎﺫﺟﺔ
( "ﺏ ﺩ" ﻗﺒﻞ ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺚ ﻋﻦ ﺍﻟﺤﻞ
Heuristics improve the efficiency of search algorithms by reducing
the effective branching factor from b to (ideally) a low constant b* such that
1 =< b* << b
)ﺍﻻﺳﺘﺪﻻﻝ ﺗﺤﺴﻴﻦ ﻛﻔﺎءﺓ ﺧﻮﺍﺭﺯﻣﻴﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺚ ﻋﻦ ﻁﺮﻳﻖ ﺗﻘﻠﻴﻞ ﻋﺎﻣﻞ ﺍﻟﺘﻔﺮﻉ ﺍﻟﻔﻌﺎﻝ ﻣﻦ "ﺏ" ﺇﻟﻰ
)ﻣﺜﺎﻟﻲ( ﺛﺎﺑﺖ ﻣﻨﺨﻔﺾ "ﺏ*" ﻣﺜﻞ
1 =< b* << b
U
U0T
U0T
(
Heuristic Functions()ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺚ ﺍﻻﺟﺘﻬﺎﺩﻱ
U
A heuristic function is a function f(n) that gives an estimation on the “cost” of getting
from node n to the goal state – so that the node with the least cost among all possible
choices can be selected for expansion first.
U
U
f(n) )ﺩﺍﻟﺔ ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺚ ﺍﻻﺟﺘﻬﺎﺩﻱ
ﺑﺤﻴﺚ ﻳﻤﻜﻦ ﺗﺤﺪﻳﺪ ﺍﻟﻌﻘﺪﺓ ﺑﺄﻗﻞ ﺗﻜﻠﻔﺔ ﺑﻴﻦ ﺟﻤﻴﻊ ﺍﻟﺨﻴﺎﺭﺍﺕ- ﺇﻟﻰ ﺣﺎﻟﺔ ﺍﻟﻬﺪﻑn ﺗﻌﻄﻲ ﺗﻘﺪﻳ ًﺮﺍ ﻟـ "ﺗﻜﻠﻔﺔ" ﺍﻻﻧﺘﻘﺎﻝ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﻌﻘﺪﺓ
(.ًﺍﻟﻤﻤﻜﻨﺔ ﻟﻠﺘﻮﺳﻊ ﺃﻭﻻ
Three approaches to defining f:
(" f" )ﺛﻼﺛﺔ ﻁﺮﻕ ﻟﺘﻌﺮﻳﻒ ﻗﻴﻤﺔ
f measures the value of the current state (its “goodness”)
"(" ﺗﻘﻴﺲ ﻗﻴﻤﺔ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻟﺔ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻟﻴﺔ )ﺟﺪﻳﺔf")
f measures the estimated cost of getting to the goal from the current state:
(" ﺗﻘﻴﺲ ﺍﻟﺘﻜﻠﻔﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﻘﺪﺭﺓ ﻟﻠﻮﺻﻮﻝ ﺇﻟﻰ ﺍﻟﻬﺪﻑ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻟﺔ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻟﻴﺔf ")
f(n) = h(n) where h(n) = an estimate of the cost to get from n to a goal
ﻫﻲ ﺗﻘﺪﻳﺮ ﻟﻠﺘﻜﻠﻔﺔ ﻟﻠﻮﺻﻮﻝ ﻣﻦh(n) )ﺣﻴﺚ
( ﺇﻟﻰ ﻫﺪﻑn
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
f measures the estimated cost of getting to the goal state from the current state and the cost
of the existing path to it. Often, in this case, we decompose f:
ﻓﻲ، ﻓﻲ ﻛﺜﻴﺮ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻷﺣﻴﺎﻥ. ﻳﻘﻴﺲ ﺍﻟﺘﻜﻠﻔﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﻘﺪﺭﺓ ﻟﻠﻮﺻﻮﻝ ﺇﻟﻰ ﺣﺎﻟﺔ ﺍﻟﻬﺪﻑ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻟﺔ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻟﻴﺔ ﻭﺗﻜﻠﻔﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺎﺭ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻟﻲ ﺇﻟﻴﻬﺎf )
f ﻧﻘﻮﻡ ﺑﺘﺤﻠﻴﻞ، )" ﻫﺬﻩ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻟﺔ
f(n) = g(n) + h(n) where g(n) = the cost to get to n (from initial state)
ﺗﺴﺎﻭﻱg(n) )ﺣﻴﺚ
nﺗﻜﻠﻔﺔ ﺍﻟﻮﺻﻮﻝ ﺇﻟﻰ
()ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻟﺔ ﺍﻷﻭﻟﻴﺔ
Approach 1: f Measures the Value of the Current State
U
Usually the case when solving optimization problems
Finding a state such that the value of the metric f is optimized
ﻋﺎﺩﺓ ﻣﺎ ﺗﻜﻮﻥ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻟﺔ ﻋﻨﺪ ﺣﻞ ﻣﺸﺎﻛﻞ ﺍﻟﺘﺤﺴﻴﻦ
fﺍﻟﻌﺜﻮﺭ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺣﺎﻟﺔ ﺑﺤﻴﺚ ﻳﺘﻢ ﺗﺤﺴﻴﻦ ﻗﻴﻤﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﻘﻴﺎﺱ
Often, in these cases, f could be a weighted sum of a set of component values:
": ﻳﻤﻜﻦ ﺃﻥ ﻳﻜﻮﻥ ﻭﺯﻧﺎ ً ﻟﻤﺠﻤﻮﻉ ﻣﻦ ﻗﻴﻢ ﺍﻟﻤﻜﻮﻧﺎﺕ ﻫﻲ،
ﻫﺬﻩ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻻﺕf )ﻓﻲ ﻛﺜﻴﺮ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻷﺣﻴﺎﻥ
N-Queens
Example: the number of queens under attack …
Data mining
Example: the “predictive-ness” (. accuracy) of a rule discovered
Approach 2: f Measures the Cost to the Goal
U
A state X would be better than a state Y if the estimated cost of getting from X to the goal is
lower than that of Y – because X would be closer to the goal than Y
ﺳﺘﻜﻮﻥ ﺃﻗﺮﺏX ﻷﻥ- X ﺇﻟﻰ ﺍﻟﻬﺪﻑ ﺃﻗﻞ ﻣﻦX ﺇﺫﺍ ﻛﺎﻧﺖ ﺍﻟﺘﻜﻠﻔﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﻘﺪﺭﺓ ﻟﻼﻧﺘﻘﺎﻝ ﻣﻦY ﺃﻓﻀﻞ ﻣﻦ ﺣﺎﻟﺔX )ﺳﺘﻜﻮﻥ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻟﺔ
(Y ﺇﻟﻰ ﺍﻟﻬﺪﻑ ﻣﻦ
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
8–Puzzle()ﻟﻐﺰ ﺍﻟﺜﻤﺎﻧﻴﺔ
U
h 1 : The number of misplaced tiles (squares with number).
R
R
(.()ﻋﺪﺩ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﺒﻼﻁ ﻓﻲ ﻏﻴﺮ ﻣﻜﺎﻧﻪ ﺍﻟﺼﺤﻴﺢ )ﺍﻟﻤﺮﺑﻌﺎﺕ ﻣﻊ ﺍﻟﺮﻗﻢ
h 2 : The sum of the distances of the tiles from their goal positions
R
R
()ﻣﺠﻤﻮﻉ ﻣﺴﺎﻓﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺒﻼﻁ ﻣﻦ ﻣﻮﺍﻗﻊ ﺍﻷﻫﺪﺍﻑ ﺍﻟﺨﺎﺻﺔ ﺑﻬﻢ
Approach 3: f measures the total cost of the solution path (Admissible Heuristic
Functions)
U
1. Greedy Best first search()ﺧﻮﺍﺭﺯﻣﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺚ ﺍﻟﺠﺸﻌﺔ
“Always chooses the successor node with the best f value” where f(n) =
h(n)
f (n) = h (n) "ﺗﺨﺘﺎﺭ ﺩﺍﺋ ًﻤﺎ ﺍﻟﻌﻘﺪﺓ ﺍﻟﻼﺣﻘﺔ ﻣﻊ ﺃﻓﻀﻞ ﻗﻴﻤﺔ ﻭﺍﺭﺩﺓ" ﺣﻴﺚ
We choose the one that is nearest to the final state among all possible choices
()ﻧﺨﺘﺎﺭ ﺍﻟﺨﻴﺎﺭ ﺍﻷﻗﺮﺏ ﺇﻟﻰ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻟﺔ ﺍﻟﻨﻬﺎﺋﻴﺔ ﺑﻴﻦ ﺟﻤﻴﻊ ﺍﻟﺨﻴﺎﺭﺍﺕ ﺍﻟﻤﻤﻜﻨﺔ
2. A* search
Best first search using an “admissible” heuristic function f that takes into
account the current cost g
g ﻭﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺗﺄﺧﺬ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻻﻋﺘﺒﺎﺭ ﺍﻟﺘﻜﻠﻔﺔ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻟﻴﺔf " ﺃﻓﻀﻞ ﺑﺤﺚ ﺃﻭﻻً ﺑﺎﺳﺘﺨﺪﺍﻡ ﺩﺍﻟﺔ ﺇﺭﺷﺎﺩﻳﺔ "ﻣﻘﺒﻮﻟﺔ
Always returns the optimal solution path
()ﺩﻭﻣﺎً ﻳﺮﺟﻊ ﻣﺴﺎﺭ ﺍﻟﺤﻞ ﺍﻷﻣﺜﻞ
ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ :ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ
)ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺚ ﺍﻟﺠﺸﻊ(Greedy Search
U
ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ :ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
Greedy Search: Time and Space Complexity ?
U
( ﺍﻟﺘﻌﻘﻴﺪ ﻭﺍﻟﻤﺴﺎﺣﺔ ﻭﺍﻟﺰﻣﻦ؟:)ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺚ ﺍﻟﺠﺸﻊ
•
Greedy search is not optimal.(.) ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺚ ﺍﻟﺠﺸﻊ ﻟﻴﺲ ﺍﻷﻣﺜﻞ
•
Greedy search is incomplete without systematic checking of repeated states.
(.)ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺚ ﺍﻟﺠﺸﻊ ﻏﻴﺮ ﻣﻜﺘﻤﻞ ﻣﻦ ﺩﻭﻥ ﺍﻟﺘﺤﻘﻖ ﺍﻟﻤﻨﺘﻈﻢ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻻﺕ ﺍﻟﻤﺘﻜﺮﺭﺓ
•
In the worst case, the Time and Space Complexity of Greedy Search are both O(bm)
P
((bm)O ﻳﻜﻮﻥ ﺗﻌﻘﻴﺪ ﺍﻟﺰﻣﺎﻥ ﻭﺍﻟﻤﺴﺎﺣﺔ ﻟﻠﺨﻮﺍﺭﺯﻣﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﺠﺸﻌﺔ، ﻓﻲ ﺃﺳﻮﺃ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻻﺕ
P
•
Where b is the branching factor and m the maximum path length
( ﻃﻮﻝ ﺍﻟﺤﺪ ﺍﻷﻗﺼﻰ ﻟﻠﻤﺴﺎﺭm ّﻉ ﻭ
ﻫﻮ ﺍﻟﻌﺎﻣﻞ ﺍﻟﻤﺘﻔﺮb )ﺣﻴﺚ
Solve this problem using the rules based system and the short path algorithm
()ﺣﻞ ﻫﺬﻩ ﺍﻟﻤﺸﻜﻠﺔ ﺑﺎﺳﺘﺨﺪﺍﻡ ﺍﻟﻨﻈﺎﻡ ﺍﻟﻘﺎﺋﻢ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻟﻘﻮﺍﻋﺪ ﻭﺧﻮﺍﺭﺯﻣﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺎﺭ ﺍﻟﻘﺼﻴﺮ
ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ :ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
A* Search (A* )ﺧﻮﺍﺭﺯﻣﻴﺔ ﺑﺤﺚ
U
eval-fn: f(n)=g(n)+h(n)
U
Greedy Search minimizes a heuristic h(n) which is an estimated cost from a node n to
the goal state. However, although greedy search can considerably cut the search time
(efficient), it is neither optimal nor complete.
ﺇﻟﻰ ﺣﺎﻟﺔn ﺍﻟﺬﻱ ﻳﻤﺜﻞ ﺍﻟﺘﻜﻠﻔﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﻘﺪﺭﺓ ﻣﻦ ﻋﻘﺪﺓh (n) ﻣﻦGreedy Search ﻳﻘﻠﻞ
ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻟﺮﻏﻢ ﻣﻦ ﺃﻥ ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺚ ﺍﻟﺠﺸﻊ ﻳﻤﻜﻦ ﺃﻥ ﻳﺨﻔﺾ ﻭﻗﺖ ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺚ ﺑﺸﻜﻞ، ﻭﻣﻊ ﺫﻟﻚ.ﺍﻟﻬﺪﻑ
.ﻛﺎﻣﻼ
ًﺎ ﻭﻻ
ﺇﻻ ﺃﻧﻪ ﻟﻴﺲ ﻣﺜﺎﻟﻴ، (ﻛﺒﻴﺮ )ﻓﻌﺎﻝ
ً
Uniform Cost Search minimizes the cost h (n) from the initial state to n. UCS is
optimal and complete but not efficient.
ﻫﻮn. UCS ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻟﺔ ﺍﻷﻭﻟﻴﺔ ﺇﻟﻰg (n) ﻳﻘﻠﻞ ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺚ ﻋﻦ ﺗﻜﻠﻔﺔ ﻣﻮﺣﺪﺓ ﻣﻦ ﺗﻜﻠﻔﺔ
ﻣﺜﺎﻟﻲ ﻭﻛﺎﻣﻞ ﻭﻟﻜﻨﻪ ﻏﻴﺮ ﻓﻌﺎﻝ
New Strategy: Combine Greedy Search and UCS to get an efficient algorithm which
is complete and optimal.
