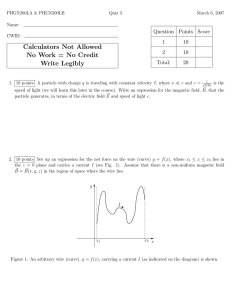
Explain the meaning of the statement ‘electric charge of a body is quantised’. Why can one ignore quantisation of electric charge when dealing with macroscopic i.e., large scale charges? An infinite line charge produces a field of 9 × 104 N/C at a distance of 2 cm. Calculate the linear charge density. When does the path traced by a moving charged particle in a magnetic field is helix? 1 5 State Ampere’s circuital Law. 1 6 Justify that the tangential component of electrostatic field is continuous from one side of a charged surface to another. Which physical quantity has its SI unit as (i) C – m (ii) Vm 1 Draw a graph to show a variation of resistance of a metal wire as a function of its diameter keeping its length and material constant. Figure shows tracks of three charged particles in a uniform electrostatic field. Which particle has the highest charge to mass ratio? 1 1 2 3 4 7 8 9 10 A regular hexagon of side 10 cm has a charge 5 μC at each of its vertices. Calculate the potential at the centre of the hexagon. 11 An electron and a proton, having equal momenta, enter a uniform magnetic field at right angles to the field lines. What will be the ratio of the radii of curvature of their trajectories? 12 Alloys usually have much (lower/higher) temperature coefficients of resistance than pure metals. Which is correct? 13 What is the nature of the force between two long straight parallel conductors when they carry currents in the (i) same direction? (ii) opposite direction? 14 compare the magnitudes of the magnetic field of the coil at its centre and at an axial point for which z = 3 . 15 Does the charge given to a metallic sphere depend on whether it is hollow or solid ? Give reason for Your answer. 16 Define 1A of current. 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 17 The storage battery of a car has an emf of 12 V. If the internal resistance of the battery is 0.4 Ω, what is the maximum current that can be drawn from the battery? 18 With circuit diagram only explain how can a galvanometer be converted into a voltmeter? 19 A wire whose cross-sectional area is increasing linearly from its one end to the other, is connected across a battery of V volts. Which of the following quantities remain constant in the wire ? (a) drift speed (b) current density? 20 A low voltage supply from which one needs high currents must have very low internal resistance. Why? 21 An oil drop of 12 excess electrons is held stationary under a constant electric field of 2.55 × 104 NC–1 in Millikan’s oil drop experiment. The density of the oil is 1.26 g cm–3. Estimate the radius of the drop. (g = 9.81 m s–2; e = 1.60 × 10–19 C). 22 Two wires A and B of the same material and having same length, have their cross sectional areas in the ratio 1:6. What would be the ratio of heat produced in these wires when same voltage is applied across each? 23 Two identical capacitors of 12 pF each are connected in series across a battery of 50 V. How much electrostatic energy is stored in the combination ? If these were connected in parallel across the same battery, how much energy will be stored in the combination now ? 24 A hollow charged conductor has a tiny hole cut into its surface. Show that the electric field in the hole is (σ/2ε0) ˆn , where ˆn is the unit vector in the outward normal direction, and σ is the surface charge density near the hole. 25 State the principle of an moving coil galvanometer. Write an expression for the current sensitivity. 26 Two charged conducting spheres of radii a and b are connected to each other by a wire. What is the ratio of electric fields at the surfaces of the two spheres? Use the result obtained to explain why charge density on the sharp and pointed ends of a conductor is higher than on its flatter portions. 27 Derive the expression for the electric field at a point on the equatorial line of the ideal electric dipole. 28 A proton and an alpha particle enter at right angles into a uniform magnetic field of intensity B. Calculate the radii of their paths when they enter the field with the same a) momentum and b) kinetic energy 29 Using Biot-Savart’s law, derive the expression for the magnetic field at a point along the axis of a circular current loop. 30 Determine the current in each branch of the network shown in Fig. 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 3 3 3 31 Describe the concept used for the selection of velocity of a charged particle. Explain the principle of the device with the help of a diagram where the same concept is used. What is the resonating condition for the said device? 32 A point charge of +2µC is kept fixed at the origin. Another point charge of +4µC is brought from a far off point to a point distant 50 cm from the origin. Calculate the electrostatic potential energy of this two charge system. Another charge of +1µC is brought to a point distant 100 cm from each of these two charges (assumed to be kept fixed). What is the work done? 33 Derive the expression for the time period of oscillation of the bar magnet in the magnetic field. 34 For the potentiometer circuit, shown in the given figure, points X and Y represent the two terminals of an unknown emf E. A student observed that when the jockey is moved from the end A to the end B of the potentiometer wire, the deflection in the galvanometer remains in the same direction. What are the two possible faults in the circuit that could result in this observation ? If the galvanometer deflection at the end B is (i) more (ii) less than that at the end A, which of the two faults, listed above, would be there in the circuit? Give reasons in support of your answer in each case. 3 3 3 3 35 How will a dia–, para – and a ferromagnetic material behave when 5 kept in a non-uniform external magnetic field? Give two examples of each of these materials. Name two main characteristics of a ferromagnetic material which help us to decide its suitability for making (i) a permanent magnet (ii) an electromagnet. Which of these two characteristics should have high or low values for each of these two types of magnets? 36 (a) In a metre bridge , the balance point is found to be at 39.5 cm from 5 the end left end A, when the resistor Y in the right gap is of 12.5 Ω. Determine the resistance of X in the left gap. Why are the connections between resistors in a Wheatstone or meter bridge made of thick copper strips? (b) Determine the balance point of the bridge above if X and Y are interchanged. (c) What happens if the galvanometer and cell are interchanged at the balance point of the bridge? Would the galvanometer show any current? 37 Find the expression for the energy density of the capacitor. Also find 5 the energy lost when the charged capacitor is disconnected from the source and connected in parallel with the uncharged capacitor. Where does this loss of energy appear?