UCS ﺍﻟﺠﻤﻊ ﺑﻴﻦ ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺚ ﺍﻟﺠﺸﻊ ﻭ:ﺍﺳﺘﺮﺍﺗﻴﺠﻴﺔ ﺟﺪﻳﺪﺓ
ﻟﻠﺤﺼﻮﻝ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺧﻮﺍﺭﺯﻣﻴﺔ ﻓﻌﺎﻟﺔ ﻛﺎﻣﻠﺔ ﻭﻣﺜﺎﻟﻴﺔ.
A* uses a heuristic function which combines g(n) and h(n): f(n) = g(n) + h(n)
g(n) is the exact cost to reach node n from the initial state. Cost so far up to node n.
h(n) is an estimation of the remaining cost to reach the goal.
ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ :ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
A* Search: Analysis()ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺍﻟﺨﻮﺍﺭﺯﻣﻴﺔ
U
•
A* is complete except if there is an infinity of nodes with f < f(G).
•
f> f (G: )ﻣﻜﺘﻤﻠﺔ ﺇﻻ ﺇﺫﺍ ﻛﺎﻥ ﻫﻨﺎﻙ ﻣﺎ ﻻ ﻧﻬﺎﻳﺔ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﻌﻘﺪ ﺣﻴﺚ
•
•
is optimal if heuristic h is admissible.
Time complexity depends on the quality of heuristic but is still exponential.
(.)ﻳﻌﺘﻤﺪ ﺗﻌﻘﻴﺪ ﺍﻟﻮﻗﺖ ﻋﻠﻰ ﻧﻮﻋﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﻜﺸﻒ ﻋﻦ ﻣﺠﺮﻳﺎﺕ ﺍﻷﻣﻮﺭ ﻭﻟﻜﻨﻪ ﻻ ﻳﺰﺍﻝ ﺃﺳﻴًﺎ
•
For space complexity, A* keeps all nodes in memory. A* has worst case O(bd) space
complexity, but an iterative deepening version is possible (IDA*).
P
P
Example:
Given the following maze problem. The point of entry is (3,5) and the exit is (0,3).
.(0،3) ( ﻭﺍﻟﻤﺨﺮﺝ3،5) ﻧﻘﻄﺔ ﺍﻟﺪﺧﻮﻝ ﻫﻲ.ﻣﻌﻄﻰ ﻟﻤﺸﻜﻠﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﺘﺎﻫﺔ ﺍﻟﺘﺎﻟﻴﺔ
Solve this problem using the rules based system and the short path algorithm
()ﺣﻞ ﻫﺬﻩ ﺍﻟﻤﺸﻜﻠﺔ ﺑﺎﺳﺘﺨﺪﺍﻡ ﺍﻟﻨﻈﺎﻡ ﺍﻟﻘﺎﺋﻢ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻟﻘﻮﺍﻋﺪ ﻭﺧﻮﺍﺭﺯﻣﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺎﺭ ﺍﻟﻘﺼﻴﺮ
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
F(n)=g(n) + h(n)
g(n)= ( |X G – X n | ) + ( | Y G – Y n | )
R
R
R
R
R
R
h(n)= incremental value is one
R
R
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
LECTURE 7 : Expert systems()ﺍﻟﻨﻈﻢ ﺍﻟﺨﺒﻴﺮﺓ
U
Topics ()ﺍﻟﻣﻭﺿﻭﻋﺎﺕ
•
Definition ()ﺍﻟﺗﻌﺭﻳﻑ
•
Why use Expert System()ﻟﻣﺎﺫﺍ ﻧﺳﺗﺧﺩﻡ ﺍﻟﻧﻅﻡ ﺍﻟﺧﺑﻳﺭﺓ
•
Human Expert Behaviors()ﺳﻠﻭﻛﻳﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺑﺷﺭ ﺍﻟﺧﺑﺭﺍء
•
Three Major ES Components()ﺍﻟﻣﻛﻭﻧﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺛﻼﺙ ﺍﻷﺳﺎﺳﻳﺔ ﻟﻠﻧﻅﻡ ﺍﻟﺧﺑﻳﺭﺓ
•
Building an Expert System()ﺑﻧﺎء ﺍﻟﻧﻅﺎﻡ ﺍﻟﺧﺑﻳﺭ
•
Problem Areas()ﻣﻧﺎﻁﻕ ﺍﻟﻣﺷﺎﻛﻝ
•
Expert Systems Benefits()ﻓﻭﺍﺋﺩ ﺍﻟﻧﻅﻡ ﺍﻟﺧﺑﻳﺭﺓ
•
Problems and Limitations()ﺍﻟﻣﺷﺎﻛﻝ ﻭﺍﻟﺣﺩﻭﺩ
•
Applications of Expert Systems ()ﺗﻁﺑﻳﻘﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻧﻅﻡ ﺍﻟﺧﺑﻳﺭﺓ
An expert system is a computer program that is designed to hold the accumulated
knowledge of one or more domain experts
()ﻧﻈﺎﻡ ﺍﻟﺨﺒﺮﺍء ﻫﻮ ﺑﺮﻧﺎﻣﺞ ﺣﺎﺳﻮﺑﻲ ﻣﺼﻤﻢ ﻻﺳﺘﻴﻌﺎﺏ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﺘﺮﺍﻛﻤﺔ ﻣﻦ ﻭﺍﺣﺪ ﺃﻭ ﺃﻛﺜﺮ ﻣﻦ ﺧﺒﺮﺍء ﺍﻟﻤﺠﺎﻝ
Objective of an expert system()ﺍﻟﻬﺪﻑ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﻨﻈﻢ ﺍﻟﺨﺒﻴﺮﺓ
To transfer expertise from an expert to a computer system
()ﻧﻘﻞ ﺍﻟﺨﺒﺮﺍﺕ ﻣﻦ ﺧﺒﻴﺮ ﺇﻟﻰ ﻧﻈﺎﻡ ﺍﻟﻜﻤﺒﻴﻮﺗﺮ
Why use Expert Systems? ()ﻟﻤﺎﺫﺍ ﻧﺴﺘﺨﺪﻡ ﺍﻟﻨﻈﻢ ﺍﻟﺨﺒﻴﺮﺓ
U
Experts are not always available. An expert system can be used anywhere, any time.
(. ﺍﻟﻨﻈﺎﻡ ﺍﻟﺨﺒﻴﺮ ﻳﻤﻜﻦ ﺍﺳﺘﺨﺪﺍﻣﻬﺎ ﻓﻲ ﺃﻱ ﻣﻜﺎﻥ ﻭﻓﻲ ﺃﻱ ﻭﻗﺖ.)ﺍﻟﺨﺒﺮﺍء ﻻ ﻳﺘﻮﻓﺮﻭﻥ ﺩﺍﺋﻤﺎ
Experts may not be good at explaining decisions
()ﻗﺪ ﻻ ﻳﻜﻮﻥ ﺍﻟﺨﺒﻴﺮ ﺟﻴﺪﺍ ﻓﻲ ﺷﺮﺡ ﺍﻟﻘﺮﺍﺭﺍﺕ
Cost effective
()ﻓﻌﺎﻟﻪ ﻣﻦ ﺣﻴﺚ ﺍﻟﺘﻜﻠﻔﺔ
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
Human Expert Behaviors()ﺳﻠﻮﻛﻴﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺒﺸﺮ ﺍﻟﺨﺒﺮﺍء
U
Recognize and formulate the problem
()ﺍﻟﺘﻌﺮﻑ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻟﻤﺸﻜﻠﺔ ﻭﺻﻴﺎﻏﺘﻬﺎ
Solve problems quickly and properly
()ﺣﻞ ﺍﻟﻤﺸﺎﻛﻞ ﺑﺴﺮﻋﺔ ﻭﺑﺸﻜﻞ ﺻﺤﻴﺢ
Explain the solution
()ﺷﺮ ﺍﻟﺤــﻞ
Learn from experience
()ﺍﻟﺘﻌﻠﻢ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﺘﺠﺮﺑﺔ
Restructure knowledge
()ﺇﻋﺎﺩﺓ ﻫﻴﻜﻠﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﺔ
Determine relevance
()ﺗﺤﺪﻳﺪ ﻣﺪﻯ ﺍﻟﺼﻠﺔ ﺑﺎﻟﻤﻮﺿﻮﻉ
Three Major ES Components()ﺍﻟﻤﻜﻮﻧﺎﺕ ﺍﻷﺳﺎﺳﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﺜﻼﺙ ﻟﻠﻨﻈﻢ ﺍﻟﺨﺒﻴﺮﺓ
U
Knowledge Base()ﻗﺎﻋﺪﺓ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﺔ
Inference Engine ()ﻣﺤﺮﻙ ﺍﻟﻔﻬﻢ ﻭﺍﻻﺳﺘﺪﻻﻝ
User Interface()ﻭﺍﺟﻬﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺘﺨﺪﻡ
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
1-User Interface()ﻭﺍﺟﻬﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺘﺨﺪﻡ
U
The user interface is the part of the system which takes in the user’s query in a
readable form and passes it to the inference engine. It then displays the results to the
user.
)ﻭﺍﺟﻬﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺘﺨﺪﻡ ﻫﻲ ﺟﺰء ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﻨﻈﺎﻡ ﺍﻟﺬﻱ ﻳﺄﺧﺬ ﻓﻲ ﺍﺳﺘﻌﻼﻡ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺘﺨﺪﻡ ﻓﻲ ﺷﻜﻞ ﻗﺎﺑﻞ ﻟﻠﻘﺮﺍءﺓ ﻭﻳﻤﺮ ﺇﻟﻰ ﻣﺤﺮﻙ
(. ﺛﻢ ﻳﻌﺮﺽ ﺍﻟﻨﺘﺎﺋﺞ ﻟﻠﻤﺴﺘﺨﺪﻡ.ﺍﻻﺳﺘﺪﻻﻝ
Types of user interface ()ﺃﻧﻮﺍﻉ ﻭﺍﺟﻬﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺘﺨﺪﻡ
NLP, or menus and graphics
2-Knowledge base()ﻗﺎﻋﺪﺓ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﺔ
U
It contains the knowledge necessary for understanding, formulating, and solving problems
()ﺃﻧﻬﺎ ﻳﺤﺘﻮﻱ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﺔ ﺍﻟﻼﺯﻣﺔ ﻟﻔﻬﻢ ﻭﺻﻴﺎﻏﺔ ﻭﺣﻞ ﺍﻟﻤﺸﺎﻛﻞ
It is the collection of facts and rules which describe all the knowledge about the problem
domain
()ﻫﻮ ﺟﻤﻊ ﺍﻟﺤﻘﺎﺋﻖ ﻭﺍﻟﻘﻮﺍﻋﺪ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺗﺼﻒ ﻛﻞ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﺔ ﺣﻮﻝ ﻣﺠﺎﻝ ﺍﻟﻤﺸﻜﻠﺔ
Two Basic Knowledge Base Elements()ﺍﻟﻌﻨﺼﺮﺍﻥ ﺃﺳﺎﺳﻴﺎﻥ ﻣﻦ ﻗﺎﻋﺪﺓ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺎﺭﻑ ﺍﻷﺳﺎﺳﻴﺔ
•
Facts()ﺍﻟﺤﻘﺎﺋﻖ
•
rules that direct the use of knowledge()ﺍﻟﻘﻮﺍﻋﺪ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺗﻮﺟﻪ ﺍﺳﺘﺨﺪﺍﻡ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﺔ
Knowledge is the primary raw material of ES()ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﺔ ﻫﻲ ﺍﻟﻤﺎﺩﺓ ﺍﻟﺨﺎﻡ ﺍﻷﻭﻟﻴﺔ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﻨﻈﻢ ﺍﻟﺨﺒﻴﺮﺓ
3-Inference Engine()ﻣﺤﺮﻙ ﺍﻟﻔﻬﻢ ﻭﺍﻻﺳﺘﺪﻻﻝ
U
The brain of the ES()ﻋﻘﻞ ﺍﻟﻨﻈﺎﻡ ﺍﻟﺨﺒﻴﺮ
The inference engine is the part of the system that chooses which facts and rules to
apply when trying to solve the user’s query
)ﻣﺤﺮﻙ ﺍﻻﺳﺘﺪﻻﻝ ﻫﻮ ﺟﺰء ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﻨﻈﺎﻡ ﺍﻟﺬﻱ ﻳﺨﺘﺎﺭ ﺃﻱ ﺍﻟﺤﻘﺎﺋﻖ ﻭﺍﻟﻘﻮﺍﻋﺪ ﻟﻠﺘﻄﺒﻴﻖ ﻋﻨﺪ ﻣﺤﺎﻭﻟﺔ ﺣﻞ ﺍﺳﺘﻌﻼﻡ
(ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺘﺨﺪﻡ
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
Explanation subsystem ()ﻧﻈﺎﻡ ﺍﻟﺸﺮﺡ ﻭﺍﻟﺘﻮﺿﻴﺢ
U
allows the program to explain its reasoning to the user.
(.)ﻳﺴﻤﺢ ﻟﻠﺒﺮﻧﺎﻣﺞ ﻟﺸﺮﺡ ﻣﻨﻄﻘﻪ ﻟﻠﻤﺴﺘﺨﺪﻡ
Knowledge base editor()ﻣﺤﺮﺭ ﻗﺎﻋﺪﺓ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﺔ
U
helps the expert or knowledge engineer to easily update and check the knowledge
base.(.) ﻳﺴﺎﻋﺪ ﺧﺒﻴﺮ ﺃﻭ ﻣﻬﻨﺪﺱ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﺔ ﻟﻠﺘﺤﺪﻳﺚ ﺑﺴﻬﻮﻟﺔ ﻭﺍﻟﺘﺤﻘﻖ ﻣﻦ ﻗﺎﻋﺪﺓ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﺔ
Building an Expert System()ﺑﻨﺎء ﺍﻟﻨﻈﻢ ﺍﻟﺨﺒﻴﺮﺓ
U
1. Knowledge Acquisition()ﺍﻛﺘﺴﺎﺏ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﺔ
2. Knowledge representation ()ﺗﻤﺜﻴﻞ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﺔ
3. Knowledge inference ()ﺍﺳﺘﺪﻻﻝ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﺔ
1. Knowledge acquisition
U
is the transformation of problem-solving expertise from experts to a computer
program for constructing or expanding the knowledge base and that Requires a
knowledge engineer
)ﻫﻮ ﺗﺤﻮﻳﻞ ﺍﻟﺨﺒﺮﺓ ﻓﻲ ﺣﻞ ﺍﻟﻤﺸﺎﻛﻞ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﺨﺒﺮﺍء ﺇﻟﻰ ﺑﺮﻧﺎﻣﺞ ﺣﺎﺳﻮﺑﻲ ﻟﺒﻨﺎء ﺃﻭ ﺗﻮﺳﻴﻊ ﻗﺎﻋﺪﺓ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﺔ ﻭ ﻳﺘﻄﻠﺐ ﺫﻟﻚ
(ﻣﻬﻨﺪﺱ ﻣﻌﺮﻓﺔ
Knowledge engineer: ()ﻣﻬﻨﺪﺱ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﺔ
U
is the job of extracting the knowledge from experts and building the expert system
knowledge base.
(.)ﻣﻬﻤﺘﻪ ﺍﺳﺘﺨﺮﺍﺝ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﺔ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﺨﺒﺮﺍء ﻭﺑﻨﺎء ﻗﺎﻋﺪﺓ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﺔ ﻧﻈﺎﻡ ﺍﻟﺨﺒﺮﺍء
Knowledge engineer should be able to extract the knowledge from the expert and
select the knowledge representation method using suitable tool. Usually also the
System Builder
)ﻭﻳﻨﺒﻐﻲ ﺃﻥ ﻳﻜﻮﻥ ﻣﻬﻨﺪﺱ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﺔ ﻗﺎﺩﺭﺍ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﺳﺘﺨﺮﺍﺝ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﺔ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﺨﺒﻴﺮ ﻭﺍﺧﺘﻴﺎﺭ ﻁﺮﻳﻘﺔ ﺗﻤﺜﻴﻞ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﺔ
(ﻋﺎﺩﺓ ﻣﺎ ﻳﻜﻮﻥ ﺃﻳﻀﺎ ﻣﻨﺸﺊ ﺍﻟﻨﻈﺎﻡ.ﺑﺎﺳﺘﺨﺪﺍﻡ ﺃﺩﺍﺓ ﻣﻨﺎﺳﺒﺔ
2. Knowledge representation ()ﺗﻤﺜﻴﻞ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﺔ
U
A widely used approach for representing knowledge in an expert systems is the
use of rules.
(IF-THEN )ﻭﻫﻨﺎﻙ ﻧﻬﺞ ﻳﺴﺘﺨﺪﻡ ﻋﻠﻰ ﻧﻄﺎﻕ ﻭﺍﺳﻊ ﻟﺘﻤﺜﻴﻞ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﺔ ﻓﻲ ﻧﻈﻢ ﺍﻟﺨﺒﺮﺍء ﻫﻮ ﺍﺳﺘﺨﺪﺍﻡ ﻗﺎﻋﺪﺓ
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
Problem Areas()ﻣﻨﺎﻁﻖ ﺍﻟﻤﺸﺎﻛﻞ ﻭﺍﻻﺣﺘﻴﺎﺝ
U
Prediction systems ()ﺃﻧﻈﻤﺔ ﺍﻟﺘﻨﺒﺆ--------Diagnostic systems()ﺃﻧﻈﻤﺔ ﺍﻟﺘﺸﺨﻴﺺ
Design systems()ﺃﻧﻈﻤﺔ ﺍﻟﺘﺼﻤﻴﻢ----------Planning systems()ﻧﻈﻢ ﺍﻟﺘﺨﻄﻴﻂ
Monitoring systems()ﺃﻧﻈﻤﺔ ﺍﻟﺮﺻﺪ------Debugging systems()ﺃﻧﻈﻤﺔ ﺍﻟﺘﺼﺤﻴﺢ
Repair systems()ﺃﻧﻈﻤﺔ ﺍﻹﺻﻼﺡ-----------Control systems()ﺃﻧﻈﻤﺔ ﺍﻟﺘﺤﻜﻢ
Expert Systems Benefits()ﻓﻮﺍﺋﺪ ﺍﻟﻨﻈﻢ ﺍﻟﺨﺒﻴﺮﺓ
U
•
•
•
Increased Output and Productivity ()ﺯﻳﺎﺩﺓ ﺍﻹﻧﺘﺎﺝ ﻭﺍﻹﻧﺘﺎﺟﻴﺔ
Decreased Decision Making Time()ﺗﻘﻠﻴﺺ ﻭﻗﺖ ﺍﺗﺨﺎﺫ ﺍﻟﻘﺮﺍﺭ
Capture rare Expertise ()ﺍﻟﺘﻘﺎﻁ ﺍﻟﺨﺒﺮﺓ ﺍﻟﻨﺎﺩﺭﺓ
•
Flexibility()ﺍﻟﻤﺮﻭﻧﺔ
•
•
•
Easier Equipment Operation ()ﺗﺴﻬﻴﻞ ﻋﻤﻠﻴﺔ ﺍﻹﻋﺪﺍﺩ
Operation in Hazardous Environments()ﺍﻟﻌﻤﻞ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺌﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺨﻄﺮﺓ
Can Work with Incomplete or Uncertain Information
()ﻳﻤﻜﻨﻬﺎ ﺍﻟﻌﻤﻞ ﻣﻊ ﻣﻌﻠﻮﻣﺎﺕ ﻏﻴﺮ ﻣﻜﺘﻤﻠﺔ ﺃﻭ ﻏﻴﺮ ﻣﺆﻛﺪﺓ
Problems and Limitations ()ﺍﻟﻤﺸﺎﻛﻞ ﻭﺍﻟﺤﺪﻭﺩ:
U
•
•
•
•
Expertise can be hard to extract from humans()ﺻﻌﻮﺑﺔ ﺍﺳﺘﺨﺮﺍﺝ ﺍﻟﺨﺒﺮﺓ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﺒﺸﺮ
Systems are not always up to date ()ﺍﻷﻧﻈﻤﺔ ﻟﻴﺴﺖ ﺩﺍﺋﻤﺎ ﺟﺎﻫﺰﺓ
ES work well only in a narrow domain of knowledge
Knowledge is not always readily available()ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﺔ ﻟﻴﺴﺖ ﺩﺍﺋﻤﺎ ﻣﺘﺎﺣﺔ ﺑﺴﻬﻮﻟﺔ
()ﺍﻟﻨﻈﻢ ﺍﻟﺨﺒﻴﺮﺓ ﺗﻌﻤﻞ ﺑﺸﻜﻞ ﺟﻴﺪ ﻓﻘﻂ ﻋﻨﺪﻣﺎ ﻧﻌﻤﻞ ﻓﻲ ﻣﺠﺎﻝ ﺿﻴﻖ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﺔ
•
Knowledge engineers are rare and expensive ()ﻣﻬﻨﺪﺳﻮ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﺔ ﻧﺎﺩﺭﻭﻥ ﻭﻣﻜﻠﻔﻮﻥ
Lack of trust by end-users()ﻋﺪﻡ ﺍﻟﺜﻘﺔ ﻣﻦ ﻗﺒﻞ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺘﺨﺪﻣﻴﻦ ﺍﻟﻨﻬﺎﺋﻴﻴﻦ
•
Applications of Expert Systems:()ﺗﻄﺒﻴﻘﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻨﻈﻢ ﺍﻟﺨﺒﻴﺮﺓ
U
PROSPECTOR:
Used by geologists to identify sites for
drilling or mining
)ﺗﺳﺗﺧﺩﻡ ﻣﻥ ﻗﺑﻝ ﺍﻟﺟﻳﻭﻟﻭﺟﻳﻳﻥ ﻟﺗﺣﺩﻳﺩ ﻣﻭﺍﻗﻊ ﻟﻠﺣﻔﺭ ﺃﻭ
(ﺍﻟﺗﻌﺩﻳﻥ
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
PUFF:
-2
Medical system
for diagnosis of respiratory conditions
()ﺍﻟﻧﻅﺎﻡ ﺍﻟﻁﺑﻲ ﻟﺗﺷﺧﻳﺹ ﺃﻣﺭﺍﺽ ﺍﻟﺟﻬﺎﺯ ﺍﻟﺗﻧﻔﺳﻲ
DESIGN ADVISOR:
Gives advice to designers of processor chips
()ﻳﻌﻁﻲ ﺍﻟﻣﺷﻭﺭﺓ ﻟﻣﺻﻣﻣﻲ ﺭﻗﺎﺋﻕ ﺍﻟﻣﻌﺎﻟﺞ
MYCIN:
Medical system for diagnosing blood disorders. First
used in 1979
ﺍﺳﺗﺧﺩﻡ ﻷﻭﻝ ﻣﺭﺓ ﻓﻲ ﻋﺎﻡ.)ﺍﻟﻧﻅﺎﻡ ﺍﻟﻁﺑﻲ ﻟﺗﺷﺧﻳﺹ ﺍﺿﻁﺭﺍﺑﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺩﻡ
(1979
LITHIAN: Gives advice to archaeologists examining stone
tools
( ﻳﻌﻁﻲ ﺍﻟﻣﺷﻭﺭﺓ ﻟﻌﻠﻣﺎء ﺍﻵﺛﺎﺭ ﻓﺣﺹ ﺍﻷﺩﻭﺍﺕ ﺍﻟﺣﺟﺭﻳﺔ:)ﻟﻳﺛﻳﺎﻥ
DENDRAL: Used to identify the structure of chemical
compounds. First used in 1965
ﺍﺳﺗﺧﺩﻡ ﻷﻭﻝ ﻣﺭﺓ ﻓﻲ. ﻳﺳﺗﺧﺩﻡ ﻟﺗﺣﺩﻳﺩ ﻫﻳﻛﻝ ﺍﻟﻣﺭﻛﺑﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻛﻳﻣﻳﺎﺋﻳﺔ:)ﺩﻧﺩﺭﺍﻝ
(1965 ﻋﺎﻡ
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
LECTURE 8 : Artificial Neural Networks
U
Definition()ﺗﻌﺮﻳﻒ:
Neural network: information processing paradigm inspired by biological nervous
systems, such as our brain
ﻣﺜﻞ ﺩﻣﺎﻏﻨﺎ، ﻧﻤﻮﺫﺝ ﻣﻌﺎﻟﺠﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﻠﻮﻣﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺘﻮﺣﻰ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻷﻧﻈﻤﺔ ﺍﻟﻌﺼﺒﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﻮﻟﻮﺟﻴﺔ:ﺍﻟﺸﺒﻜﺔ ﺍﻟﻌﺼﺒﻴﺔ
Structure: large number of highly interconnected processing elements (neurons)
working together
( ﻋﺪﺩ ﻛﺒﻴﺮ ﻣﻦ ﻋﻨﺎﺻﺮ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺎﻟﺠﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﺘﺮﺍﺑﻄﺔ ﻟﻠﻐﺎﻳﺔ )ﺍﻟﺨﻼﻳﺎ ﺍﻟﻌﺼﺒﻴﺔ( ﺗﻌﻤﻞ ﻣﻌًﺎ:)ﺍﻟﺒﻨﻴﺔ
Like people, they learn from experience (by example)
(( ﻳﺘﻌﻠﻤﻮﻥ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﺘﺠﺮﺑﺔ )ﻋﻠﻰ ﺳﺒﻴﻞ ﺍﻟﻤﺜﺎﻝ، )ﻣﺜﻞ ﺍﻟﻨﺎﺱ
Biological Neurons:()ﺍﻟﺨﻼﻳﺎ ﺍﻟﻌﺼﺒﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﻮﻟﻮﺟﻴﺔ
U
1- Soma or body cell - is a large, round central body in which almost all
the logical functions of the neuron are realized.
ﻫﻮ ﺟﺴﻢ ﻣﺮﻛﺰﻱ ﻛﺒﻴﺮ ﻣﺴﺘﺪﻳﺮ ﻳﺘﻢ ﻓﻴﻪ ﺗﺤﻘﻴﻖ ﺟﻤﻴﻊ ﺍﻟﻮﻅﺎﺋﻒ ﺍﻟﻤﻨﻄﻘﻴﺔ ﻟﻠﻌﺼﺒﻮﻥ ﺗﻘﺮﻳﺒًﺎ- ﺳﻮﻣﺎ ﺃﻭ ﺧﻠﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﺠﺴﻢ.
2- The axon (output), is a nerve fibre attached to the soma which can
serve as a final output channel of the neuron. An axon is usually highly
branched.
ﻫﻮ ﻋﺒﺎﺭﺓ ﻋﻦ ﺃﻟﻴﺎﻑ ﻋﺼﺒﻴﺔ ﻣﺮﺗﺒﻄﺔ ﺑﺎﻟـ ﺳﻮﻣﺎ ﻭﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﻳﻤﻜﻦ ﺃﻥ ﺗﻜﻮﻥ ﺑﻤﺜﺎﺑﺔ ﻗﻨﺎﺓ ﺧﺮﺝ ﻧﻬﺎﺋﻴﺔ ﻣﻦ، (ﺍﻟﻤﺤﻮﺭ )ﺍﻟﻤﺨﺮﺝ
ﻭﻋﺎﺩﺓ ﻣﺎ ﻳﻜﻮﻥ ﺍﻟﻤﺤﻮﺭ ﻋﺼﺒﻲ ﻟﻠﻐﺎﻳﺔ.ﺍﻟﻌﺼﺒﻮﻥ.
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
3- the dendrites (inputs)- represent a highly branching tree of fibres.
These long irregularly shaped nerve fibres (processes) are attached to
the soma.
ﻫﺬﻩ ﺍﻷﻟﻴﺎﻑ ﺍﻟﻌﺼﺒﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﻄﻮﻳﻠﺔ ﺍﻟﺸﻜﻞ ﻏﻴﺮ ﺍﻟﻤﻨﺘﻈﻤﺔ. ﺷﺠﺮﺓ ﻣﺘﻔﺮﻋﺔ ﻟﻠﻐﺎﻳﺔ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻷﻟﻴﺎﻑ- (ﺗﻤﺜﻞ ﺍﻟﺘﺸﻌﺒﺎﺕ )ﺍﻟﻤﺪﺧﻼﺕ
)ﺍﻟﻌﻤﻠﻴﺎﺕ( ﺗﻌﻠﻖ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻟﺴﻮﻣﺎ.
4- Synapses are specialized contacts on a neuron which are the
termination points for the axons from other neurons.
ﺍﻟﻤﺸﺎﺑﻚ ﻫﻲ ﺟﻬﺎﺕ ﺍﺗﺼﺎﻝ ﻣﺘﺨﺼﺼﺔ ﻋﻠﻰ ﻋﺼﺒﻮﻥ ﻭﻫﻲ ﻧﻘﺎﻁ ﺍﻧﺘﻬﺎء ﻟﻠﻤﺤﺎﻭﺭ ﻣﻦ ﻋﺼﺒﻮﻧﺎﺕ ﺃﺧﺮﻯ
Synapses
Axon from
th
Soma
Dendrites
The schematic model
of a biological neuron
Axon
Dendrite
from
ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ :ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
Activation Functions
U
Learning()ﺍﻟﺘﻌﻠﻢ
U
A main property of a neuron and of a neural network is their ability to learn from its
environment, and to improve its performance through learning.
ﻭﺗﺤﺴﻴﻦ ﺃﺩﺍﺋﻬﺎ ﻣﻦ ﺧﻼﻝ، )ﺇﻥ ﺍﻟﺨﺎﺻﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﺮﺋﻴﺴﻴﺔ ﻟﺨﻠﻴﺔ ﻋﺼﺒﻴﺔ ﻭﺷﺒﻜﺔ ﻋﺼﺒﻴﺔ ﻫﻲ ﻗﺪﺭﺗﻬﺎ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻟﺘﻌﻠﻢ ﻣﻦ ﺑﻴﺌﺘﻬﺎ
(.ﺍﻟﺘﻌﻠﻢ
A neuron (a neural network) learns about its environment through an iterative process
of adjustments applied to its synaptic weights.
)ﻳﺘﻌﺮﻑ ﺍﻟﻌﺼﺒﻮﻥ )ﺷﺒﻜﺔ ﻋﺼﺒﻴﺔ( ﻋﻠﻰ ﺑﻴﺌﺘﻪ ﻣﻦ ﺧﻼﻝ ﻋﻤﻠﻴﺔ ﺗﻜﺮﺍﺭﻳﺔ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﺘﻌﺪﻳﻼﺕ ﺍﻟﻤﻄﺒﻘﺔ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺃﻭﺯﺍﻧﻬﺎ
(.ﺍﻟﻤﺸﺒﻜﻴﺔ
Ideally, a network (a single neuron) becomes more knowledgeable about its
environment after each iteration of the learning process.
(. ﺗﺼﺒﺢ ﺍﻟﺸﺒﻜﺔ )ﺧﻠﻴﺔ ﻋﺼﺒﻴﺔ ﻭﺍﺣﺪﺓ( ﺃﻛﺜﺮ ﺩﺭﺍﻳﺔ ﺑﺒﻴﺌﺘﻬﺎ ﺑﻌﺪ ﻛﻞ ﺗﻜﺮﺍﺭ ﻟﻌﻤﻠﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﺘﻌﻠﻢ، )ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﻨﺎﺣﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﺜﺎﻟﻴﺔ
Learning is Continuous process of(ﺍﻟﺘﻌﻠﻢ ﻫﻮ ﻋﻤﻠﻴﺔ ﻣﺴﺘﻤﺮﺓ ﻣﻦ:)
Evaluate output ()ﺗﻘﻴﻴﻢ ﺍﻻﻧﺘﺎﺝ
Adapt weights()ﺗﻜﻴﻒ ﺍﻷﻭﺯﺍﻥ
Take new inputs()ﺗﻘﺒﻞ ﻣﺪﺧﻼﺕ ﺟﺪﻳﺪﺓ
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
Let T be a desired output of a neuron (of a network) for a certain input vector
ﻳﻜﻮﻥ ﺍﻟﻤﺨﺮﺝ ﺍﻟﻤﻄﻠﻮﺏ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﺨﻼﻳﺎ ﺍﻟﻌﺼﺒﻴﺔ )ﻣﻦ ﺷﺒﻜﺔ( ﻟﻤﺘﺠﻪ ﺇﺩﺧﺎﻝ ﻣﻌﻴﻦT ﺩﻉ
and Y be an actual output of a neuron
If T=Y, there is nothing to learn.
ﻳﻜﻮﻥ ﺍﻟﻨﺎﺗﺞ ﺍﻟﻔﻌﻠﻲ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﺨﻼﻳﺎ ﺍﻟﻌﺼﺒﻴﺔY ﻭ
If T≠Y, then a neuron has to learn, in order to ensure that after adjustment of the
weights, its actual output will coincide with a desired output
. ﻻ ﻳﻮﺟﺪ ﺷﻲء ﻟﻠﺘﻌﻠﻢ، T = Y ﺇﺫﺍ
ﺳﻴﺘﺰﺍﻣﻦ ﻧﺎﺗﺠﻬﺎ، ﻣﻦ ﺃﺟﻞ ﺿﻤﺎﻥ ﺃﻧﻪ ﺑﻌﺪ ﺿﺒﻂ ﺍﻷﻭﺯﺍﻥ، ﻓﻴﺠﺐ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻟﺨﻼﻳﺎ ﺍﻟﻌﺼﺒﻴﺔ ﺃﻥ ﺗﺘﻌﻠﻢ، T ≠ Y ﺇﺫﺍ ﻛﺎﻥ
ﺍﻟﻔﻌﻠﻲ ﻣﻊ ﺍﻟﻨﺎﺗﺞ ﺍﻟﻤﺮﻏﻮﺏ
If T≠Y, then is the error .
ﺇﺫﺍ ﻛﺎﻥT ≠ Y ﻓﻬﺬﺍ ﻫﻮ ﺍﻟﺨﻄﺄ،.
A goal of learning is to adjust the weights in such a way that for a new actual output
we will have the following: Y= Y + ∂ = T
Y= Y + ∂ = T
ﺍﻟﻬﺪﻑ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﺘﻌﻠﻢ ﻫﻮ ﺿﺒﻂ ﺍﻷﻭﺯﺍﻥ ﺑﻄﺮﻳﻘﺔ ﺗﺠﻌﻞ ﺍﻟﻨﺎﺗﺞ ﺍﻟﻔﻌﻠﻲ ﺍﻟﺠﺪﻳﺪ ﻫﻮ ﺍﻟﺘﺎﻟﻲ:
Information flow is unidirectional()ﺗﺪﻓﻖ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﻠﻮﻣﺎﺕ ﻳﻜﻮﻥ ﺃﺣﺎﺩﻱ ﺍﻻﺗﺠﺎﻩ
Data is presented to Input layer() ﻳﺘﻢ ﺗﻘﺪﻳﻢ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻧﺎﺕ ﻟﻄﺒﻘﺔ ﺍﻹﺩﺧﺎﻝ
Passed on to Hidden Layer()ﻣﺮﻭﺭﺍ ﻋﻠﻰ ﻁﺒﻘﺔ ﻣﺨﻔﻴﺔ
Passed on to Output layer()ﻣﺮﻭﺭﺍ ﻋﻠﻰ ﻁﺒﻘﺔ ﺍﻹﺧﺮﺍﺝ
Information is distributed() ﻭﻳﺘﻢ ﺗﻮﺯﻳﻊ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﻠﻮﻣﺎﺕ
Information processing is parallel() ﻭﻳﺘﻢ ﻣﻌﺎﻟﺠﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﻠﻮﻣﺎﺕ ﺑﺎﻟﺘﻮﺍﺯﻱ
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
Feeding data through the net(:)ﺗﻐﺬﻳﺔ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻧﺎﺕ ﻋﺒﺮ ﺍﻟﺸﺒﻜﺔ
U
(1 × 0.25) + (0.5 × (-1.5)) = 0.25 + (-0.75) = - 0.5
Squashing:
1
= 0.3775
1 + e0.5
Example: Voice Recognition( ﺍﻟﺘﻌﺮﻑ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻟﺼﻮﺕ:)ﻣﺜﺎﻝ
U
Task: Learn to discriminate between two different voices saying “Hello”
( ﺗﻌﻠﻢ ﺍﻟﺘﻤﻴﻴﺰ ﺑﻴﻦ ﺻﻮﺗﻴﻦ ﻣﺨﺘﻠﻔﻴﻦ ﻗﺎﺋﻠﻴﻦ "ﻣﺮﺣﺒًﺎ:)"ﺍﻟﻤﻬﻤﺔ
Sources()ﻣﺼﺎﺩﺭ ﺍﻟﺼﻮﺕ
o Steve Simpson()ﺳﺘﻴﻒ
o David Raubenheimer()ﺩﻳﻔﻴﺪ
Format()ﺍﻟﺸﻜﻞ
o
o
Frequency distribution (60 bins)(( ﺑﺮﻣﻴﻞ60) ) ﺗﻮﺯﻳﻊ ﺍﻟﺘﺮﺩﺩ
Analogy: cochlea( ﻗﻮﻗﻌﺔ:)ﺍﻟﻘﻴﺎﺱ
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
Network architecture( )ﻣﻌﻤﺎﺭﻳﺔ ﺍﻟﺸﺒﻜﺔ
U
Feed forward network()ﺍﻟﺘﻐﺬﻳﺔ ﺍﻷﻣﺎﻣﻴﺔ ﻟﻠﺸﺒﻜﺔ
60 input (one for each frequency bin)
)ﻣﺪﺧﻞ )ﻭﺍﺣﺪ ﻟﻜﻞ ﺻﻨﺪﻭﻕ ﺗﺮﻭﺱ60
6 hidden
ﻣﺨﻔﻲ6
2 output (01 for “Steve”, 10 for “David”)
("David" ﻟـ10 ،Steve" " ﻟـ01) ﻣﺨﺮﺝ2
Presenting the data (untrained network)
U
(()ﺗﻘﺪﻳﻢ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻧﺎﺕ )ﺷﺒﻜﺔ ﻏﻴﺮ ﻣﺪﺭﺑﺔ
ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ :ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ
)ﺣﺴﺎﺏ ﻧﺴﺒﺔ ﺍﻟﺨﻄﺄ(Calculate error
U
)ﺧﻄﺄ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﺸﺒﻜﺔ ﻭﺿﺒﻂ ﺍﻷﻭﺯﺍﻥ(Network error and adjust weights
U
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
Presenting the data (trained network)(() ﺗﻘﺪﻳﻢ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻧﺎﺕ )ﺷﺒﻜﺔ ﻣﺪﺭﺑﺔ
U
Learning methods()ﻁﺮﻕ ﺍﻟﺘﻌﻠﻢ
U
Supervised learning()ﺍﻟﺘﻌﻠﻢ ﺗﺤﺖ ﺍﻹﺷﺮﺍﻑ
In supervised training, both the inputs and the outputs are provided. The
network then processes the inputs and compares its resulting outputs
against the desired outputs.
ﺛﻢ ﺗﻘﻮﻡ ﺍﻟﺸﺒﻜﺔ ﺑﻤﻌﺎﻟﺠﺔ. ﻳﺘﻢ ﺗﻮﻓﻴﺮ ﻛﻞ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﻤﺪﺧﻼﺕ ﻭﺍﻟﻤﺨﺮﺟﺎﺕ، ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﺘﺪﺭﻳﺐ ﺗﺤﺖ ﺇﺷﺮﺍﻑ
ﺍﻟﻤﺪﺧﻼﺕ ﻭﺗﻘﺎﺭﻥ ﻣﺨﺮﺟﺎﺗﻬﺎ ﺍﻟﻨﺎﺗﺠﺔ ﻣﻘﺎﺑﻞ ﺍﻟﻤﺨﺮﺟﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻤﺮﻏﻮﺑﺔ
Unsupervised learning()ﺍﻟﺘﻌﻠﻢ ﺑﺪﻭﻥ ﺇﺷﺮﺍﻑ
In unsupervised training, the network is provided with inputs but not with desired
outputs. The system itself must then decide what features it will use to group the input
data.
. ﻳﺠﺐ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻟﻨﻈﺎﻡ ﻧﻔﺴﻪ. ﻳﺘﻢ ﺗﺰﻭﻳﺪ ﺍﻟﺸﺒﻜﺔ ﺑﺎﻟﻤﺪﺧﻼﺕ ﻭﻟﻜﻦ ﻟﻴﺲ ﺑﺎﻟﻨﻮﺍﺗﺞ ﺍﻟﻤﻄﻠﻮﺑﺔ، ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﺘﺪﺭﻳﺐ ﻏﻴﺮ ﺍﻟﺨﺎﺿﻊ ﻟﻺﺷﺮﺍﻑ
ﺃﻥ ﻳﻘﺮﺭ ﺑﻌﺪ ﺫﻟﻚ ﺍﻟﻤﻴﺰﺍﺕ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺳﻴﺴﺘﺨﺪﻣﻬﺎ ﻟﺘﺠﻤﻴﻊ ﺑﻴﺎﻧﺎﺕ ﺍﻹﺩﺧﺎﻝ.
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
Applications of Artificial Neural Networks()ﺗﻄﺒﻴﻘﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺸﺒﻜﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻌﺼﺒﻴﺔ ﺍﻻﺻﻄﻨﺎﻋﻴﺔ
U
How to compute the outputs in Artificial Neural Networks?
U
()ﻛﻴﻒ ﻧﺤﺴﺐ ﺍﻟﻤﺨﺮﺟﺎﺕ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﺸﺒﻜﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻌﺼﺒﻴﺔ ﺍﻻﺻﻄﻨﺎﻋﻴﺔ؟
y = ∑ xi wi
yt =
1
1 + e− y
ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ :ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ
=)y 11= =(0.65x0.11)+ (0.42x0.3)+(0.70x0.5)+(0.22x0.2
0.5915
R
R
y 12==(0.65x0.2)+
(0.42x0.02)+(0.70x0.03)+(0.22x0.23)= 0.21
R
R
ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ :ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ
y 13==(0.65x0.01)+
(0.42x0.4)+(0.70x0.99)+(0.22x0.6)= 0.999
R
R
ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ :ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ
0.7308
0.5523
0.6437
ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ :ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ
= )y 21==(0.6437x0.12)+ (0.5523x0.8)+(0.7308x0.3
0.7383
R
R
ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ :ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ
= )y 22==(0.6437x0.0.33)+ (0.5523x0.05)+(0.7308x0.9
0.8977
R
R
= )y 23= =(0.6437x0.6)+ (0.5523x0.11)+(0.7308x0.1
0.5200
R
R
ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ :ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
LECTURE 9 : Data mining
U
U
Why Mine Data?()ﻟﻤﺎﺫﺍ ﺍﻟﺘﻨﻘﻴﺐ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻧﺎﺕ
o Lots of data is being collected
()ﻳﺘﻢ ﺟﻤﻊ ﺍﻟﻜﺜﻴﺮ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻧﺎﺕ
o Web data, e-commerce
()ﺑﻴﺎﻧﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻮﻳﺐ ﻭﺍﻟﺘﺠﺎﺭﺓ ﺍﻹﻟﻜﺘﺮﻭﻧﻴﺔ
o purchases at department/ grocery stores
)ﺍﻟﻤﺸﺘﺮﻳﺎﺕ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﻘﺴﻢ/
(ﻣﺤﻼﺕ ﺍﻟﺒﻘﺎﻟﺔ
o Bank/Credit Card transactions
ﺑﻄﺎﻗﺔ ﺍﻻﺋﺘﻤﺎﻥ/ )ﺍﻟﺒﻨﻚ
(ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺎﻣﻼﺕ
Computers have become cheaper and more powerful
()ﺃﺻﺒﺤﺖ ﺃﺟﻬﺰﺓ ﺍﻟﻜﻤﺒﻴﻮﺗﺮ ﺃﺭﺧﺺ ﻭﺃﻛﺜﺮ ﻗﻮﺓ
Competitive Pressure is Strong
()ﺍﻟﻀﻐﻂ ﺍﻟﺘﻨﺎﻓﺴﻲ ﺻﺎﺭ ﺃﻗﻮﻱ
Provide better, customized services for an edge (e.g. in Customer Relationship
Management)
ﻓﻲ، )ﺗﻘﺪﻳﻢ ﺧﺪﻣﺎﺕ ﺃﻓﻀﻞ ﻭﻣﺨﺼﺼﺔ ﻟﻠﺤﺎﻓﺔ )ﻋﻠﻰ ﺳﺒﻴﻞ ﺍﻟﻤﺜﺎﻝ
((ﺇﺩﺍﺭﺓ ﻋﻼﻗﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻌﻤﻼء
Data collected and stored at enormous speeds (GB/hour)
(( ﺳﺎﻋﺔ/ )ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻧﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﻳﺘﻢ ﺟﻤﻌﻬﺎ ﻭﺗﺨﺰﻳﻨﻬﺎ ﺑﺴﺮﻋﺎﺕ ﻫﺎﺋﻠﺔ )ﺟﻴﺠﺎﺑﺎﻳﺖ
– remote sensors on a satellite
()ﺃﺟﻬﺰﺓ ﺍﻻﺳﺘﺸﻌﺎﺭ ﻋﻦ ﺑﻌﺪ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻟﻘﻤﺮ ﺍﻟﺼﻨﺎﻋﻲ
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
– telescopes scanning the skies
()ﺍﻟﺘﻠﺴﻜﻮﺑﺎﺕ ﻣﺎﺳﺢ ﺍﻟﺴﻤﺎء
– microarrays generating gene expression data
()ﻣﻴﻜﺮﻭﺃﺭﺱ ﺗﻮﻟﻴﺪ ﺑﻴﺎﻧﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺘﻌﺒﻴﺮ ﺍﻟﺠﻴﻨﻲ
– scientific simulations generating terabytes of data
()ﺍﻟﻤﺤﺎﻛﺎﺓ ﺍﻟﻌﻠﻤﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺗﻮﻟﺪ ﺗﻴﺮﺍ ﺑﺎﻳﺖ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻧﺎﺕ
Traditional techniques infeasible for raw data
()ﺍﻟﺘﻘﻨﻴﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺘﻘﻠﻴﺪﻳﺔ ﻏﻴﺮ ﻣﺠﺪﻳﺔ ﻟﻠﺒﻴﺎﻧﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺨﺎﻡ
Data mining may help scientists
()ﻗﺪ ﻳﺴﺎﻋﺪ ﺍﺳﺘﺨﺮﺍﺝ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻧﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻌﻠﻤﺎء
– in classifying and segmenting data
()ﻓﻲ ﺗﺼﻨﻴﻒ ﻭﺗﻘﺴﻴﻢ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻧﺎﺕ
– in Hypothesis Formation
()ﻓﻲ ﺗﺸﻜﻴﻞ ﺍﻟﻔﺮﺿﻴﺔ
Mining Large Data Sets – Motivation()ﺩﻭﺍﻓﻊ ﺍﻟﺘﻨﻘﻴﺐ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻧﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻀﺨﻤﺔ
U
There is often information “hidden” in the data that is not readily evident
()ﻏﺎﻟﺒًﺎ ﻣﺎ ﺗﻜﻮﻥ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﻠﻮﻣﺎﺕ "ﻣﺨﻔﻴﺔ" ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻧﺎﺕ ﻏﻴﺮ ﺍﻟﻮﺍﺿﺤﺔ
Human analysts may take weeks to discover useful information
()ﻗﺪ ﻳﺴﺘﻐﺮﻕ ﺍﻟﻤﺤﻠﻠﻮﻥ ﺍﻟﺒﺸﺮﻳﻮﻥ ﺃﺳﺎﺑﻴﻊ ﻻﻛﺘﺸﺎﻑ ﻣﻌﻠﻮﻣﺎﺕ ﻣﻔﻴﺪﺓ
Much of the data is never analyzed at all
()ﻻ ﻳﺘﻢ ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ ﺍﻟﻜﺜﻴﺮ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻧﺎﺕ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻹﻁﻼﻕ
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
What is Data Mining?()ﻣﺎ ﻫﻭ ﺍﻟﺗﻧﻘﻳﺏ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﺑﻳﺎﻧﺎﺕ
U
Many Definitions:()ﻋﺪﺓ ﺗﻌﺮﻳﻔﺎﺕ
Non-trivial extraction of implicit, previously unknown and potentially useful information
from data
()ﺍﺳﺘﺨﺮﺍﺝ ﻏﻴﺮ ﺿﺌﻴﻞ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﻠﻮﻣﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻀﻤﻨﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﻟﻢ ﺗﻜﻦ ﻣﻌﺮﻭﻓﺔ ﻣﻦ ﻗﺒﻞ ﻭﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﻤﺤﺘﻤﻞ ﺃﻥ ﺗﻜﻮﻥ ﻣﻔﻴﺪﺓ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻧﺎﺕ
Exploration & analysis, by automatic or semi-automatic means, of large quantities of data in
order to discover meaningful patterns
ﻟﻜﻤﻴﺎﺕ ﻛﺒﻴﺮﺓ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻧﺎﺕ ﻣﻦ ﺃﺟﻞ ﺍﻛﺘﺸﺎﻑ ﺃﻧﻤﺎﻁ ﺫﺍﺕ، ﻋﻦ ﻁﺮﻳﻖ ﻭﺳﺎﺋﻞ ﺁﻟﻴﺔ ﺃﻭ ﺷﺒﻪ ﺁﻟﻴﺔ، )ﺍﺳﺘﻜﺸﺎﻑ ﻭﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ
(ﻣﻐﺰﻯ
What is (not) Data Mining?()ﻣﺎ ﻟﻳﺱ ﺗﻧﻘﻳﺑﺎ ً ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﺑﻳﺎﻧﺎﺕ
U
Dividing the customers of a company according to their gender.
(.)ﺗﻘﺴﻴﻢ ﻋﻤﻼء ﺍﻟﺸﺮﻛﺔ ﻭﻓﻘًﺎ ﻟﻨﻮﻋﻬﻢ
Monitoring the heart rate of a patient for abnormalities.
(.)ﺭﺻﺪ ﻣﻌﺪﻝ ﺿﺮﺑﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻘﻠﺐ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﻤﺮﻳﺾ ﻋﻦ ﺍﻟﺘﺸﻮﻫﺎﺕ
Dividing the customers of a company according to their profitability.
(.)ﺗﻘﺴﻴﻢ ﻋﻤﻼء ﺍﻟﺸﺮﻛﺔ ﻭﻓﻘًﺎ ﻟﺮﺑﺤﻴﺘﻬﺎ
Computing the total sales of a company.
(.)ﺣﺴﺎﺏ ﺇﺟﻤﺎﻟﻲ ﻣﺒﻴﻌﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺸﺮﻛﺔ
Predicting the future stock price of a company using historical records.
(.)ﺗﻮﻗﻊ ﺳﻌﺮ ﺍﻟﺴﻬﻢ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺘﻘﺒﻠﻲ ﻟﺸﺮﻛﺔ ﺗﺴﺘﺨﺪﻡ ﺍﻟﺴﺠﻼﺕ ﺍﻟﺘﺎﺭﻳﺨﻴﺔ
Sorting a student database based on student identification numbers.
(.)ﻓﺮﺯ ﻗﺎﻋﺪﺓ ﺑﻴﺎﻧﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻄﻼﺏ ﺑﻨﺎء ﻋﻠﻰ ﺃﺭﻗﺎﻡ ﺗﻌﺮﻳﻒ ﺍﻟﻄﺎﻟﺐ
Predicting the outcomes of tossing a (fair) pair of dice.
(.)ﺗﻮﻗﻊ ﻧﺘﺎﺋﺞ ﺇﻟﻘﺎء ﺯﻭﺝ )ﻧﺰﻳﻪ( ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﻨﺮﺩ
Monitoring seismic waves for earthquake activities
()ﺭﺻﺪ ﺍﻟﻤﻮﺟﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺰﻟﺰﺍﻟﻴﺔ ﻷﻧﺸﻄﺔ ﺍﻟﺰﻟﺰﺍﻝ
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
Data Mining Tasks()ﻣﻬﺎﻡ ﺍﻟﺘﻨﻘﻴﺐ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻧﺎﺕ
U
•Prediction Methods()ﻁﺮﻕ ﺍﻟﺘﻨﺒﺆ
–Use some variables to predict unknown or future values of other variables.
(.)ﺍﺳﺘﺨﺪﻡ ﺑﻌﺾ ﺍﻟﻤﺘﻐﻴﺮﺍﺕ ﻟﻠﺘﻨﺒﺆ ﺑﺎﻟﻘﻴﻢ ﻏﻴﺮ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻭﻓﺔ ﺃﻭ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺘﻘﺒﻠﻴﺔ ﻟﻠﻤﺘﻐﻴﺮﺍﺕ ﺍﻷﺧﺮﻯ
•Description Methods()ﻁﺮﻕ ﺍﻟﻮﺻﻒ
–Find human-interpretable patterns that describe the data.
(.)ﺍﺑﺤﺚ ﻋﻦ ﺍﻷﻧﻤﺎﻁ ﺍﻟﻘﺎﺑﻠﺔ ﻟﻠﺘﻔﺴﻴﺮ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺗﺼﻒ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻧﺎﺕ
4. Classification [Predictive]
(()ﺍﻟﺗﺻﻧﻳﻑ )ﺗﻧﺑﺅﻱ
5. •Clustering [Descriptive]
(()ﺗﺟﻣﻳﻊ)ﻭﺻﻔﻲ
6. •Association Rule Discovery [Descriptive]
(()ﺍﻛﺗﺷﺎﻑ ﺭﺍﺑﻁﺔ ﺍﻟﻌﻼﻗﺔ )ﻭﺻﻔﻲ
7. •Sequential Pattern Discovery [Descriptive]
(()ﺍﻛﺘﺸﺎﻑ ﻧﻤﻂ ﺗﺴﻠﺴﻠﻲ )ﻭﺻﻔﻲ
8. •Regression [Predictive]
(()ﺍﻟﺗﺭﺍﺟﻊ )ﺗﻧﺑﺅﻱ
9. •Deviation Detection [Predictive]
(()ﻛﺸﻒ ﺍﻻﻧﺤﺮﺍﻑ)ﺗﻨﺒﺆﻱ
Classification: Definition()ﺗﻌﺭﻳﻑ ﺍﻟﺗﺻﻧﻳﻑ
U
Given a collection of records (training set )
–Each record contains a set of attributes, one of the attributes is the class.
))ﺑﺎﻟﻨﻈﺮ ﺇﻟﻰ ﻣﺠﻤﻮﻋﺔ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﺴﺠﻼﺕ )ﻣﺠﻤﻮﻋﺔ ﺍﻟﺘﺪﺭﻳﺐ
- (. ﻭﺍﺣﺪﺓ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﺴﻤﺎﺕ ﻫﻲ ﺍﻟﻔﺌﺔ، ﻳﺤﺘﻮﻱ ﻛﻞ ﺳﺠﻞ ﻋﻠﻰ ﻣﺠﻤﻮﻋﺔ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﺴﻤﺎﺕ
Find a model for class attribute as a function of the values of other attributes.
(.)ﺍﺑﺤﺚ ﻋﻦ ﻧﻤﻮﺫﺝ ﻟﺴﻤﺔ ﺍﻟﻔﺌﺔ ﻛﺪﺍﻟﺔ ﻟﻘﻴﻢ ﺍﻟﺴﻤﺎﺕ ﺍﻷﺧﺮﻯ
Goal: previously unseen records should be assigned a class as accurately as possible.
–A test sets used to determine the accuracy of the model. Usually, the given data set is
divided into training and test sets, with training set used to build the model and test set used
to validate it.
ﻳﺠﺐ ﺗﻌﻴﻴﻦ ﻣﻔﻜﺮﺍﺕ ﻏﻴﺮ ﻣﺮﺋﻴﺔ ﻣﺴﺒﻘًﺎ ﻓﺌﺔ ﺑﺪﻗﺔ ﻗﺪﺭ ﺍﻹﻣﻜﺎﻥ:)ﺍﻟﻬﺪﻑ.
- ﻳﺘﻢ ﺗﻘﺴﻴﻢ ﻣﺠﻤﻮﻋﺔ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻧﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﻴﻨﺔ ﺇﻟﻰ ﻣﺠﻤﻮﻋﺎﺕ ﺗﺪﺭﻳﺐ، ﻋﺎﺩﺓ.ﻣﺠﻤﻮﻋﺔ ﺍﺧﺘﺒﺎﺭ ﺗﺴﺘﺨﺪﻡ ﻟﺘﺤﺪﻳﺪ ﺩﻗﺔ ﺍﻟﻨﻤﻮﺫﺝ
(. ﻣﻊ ﻣﺠﻤﻮﻋﺔ ﺗﺪﺭﻳﺐ ﺗﺴﺘﺨﺪﻡ ﻟﺒﻨﺎء ﺍﻟﻨﻤﻮﺫﺝ ﻭﻣﺠﻤﻮﻋﺔ ﺍﻻﺧﺘﺒﺎﺭ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺘﺨﺪﻣﺔ ﻟﻠﺘﺤﻘﻖ ﻣﻦ ﺻﺤﺘﻬﺎ، ﻭﺍﺧﺘﺒﺎﺭ
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
Classification Example()ﻣﺛﺎﻝ ﻟﻠﺗﺻﻧﻳﻑ
U
Classification: Application 1( ﺍﻟﺘﻄﺒﻴﻖ ﺍﻷﻭﻝ: )ﺍﻟﺘﺼﻨﻴﻒ
U
Direct Marketing()ﺍﻟﺘﺴﻮﻳﻖ ﺍﻟﻤﺒﺎﺷﺮ
–Goal: Reduce cost of mailing by targeting set of consumers likely to buy a new cell-phone
product.
- ﺗﻘﻠﻴﻞ ﺗﻜﻠﻔﺔ ﺍﻟﺒﺮﻳﺪ ﻋﻦ ﻁﺮﻳﻖ ﺍﺳﺘﻬﺪﺍﻑ ﻣﺠﻤﻮﻋﺔ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺘﻬﻠﻜﻴﻦ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﻤﺮﺟﺢ ﺃﻥ ﻳﺸﺘﺮﻭﺍ ﻣﻨﺘﺞ ﻫﺎﺗﻒ ﺧﻠﻴﻮﻱ:)ﺍﻟﻬﺪﻑ
(ﺟﺪﻳﺪ.
Approach()ﺍﻟﻤﻨﻬﺠﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺘﺨﺪﻣﺔ ﻟﻠﻮﺻﻮﻝ ﻟﻠﻬﺪﻑ
Use the data for a similar product introduced before.
(.)ﺍﺳﺘﺨﺪﻡ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻧﺎﺕ ﻟﻤﻨﺘﺞ ﻣﺸﺎﺑﻪ ﺗﻢ ﺗﻘﺪﻳﻤﻪ ﻣﻦ ﻗﺒﻞ
We know which customers decided to buy and which decided otherwise. This {buy, don’t
buy}decision forms the class attribute.
(. ﻻ ﺗﺸﺘﺮﻱ{ ﺳﻤﺔ ﺍﻟﺼﻒ، ﻳﺸ ّﻜﻞ ﻗﺮﺍﺭ }ﺷﺮﺍء.)ﻧﺤﻦ ﻧﻌﺮﻑ ﺍﻟﻌﻤﻼء ﺍﻟﺬﻳﻦ ﻗﺮﺭﻭﺍ ﺍﻟﺸﺮﺍء ﻭﺍﻟﺬﻱ ﻗﺮﺭ ﺧﻼﻑ ﺫﻟﻚ
Collect various demographic, lifestyle, and company-interaction related information about all
such customers.
ﻭﺍﻟﺘﻔﺎﻋﻞ ﺑﻴﻦ ﺍﻟﺸﺮﻛﺎﺕ ﺣﻮﻝ ﺟﻤﻴﻊ ﻫﺆﻻء، ﻭﻧﻤﻂ ﺍﻟﺤﻴﺎﺓ، )ﺟﻤﻊ ﻣﺨﺘﻠﻒ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﻠﻮﻣﺎﺕ ﺫﺍﺕ ﺍﻟﺼﻠﺔ ﺍﻟﺪﻳﻤﻮﻏﺮﺍﻓﻴﺔ
(.ﺍﻟﻌﻤﻼء
–Type of business, where they stay, how much they earn, etc.
(. ﻭﻣﺎ ﺇﻟﻰ ﺫﻟﻚ، ﻭﻣﻘﺪﺍﺭ ﻣﺎ ﻳﻜﺴﺒﻮﻧﻪ، ﺣﻴﺚ ﻳﻘﻴﻤﻮﻥ، ﻧﻮﻉ ﺍﻟﻨﺸﺎﻁ ﺍﻟﺘﺠﺎﺭﻱ-)
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
Classification: Application 2 ( ﺍﻟﺘﻄﺒﻴﻖ ﺍﻟﺜﺎﻧﻲ: )ﺍﻟﺘﺼﻨﻴﻒ
U
Fraud Detection()ﺍﻟﻜﺸﻒ ﻋﻦ ﺍﻟﻐﺶ
Goal: Predict fraudulent cases in credit card transactions.
(. ﺍﻟﺘﻨﺒﺆ ﺑﺎﻟﺤﺎﻻﺕ ﺍﻻﺣﺘﻴﺎﻟﻴﺔ ﻓﻲ ﻣﻌﺎﻣﻼﺕ ﺑﻄﺎﻗﺎﺕ ﺍﻻﺋﺘﻤﺎﻥ:)ﺍﻟﻬﺪﻑ
Approach()ﺍﻟﻤﻨﻬﺠﻴﺔ
Use credit card transactions and the information on its account-holder as attributes.
(.)ﺍﺳﺘﺨﺪﻡ ﻣﻌﺎﻣﻼﺕ ﺑﻄﺎﻗﺎﺕ ﺍﻻﺋﺘﻤﺎﻥ ﻭﺍﻟﻤﻌﻠﻮﻣﺎﺕ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺻﺎﺣﺐ ﺍﻟﺤﺴﺎﺏ ﺍﻟﺨﺎﺹ ﺑﻬﺎ ﻛﺴﻤﺎﺕ
o When does a customer buy, what does he buy, how often he pays on time, etc
( ﻭﻣﺎ ﺇﻟﻰ ﺫﻟﻚ، ﻭﻛﻢ ﻣﺮﺓ ﻳﺪﻓﻊ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﻮﻗﺖ ﺍﻟﻤﻨﺎﺳﺐ، ﻣﺎﺫﺍ ﻳﺸﺘﺮﻱ، )ﻣﺘﻰ ﻳﺸﺘﺮﻱ ﺍﻟﻌﻤﻴﻞ
Label past transactions as fraud or fair transactions. This forms the class attribute.
(. ﻫﺬﺍ ﺷﻜﻞ ﺳﻤﺔ ﺍﻟﻄﺒﻘﺔ.)ﻗﻢ ﺑﺘﺴﻤﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺎﻣﻼﺕ ﺍﻟﺴﺎﺑﻘﺔ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺃﻧﻬﺎ ﺍﺣﺘﻴﺎﻝ ﺃﻭ ﻣﻌﺎﻣﻼﺕ ﻋﺎﺩﻟﺔ
Learn a model for the class of the transactions.
(.)ﺗﻌﻠﻢ ﻧﻤﻮﺫﺝ ﻟﻔﺌﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺎﻣﻼﺕ
Use this model to detect fraud by observing credit card transactions on an account.
(.)ﺍﺳﺘﺨﺪﻡ ﻫﺬﺍ ﺍﻟﻨﻤﻮﺫﺝ ﻟﻠﻜﺸﻒ ﻋﻦ ﺍﻻﺣﺘﻴﺎﻝ ﻣﻦ ﺧﻼﻝ ﻣﺮﺍﻗﺒﺔ ﻣﻌﺎﻣﻼﺕ ﺑﻄﺎﻗﺎﺕ ﺍﻻﺋﺘﻤﺎﻥ ﻓﻲ ﺃﺣﺪ ﺍﻟﺤﺴﺎﺑﺎﺕ
Classification: Application 3 ( ﺍﻟﺘﻄﺒﻴﻖ ﺍﻟﺜﺎﻟﺚ: )ﺍﻟﺘﺼﻨﻴﻒ
U
Customer Attrition()ﺍﺳﺘﻨﺰﺍﻑ ﺍﻟﻌﻤﻼء
Goal: To predict whether a customer is likely to be lost to a competitor
( ﺍﻟﺘﻨﺒﺆ ﺑﻤﺎ ﺇﺫﺍ ﻛﺎﻥ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﻤﺤﺘﻤﻞ ﺃﻥ ﻳُﻔﻘﺪ ﺍﻟﻌﻤﻴﻞ ﻋﻠﻰ ﻣﻨﺎﻓﺲ:)ﺍﻟﻬﺪﻑ
Approach()ﺍﻟﻤﻨﻬﺠﻴﺔ
Use detailed record of transactions with each of the past and present customers, to find
attributes
( ﻟﻠﻌﺜﻮﺭ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻟﺴﻤﺎﺕ، )ﺍﺳﺘﺨﺪﻡ ﺳﺠﻞ ﻣﻔﺼﻞ ﻟﻠﻤﻌﺎﻣﻼﺕ ﻣﻊ ﻛﻞ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﻌﻤﻼء ﺍﻟﺴﺎﺑﻘﻴﻦ ﻭﺍﻟﺤﺎﻟﻴﻴﻦ
How often the customer calls, where he calls, what time-of-the day he calls most, his
financial status, marital status, etc.
، ﻭﺿﻌﻪ ﺍﻟﻤﺎﻟﻲ، ﻓﻲ ﺃﻱ ﻭﻗﺖ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﻴﻮﻡ ﺍﻟﺬﻱ ﻳﺘﺼﻞ ﺑﻪ ﺃﻛﺜﺮ، ﺣﻴﺚ ﻳﺘﺼﻞ، )ﻋﺪﺩ ﺍﻟﻤﺮﺍﺕ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﻳﺘﺼﻞ ﺑﻬﺎ ﺍﻟﻌﻤﻴﻞ
(. ﻭﻣﺎ ﺇﻟﻰ ﺫﻟﻚ، ﺣﺎﻟﺘﻪ ﺍﻻﺟﺘﻤﺎﻋﻴﺔ
Label the customers as loyal or disloyal.
(.ﺼﺎ ﺃﻭ ﺧﺎﺋﻨًﺎ
ً )ﺿﻊ ﻋﻼﻣﺔ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻟﻌﻤﻼء ﺑﺎﻋﺘﺒﺎﺭﻩ ﻣﺨﻠ
Find a model for loyalty.
(.)ﺍﻟﻌﺜﻮﺭ ﻋﻠﻰ ﻧﻤﻮﺫﺝ ﻟﻠﻮﻻء
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
Classification: Application 4 ( ﺍﻟﺘﻄﺒﻴﻖ ﺍﻟﺮﺍﺑﻊ: )ﺍﻟﺘﺼﻨﻴﻒ
U
Sky Survey Cataloging
Goal: To predict class (star or galaxy) of sky objects, especially visually faint ones, based on
the telescopic survey images (from Palomar Observatory).
ﺑﻨﺎ ًء ﻋﻠﻰ ﺻﻮﺭ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺢ ﺍﻟﺘﻠﺴﻜﻮﺑﻲ، ﺧﺎﺻﺔ ﺍﻷﺟﺴﺎﻡ ﺍﻟﻤﺮﺋﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﺒﺎﻫﺘﺔ، ( ﺍﻟﺘﻨﺒﺆ ﺑﺎﻷﺟﺴﺎﻡ ﺍﻟﺴﻤﺎﻭﻳﺔ )ﺍﻟﻨﺠﻤﻴﺔ ﺃﻭ ﺍﻟﻤﺠﺮﺓ:ﺍﻟﻬﺪﻑ
.(Palomar Observatory )ﻣﻦ ﻣﺮﺻﺪ ﺑﺎﻟﻮﻣﺎﺭ
–3000 images with 23,040 x 23,040 pixels per image.
. ﺑﻜﺴﻞ ﻟﻜﻞ ﺻﻮﺭﺓ23،040 × 23،040 ﺻﻮﺭﺓ ﺑﻤﻌﺪﻝ3000 -)
(
–Approach()ﺍﻟﻤﻨﻬﺠﻴﺔ
Segment the image. (.)ﺗﻘﺴﻴﻢ ﺍﻟﺼﻮﺭﺓ
Measure image attributes (features) -40 of them per object.
(. ﻣﻨﻬﺎ ﻟﻜﻞ ﻛﺎﺋﻦ40- ()ﻗﻴﺎﺱ ﺳﻤﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺼﻮﺭﺓ )ﻣﻴﺰﺍﺕ
Model the class based on these features.
(.)ﻗﻢ ﺑﺘﻄﻮﻳﺮ ﺍﻟﻨﻤﻮﺫﺝ ﺑﻨﺎ ًء ﻋﻠﻰ ﻫﺬﻩ ﺍﻟﻤﻴﺰﺍﺕ
Success Story: Could find 16 new high red-shift quasars, some of the farthest objects that are
difficult to find!
(! ﺑﻌﺾ ﻣﻦ ﺃﺑﻌﺪ ﺍﻷﺷﻴﺎء ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﻳﺼﻌﺐ ﺍﻟﻌﺜﻮﺭ ﻋﻠﻴﻬﺎ، ﻛﻮﺍﺯﺍﺭًﺍ ﺟﺪﻳﺪًﺍ ﻋﺎﻟﻲ ﺍﻟﻨﻮﺑﺔ ﺍﻟﺤﻤﺮﺍء16 ﻗﺪ ﺗﺠﺪ:)ﻗﺼﺔ ﻧﺠﺎﺡ
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
Clustering Definition()ﺗﻌﺮﻳﻒ ﺍﻟﺘﺠﻤﻴﻊ
U
Given a set of data points, each having a set of attributes, and a similarity measure
among them, find clusters such that.
ﺍﻭﺟﺪ ﻣﺠﻤﻮﻋﺎﺕ ﻣﻦ ﻫﺬﺍ ﺍﻟﻘﺒﻴﻞ، ﻭﻣﻘﻴﺎﺱ ﺗﺸﺎﺑﻪ ﺑﻴﻨﻬﺎ، ﻟﻜﻞ ﻣﻨﻬﺎ ﻣﺠﻤﻮﻋﺔ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﺴﻤﺎﺕ، )ﻣﻌﻄﻰ ﻣﺠﻤﻮﻋﺔ ﻣﻦ ﻧﻘﺎﻁ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻧﺎﺕ
(ﺍﻭ ﻣﻦ ﻫﺬﻩ ﺍﻟﺘﺸﺎﺑﻪ
–Data points in one cluster are more similar to one another.
( ﺗﻜﻮﻥ ﻧﻘﺎﻁ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻧﺎﺕ ﻓﻲ ﻣﺠﻤﻮﻋﺔ ﻭﺍﺣﺪﺓ ﺃﻛﺜﺮ ﺗﺸﺎﺑﻬﺎً ﻣﻊ ﺑﻌﻀﻬﺎ ﺍﻟﺒﻌﺾ.)
–Data points in separate clusters are less similar to one another.
- ()ﻧﻘﺎﻁ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻧﺎﺕ ﻓﻲ ﻣﺠﻤﻮﻋﺎﺕ ﻣﻨﻔﺼﻠﺔ ﺃﻗﻞ ﺗﺸﺎﺑﻬﺎ ً ﻣﻊ ﺑﻌﻀﻬﺎ ﺍﻟﺒﻌﺾ.
Similarity Measures:
(:)ﻣﻘﺎﻳﻴﺲ ﺍﻟﺘﺸﺎﺑﻪ
–
–
Euclidean Distance if attributes are continuous.
( .)ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺎﻓﺔ "ﺍﻻﻗﻠﻴﺪﻳﺔ" ﺇﺫﺍ ﻛﺎﻧﺖ ﺍﻟﺴﻤﺎﺕ ﻣﺴﺘﻤﺮﺓ
Other Problem-specific Measures.
()ﻣﻘﺎﻳﻴﺲ ﺧﺎﺻﺔ ﺍﺧﺮﻯ ﻟﻠﻤﺸﺎﻛﻞ
Illustrating Clustering
U
()ﺗﻮﺿﻴﺢ ﺍﻟﻤﺠﻤﻮﻋﺎﺕ
Euclidean Distance Based Clustering in 3-D space.
(.ﺍﻷﺑﻌﺎﺩ
ﻋﻠﻰ ﺃﺳﺎﺱ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺎﻓﺔ ﺍﻟﻌﻨﻘﻮﺩﻳﺔ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﻔﻀﺎء ﺛﻼﺛﻲ
)"ﺍﻻﻗﻠﻴﺪﻳﺔ" ﺗﻘﻮﻡ
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
Clustering: Application 1( ﺍﻟﺘﻄﺒﻴﻖ ﺍﻷﻭﻝ: )ﺍﻟﺘﺠﻤﻴﻊ
U
Market Segmentation:
(:)ﺗﺠﺰﺋﺔ ﺍﻟﺴﻮﻕ
–Goal: subdivide a market into distinct subsets of customers where any subset may
conceivably be selected as a market target to be reached with a distinct marketing mix.
" ﺗﻘﺴﻴﻢ ﺍﻟﺴﻮﻕ ﺇﻟﻰ ﻣﺠﻤﻮﻋﺎﺕ ﻓﺮﻋﻴﺔ ﻣﺘﻤﻴﺰﺓ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﻌﻤﻼء ﺣﻴﺚ ﻳﻤﻜﻦ ﺍﺧﺘﻴﺎﺭ ﺃﻱ ﻣﺠﻤﻮﻋﺔ ﻓﺮﻋﻴﺔ "ﻛﺴﻮﻕ ﻫﺪﻑ:ﺍﻟﻬﺪﻑ
ﻳﺘﻢ ﺍﻟﻮﺻﻮﻝ ﺇﻟﻴﻪ ﻣﻊ ﻣﺰﻳﺞ ﺗﺴﻮﻳﻘﻲ ﻣﺘﻤﻴﺰ.
–Approach:
()ﺍﻟﻤﻨﻬﺠﻴﺔ
•
Collect different attributes of customers based on their geographical and lifestyle related
information.
(.)ﺟﻤﻊ ﺧﺼﺎﺋﺺ ﻣﺨﺘﻠﻔﺔ ﻟﻠﻌﻤﻼء ﺍﺳﺘﻨﺎﺩًﺍ ﺇﻟﻰ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﻠﻮﻣﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺠﻐﺮﺍﻓﻴﺔ ﺫﺍﺕ ﺍﻟﺼﻠﺔ ﺑﻨﻤﻂ ﺍﻟﺤﻴﺎﺓ
•Find clusters of similar customers.
(.)ﻟﺒﺤﺚ ﻋﻦ ﻣﺠﻤﻮﻋﺎﺕ ﻣﻦ ﻋﻤﻼء ﻣﺸﺎﺑﻬﻴﻦ
•Measure the clustering quality by observing buying patterns of customers in same cluster vs.
those from different clusters.
(.)ﻗﻴﺎﺱ ﺟﻮﺩﺓ ﺍﻟﺘﺠﻤﻴﻊ ﻣﻦ ﺧﻼﻝ ﻣﺮﺍﻗﺒﺔ ﺃﻧﻤﺎﻁ ﺷﺮﺍء ﺍﻟﻌﻤﻼء ﻓﻲ ﻧﻔﺲ ﺍﻟﻣﺠﻤﻮﻋﺔ ﻣﻘﺎﺑﻞ ﺗﻠﻚ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺘﻤﺪﺓ ﻣﻦ ﻣﺠﻤﻮﻋﺎﺕ ﻣﺨﺘﻠﻔﺔ
Clustering: Application 2 ( ﺍﻟﺘﻄﺒﻴﻖ ﺍﻟﺜﺎﻧﻲ: )ﺍﻟﺘﺠﻤﻴﻊ
U
Document Clustering:
()ﺗﺠﻤﻴﻊ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺘﻨﺪﺍﺕ
–Goal: To find groups of documents that are similar to each other based on the important
terms appearing in them.
ﻟﻠﻌﺜﻮﺭ ﻋﻠﻰ ﻣﺠﻤﻮﻋﺎﺕ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺘﻨﺪﺍﺕ ﺍﻟﻤﺸﺎﺑﻬﺔ ﻟﺒﻌﻀﻬﺎ ﺍﻟﺒﻌﺾ ﺍﺳﺘﻨﺎﺩًﺍ ﺇﻟﻰ ﺍﻟﻤﺼﻄﻠﺤﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻤﻬﻤﺔ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺗﻈﻬﺮ:)ﺍﻟﻬﺪﻑ
(.ﻓﻴﻬﺎ
–Approach: To identify frequently occurring terms in each document. Form a similarity
measure based on the frequencies of different terms. Use it to cluster.
(. ﺍﺳﺘﺨﺪﺍﻣﻪ ﺇﻟﻰ ﺍﻟﻜﺘﻠﺔ. ﺷﻜﻞ ﺗﺪﺑﻴﺮ ﺗﺸﺎﺑﻪ ﻳﺴﺘﻨﺪ ﺇﻟﻰ ﺗﺮﺩﺩﺍﺕ ﻣﺨﺘﻠﻔﺔ.)ﻟﺘﺤﺪﻳﺪ ﺍﻟﻤﺼﻄﻠﺤﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻤﺘﻜﺮﺭﺓ ﻓﻲ ﻛﻞ ﻭﺛﻴﻘﺔ
–Gain: ()ﺍﻟﺮﺑﺢ ﺍﻭ ﺍﻟﻔﺎﺋﺪﺓ
Information Retrieval can utilize the clusters to relate a new document or search term to
clustered documents.
(.)ﻳﻤﻜﻦ ﺍﺳﺘﺨﺪﺍﻡ ﺍﺳﺘﺮﺟﺎﻉ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﻠﻮﻣﺎﺕ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﻤﺠﻤﻮﻋﺎﺕ ﻟﺮﺑﻂ ﻭﺛﻴﻘﺔ ﺟﺪﻳﺪﺓ ﺃﻭ ﻋﺒﺎﺭﺓ ﺑﺤﺚ ﺇﻟﻰ ﻣﺴﺘﻨﺪﺍﺕ ﺍﻟﻤﺠﻤﻮﻋﺔ
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
Illustrating Document Clustering()ﺗﻮﺿﻴﺢ ﻟﺘﺠﻤﻴﻊ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺘﻨﺪﺍﺕ
U
Clustering Points: 3204 Articles of Los Angeles Times.
(. ﻣﻘﺎﻟﺔ ﻣﻦ ﻣﺠﻠﺔ ﻟﻮﺱ ﺍﻧﺠﻠﻴﺲ ﺗﺎﻳﻤﺰ3204 :)ﻧﻘﺎﻁ ﺍﻟﺘﺠﻤﻊ
Similarity Measure: How many words are common in these documents (after some word
filtering).
(.( ﻋﺪﺩ ﺍﻟﻜﻠﻤﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺸﺎﺋﻌﺔ ﺍﻭ ﺍﻟﻤﺘﻜﺮﺭﺓ ﻓﻲ ﻫﺬﻩ ﺍﻟﻮﺛﺎﺋﻖ )ﺑﻌﺪ ﺗﺼﻔﻴﺔ ﺑﻌﺾ ﺍﻟﻜﻠﻤﺎﺕ:)ﻣﻘﻴﺎﺱ ﺍﻟﺘﺸﺎﺑﻪ
Clustering of S&P 500 Stock Data Discovered
U
Observe Stock Movements every day.
(.)ﻣﺮﺍﻗﺒﺔ ﺗﺤﺮﻛﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻤﺨﺰﻭﻥ ﻛﻞ ﻳﻮﻡ
Clustering points: Stock-{UP/DOWN}
( ﺍﻟﻤﺨﺰﻭﻥ: ﻧﻘﺎﻁ ﺍﻟﺘﺠﻤﻴﻊ- {UP / DOWN} )
Similarity Measure: Two points are more similar if the events described by them frequently
happen together on the same day.
ﺗﻜﻮﻥ ﺍﻟﻨﻘﻄﺘﺎﻥ ﺃﻛﺜﺮ ﺗﺸﺎﺑﻬﺎ ً ﺇﺫﺍ ﻛﺎﻧﺖ ﺍﻷﺣﺪﺍﺙ:)ﻣﻘﻴﺎﺱ ﺍﻟﺘﺸﺎﺑﻪ
(.ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺗﻢ ﻭﺻﻔﻬﺎ ﻣﻦ ﻗﺒﻠﻬﻢ ﺣﺪﺛﺖ ﻓﻲ ﻛﺜﻴﺮ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻷﺣﻴﺎﻥ ﻣﻌﺎ ﻓﻲ ﻧﻔﺲ ﺍﻟﻴﻮﻡ
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
Association Rule Discovery()ﻣﻛﺗﺷﻔﺎﺕ ﺭﻭﺍﺑﻁ ﺍﻟﻌﻼﻗﺔ
U
Given a set of records each of which contain some number of items from a given collection;
)ﻣﻌﻄﻰ ﻣﺠﻤﻮﻋﺔ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﺴﺠﻼﺕ ﺗﺤﺘﻮﻱ ﻛﻞ ﻣﻨﻬﺎ ﻋﻠﻰ ﻋﺪﺩ ﻣﻦ
(ﺍﻟﻌﻨﺎﺻﺮ ﻣﻦ ﺗﺠﻤﻴﻌﻪ ﻣﻌﻴﻨﺔ ؛
Produce dependency rules which will predict occurrence of an item based on occurrences of
other items.
)ﺇﻧﺘﺎﺝ ﻗﻮﺍﻋﺪ ﺍﻟﺘﺒﻌﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﻣﻦ ﺷﺄﻧﻬﺎ ﺍﻟﺘﻨﺒﺆ ﺑﺎﻟﺤﺪﻭﺙ
(.ﻣﻦ ﻋﻨﺼﺮ ﻳﺴﺘﻨﺪ ﺇﻟﻰ ﺗﻜﺮﺍﺭﺍﺕ ﺍﻟﻌﻨﺎﺻﺮ ﺍﻷﺧﺮﻯ
Association Rule Discovery: Application 1( ﺍﻟﺘﻄﺒﻴﻖ ﺍﻷﻭﻝ: )ﻣﻜﺘﺸﻔﺎﺕ ﺭﻭﺍﺑﻂ ﺍﻟﻌﻼﻗﺔ
U
Marketing and Sales Promotion:
(:)ﺍﻟﺗﺳﻭﻳﻕ ﻭﺍﻟﻣﺑﻳﻌﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺗﺭﻭﻳﺞ
Let the rule discovered be
{Bagels, … } --> {Potato Chips}
)ﺩﻉ ﺍﻟﻘﺎﻋﺪﺓ ﺗﻜﺘﺸﻒ
({Potato Chips} <- {…،Bagels}
Potato Chipsas consequent=> Can be used to determine what should be done to boost its
sales.
Bagels in the antecedent=> Can be used to see which products would be affected if the
store discontinues selling bagels.
(.)ﺍﻟﻛﺑﺳﻭﻻﺕ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﺣﺎﻟﺔ ﺍﻟﺳﺎﺑﻘﺔ =< ﻳﻣﻛﻥ ﺍﺳﺗﺧﺩﺍﻣﻬﺎ ﻟﻣﻌﺭﻓﺔ ﺃﻱ ﺍﻟﻣﻧﺗﺟﺎﺕ ﺳﺗﺗﺄﺛﺭ ﺇﺫﺍ ﺗﻭﻗﻑ ﺍﻟﻣﺗﺟﺭ ﻋﻥ ﺑﻳﻊ ﺍﻟﻛﻌﻙ
Bagels in antecedent and Potato chips in consequent=> Can be used to see what products
should be sold with Bagels to promote sale of Potato chips!
)ﺍﻟﻛﻌﻙ ﻓﻲ ﺭﻗﺎﺋﻕ ﺍﻟﺑﻁﺎﻁﺱ ﻓﻲ ﻭﻗﺕ ﻻﺣﻕ =< ﻳﻣﻛﻥ ﺍﺳﺗﺧﺩﺍﻣﻬﺎ ﻟﻣﻌﺭﻓﺔ ﻣﺎ ﻳﻧﺑﻐﻲ ﺑﻳﻊ ﺍﻟﻣﻧﺗﺟﺎﺕ ﻣﻊ ﺍﻟﺧﺑﺯ ﻟﺗﻌﺯﻳﺯ ﺑﻳﻊ
(!ﺭﻗﺎﺋﻕ ﺍﻟﺑﻁﺎﻁﺱ
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
Association Rule Discovery: Application 2( ﺍﻟﺘﻄﺒﻴﻖ ﺍﻟﺜﺎﻧﻲ: )ﻣﻜﺘﺸﻔﺎﺕ ﺭﻭﺍﺑﻂ ﺍﻟﻌﻼﻗﺔ
U
Supermarket shelf management.
()ﺍﺩﺍﺭﺓ ﺭﻓﻮﻑ ﺍﻟﺴﻮﺑﺮ ﻣﺎﺭﻛﺖ
–Goal: To identify items that are bought together by sufficiently many customers.
(. ﺗﺤﺪﻳﺪ ﺍﻟﻌﻨﺎﺻﺮ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺗﻢ ﺷﺮﺍﺅﻫﺎ ﻣﻌًﺎ ﺑﻮﺍﺳﻄﺔ ﺍﻟﻌﺪﻳﺪ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﻌﻤﻼء:)ﺍﻟﻬﺪﻑ
–Approach: Process the point-of-sale data collected with barcode scanners to find
dependencies among items.
(. ﻣﻌﺎﻟﺠﺔ ﺑﻴﺎﻧﺎﺕ ﻧﻘﻄﺔ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﻊ ﺍﻟﺘﻲ ﺗﻢ ﺟﻤﻌﻬﺎ ﻣﻊ ﻣﺎﺳﺤﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺒﺎﺭﻛﻮﺩ ﻟﻠﻌﺜﻮﺭ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻟﺘﺒﻌﻴﺎﺕ ﺑﻴﻦ ﺍﻟﻌﻨﺎﺻﺮ: ﺍﻟﻤﻨﻬﺠﻴﺔ-)
–A classic rule –(()ﻗﺎﻋﺪﺓ ﻛﻼﺳﻴﻜﻴﺔ)ﺗﻘﻠﻴﺪﻳﺔ
If a customer buys diaper and milk, then he is very likely to buy water.
(!. ﻓﻤﻦ ﺍﻟﻤﺮﺟﺢ ﺃﻥ ﻳﺸﺘﺮﻱ ﺍﻟﻤﺎء، )ﺇﺫﺍ ﺍﺷﺘﺮﻯ ﺃﺣﺪ ﺍﻟﻌﻤﻼء ﺣﻔﺎﺿﺎﺕ ﻭﺣﻠﻴﺒًﺎ
So, don’t be surprised if you find six-packs stacked next to diapers!
(! ﻻ ﺗﻔﺎﺟﺊ ﺇﺫﺍ ﻭﺟﺪﺕ ﺳﺘﺔ ﺣﺰﻡ ﻣﻜﺪﺳﺔ ﺑﺠﻮﺍﺭ ﺣﻔﺎﺿﺎﺕ، )ﻟﺬﺍ
Association Rule Discovery: Application 3 ( ﺍﻟﺘﻄﺒﻴﻖ ﺍﻟﺜﺎﻟﺚ: )ﻣﻜﺘﺸﻔﺎﺕ ﺭﻭﺍﺑﻂ ﺍﻟﻌﻼﻗﺔ
U
Inventory Management:
(ﺍﺩﺍﺭﺓ ﺍﻟﻤﺨﺰﻭﻥ:)
–Goal: A consumer appliance repair company wants to anticipate the nature of repairs on its
consumer products and keep the service vehicles equipped with right parts to reduce on
number of visits to consumer households.
ﺷﺮﻛﺔ ﺇﺻﻼﺡ ﺍﻷﺟﻬﺰﺓ ﺍﻻﺳﺘﻬﻼﻛﻴﺔ ﺗﺮﻏﺐ ﻓﻲ ﺗﻮﻗﻊ ﻁﺒﻴﻌﺔ ﺍﻹﺻﻼﺣﺎﺕ ﻋﻠﻰ ﻣﻨﺘﺠﺎﺗﻬﺎ ﺍﻻﺳﺘﻬﻼﻛﻴﺔ ﻭﺍﻟﺤﻔﺎﻅ: ﺍﻟﻬﺪﻑ-)
(.ﻋﻠﻰ ﻣﺮﻛﺒﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺨﺪﻣﺔ ﻣﺠﻬﺰﺓ ﺑﺎﻷﺟﺰﺍء ﺍﻟﺼﺤﻴﺤﺔ ﻟﺘﻘﻠﻴﻞ ﻋﺪﺩ ﺍﻟﺰﻳﺎﺭﺍﺕ ﺇﻟﻰ ﺍﻷﺳﺮ ﺍﻻﺳﺘﻬﻼﻛﻴﺔ
–Approach: Process the data on tools and parts required in previous repairs at different
consumer locations and discover the co-occurrence patterns.
ﻣﻌﺎﻟﺠﺔ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻧﺎﺕ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻷﺩﻭﺍﺕ ﻭﻗﻄﻊ ﺍﻟﻐﻴﺎﺭ ﺍﻟﻤﻄﻠﻮﺑﺔ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻹﺻﻼﺣﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺴﺎﺑﻘﺔ ﻓﻲ ﻣﻮﺍﻗﻊ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺘﻬﻠﻜﻴﻦ: ﺍﻟﻤﻨﻬﺠﻴﺔ-)
(.ﺍﻟﻤﺨﺘﻠﻔﺔ ﻭﺍﻛﺘﺸﺎﻑ ﺃﻧﻤﺎﻁ ﺍﻟﻤﺘﺰﺍﻣﻨﺔ
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
Sequential Pattern Discovery: Definition
U
(: ﺍﻛﺘﺸﺎﻑ ﺍﻻﻧﻤﺎﻁ ﺍﻟﻤﺘﺴﻠﺴﻠﺔ: )ﺗﻌﺮﻳﻒ
Given is a set of objects, with each object associated with its own timeline of events, find
rules that predict strong sequential dependencies among different events.
ﻭﺇﻳﺠﺎﺩ ﻗﻮﺍﻋﺪ ﺗﺘﻨﺒﺄ ﺑﺘﺒﻌﻴﺔ، ﻣﻊ ﺍﺭﺗﺒﺎﻁ ﻛﻞ ﻛﺎﺋﻦ ﺑﺠﺪﻭﻝ ﺯﻣﻨﻲ ﺧﺎﺹ ﺑﺎﻷﺣﺪﺍﺙ، )ﻣﻌﻄﻰ ﻣﺠﻤﻮﻋﺔ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﻜﺎﺋﻨﺎﺕ
(.ﻣﺘﺴﻠﺴﻠﺔ ﻗﻮﻳﺔ ﺑﻴﻦ ﺍﻷﺣﺪﺍﺙ ﺍﻟﻤﺨﺘﻠﻔﺔ
Rules are formed by first disoveringpatterns. Event
occurrences in the patterns are governed by timing
constraints.
ﺗﺨﻀﻊ ﺃﺣﺪﺍﺙ ﺍﻷﺣﺪﺍﺙ ﻓﻲ.)ﻳﺘﻢ ﺗﺸﻜﻴﻞ ﺍﻟﻘﻮﺍﻋﺪ ﻋﻦ ﻁﺮﻳﻖ ﺍﻟﻜﺸﻒ ﺍﻷﻭﻝ ﻋﻦ ﺍﻷﻣﺮﺍﺽ
(.ﺍﻷﻧﻤﺎﻁ ﻟﻘﻴﻮﺩ ﺍﻟﺘﻮﻗﻴﺖ
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
Regression()ﺍﻻﻧﺤﺪﺍﺭ ﺍﻭ ﺍﻟﺘﺮﺍﺟﻊ
U
•Predict a value of a given continuous valued variable based on the values of other variables,
assuming a linear or nonlinear model of dependency.
(. ﺑﺎﻓﺘﺮﺍﺽ ﻧﻤﻮﺫﺝ ﺗﺒﻌﻴﺔ ﺧﻄﻲ ﺃﻭ ﻏﻴﺮ ﺧﻄﻲ، )• ﺗﻮﻗﻊ ﻗﻴﻤﺔ ﻟﻤﺘﻐﻴﺮ ﻣﻌﻴﻦ ﻣﺴﺘﻤﺮ ﻗﺎﺋﻢ ﻋﻠﻰ ﻗﻴﻢ ﺍﻟﻤﺘﻐﻴﺮﺍﺕ ﺍﻷﺧﺮﻯ
Greatly studied in statistics, neural network fields.
(. ﻭﺣﻘﻮﻝ ﺍﻟﺸﺒﻜﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻌﺼﺒﻴﺔ، )ﺩﺭﺳﺖ ﺑﺸﻜﻞ ﻛﺒﻴﺮ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻹﺣﺼﺎءﺍﺕ
Examples:
–Predicting sales amounts of new product based on advertising expenditure.
(. ﺍﻋﺘﻤﺎﺩ ﻣﺒﺎﻟﻎ ﻣﺒﻴﻌﺎﺕ ﻟﻤﻨﺘﺞ ﺟﺪﻳﺪ ﻳﻌﺘﻤﺪ ﻋﻠﻰ ﻧﻔﻘﺎﺕ ﺍﻹﻋﻼﻥ-)
–Predicting wind velocities as a function of temperature, humidity, air pressure, etc.
(. ﺇﻟﺦ، ﺗﻌﺰﻳﺰ ﺳﺮﻋﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺮﻳﺎﺡ ﻛﺪﺍﻟﺔ ﻟﻠﺤﺮﺍﺭﺓ ﻭﺍﻟﺮﻁﻮﺑﺔ ﻭﺿﻐﻂ ﺍﻟﻬﻮﺍء-)
–Time series prediction of stock market indices.
(. ﺗﻮﻗﻴﺖ ﺳﻠﺴﻠﺔ ﺍﻟﺘﻨﺒﺆ ﻟﻤﺆﺷﺮﺍﺕ ﺳﻮﻕ ﺍﻷﻭﺭﺍﻕ ﺍﻟﻤﺎﻟﻴﺔ-)
Deviation/Anomaly Detection( ﺍﻟﻜﺸﻒ ﻋﻦ ﺍﻟﺸﺬﻭﺫ/ )ﺍﻻﻧﺤﺮﺍﻑ
U
•
Detect significant deviations from normal behavior
()• ﻛﺸﻒ ﺍﻧﺤﺮﺍﻓﺎﺕ ﻛﺒﻴﺮﺓ ﻋﻦ ﺍﻟﺴﻠﻮﻙ ﺍﻟﻌﺎﺩﻱ
•Applications:
(:)• ﺍﻟﺘﻄﺒﻴﻘﺎﺕ
–Credit Card Fraud Detection
()ﻛﺸﻒ ﺍﺣﺘﻴﺎﻝ ﺑﻄﺎﻗﺔ ﺍﻻﺋﺘﻤﺎﻥ
–Network Intrusion Detection
()ﻛﺸﻒ ﺷﺒﻜﺔ ﺍﻟﺘﺪﺧﻞ
Typical network traffic at University level may reach over 100 million connections per
day
( ﻣﻠﻴﻮﻥ ﺗﻮﺻﻴﻠﺔ ﻳﻮﻣﻴًﺎ100 )ﻗﺪ ﺗﺼﻞ ﺣﺮﻛﺔ ﻣﺮﻭﺭ ﺍﻟﺸﺒﻜﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺘﺎﺩﺓ ﻋﻠﻰ ﻣﺴﺘﻮﻯ ﺍﻟﺠﺎﻣﻌﺔ ﺇﻟﻰ ﺃﻛﺜﺮ ﻣﻦ
ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ: ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ
Data Mining Project Cycle()ﺩﻭﺭﺓ ﻣﺸﺮﻭﻉ ﺗﻨﻘﻴﺐ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻧﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺒﻴﺎﻧﺎﺕ
U
Data Collection()ﺟﻣﻊ ﺍﻟﺑﻳﺎﻧﺎﺕ
Data Cleaning and Transformation()ﺗﻧﻅﻳﻑ ﺍﻟﺑﻳﺎﻧﺎﺕ ﻭﺗﺣﻭﻳﻠﻬﺎ
Numerical transformation()ﺍﻟﺗﺣﻭﻳﻝ ﺍﻟﻌﺩﺩﻱ
Grouping()ﺍﻟﺗﺟﻣﻳﻊ
Aggregation()ﺍﻟﺗﻛﺩﻳﺱ
Missing value handling()ﺍﻟﺗﻌﺎﻣﻝ ﻣﻊ ﺍﻟﻘﻳﻡ ﺍﻟﻣﻔﻘﻭﺩﺓ
Removing outliers()ﺇﺯﺍﻟﺔ ﺍﻟﻘﻳﻡ ﺍﻟﻣﺗﻁﺭﻓﺔ
Model Building()ﺑﻧﺎء ﺍﻟﻧﻣﻭﺫﺝ
Model Assessment()ﺗﻘﻳﻳﻡ ﺍﻟﻧﻣﻭﺫﺝ
Application Integration()ﺗﻛﺎﻣﻝ ﺍﻟﺗﻁﺑﻳﻕ
Model Management()ﺇﺩﺍﺭﺓ ﺍﻟﻧﻣﺎﺫﺝ
ﺇﻋﺩﺍﺩ :ﻣﺟﺎﻫﺩ ﺟــﻌﻔﺭ
)ﺍﻟﺨﻮﺍﺭﺯﻣﻴﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺠﻴﻨﻴﺔ(LECTURE 10 : GENETI C ALGORI THM S
U
ﺷﻴﺘﻬﺎ ﺑﺎﻟﻌﺮﺑﻲ ﺃﺻﻼً ):
ﺗﻢ ﺑﺤﻤﺪ ﷲ ..




