Year 8 Digital Technologies Unit Plan: Computational Thinking
advertisement

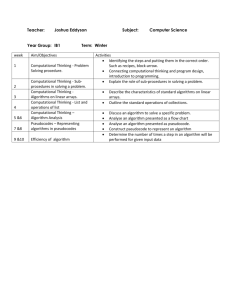
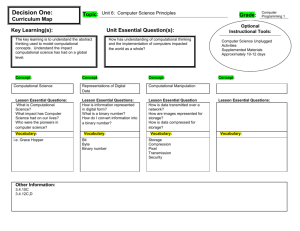
CLEVELAND STATE HIGH SCHOOL - UNIT PLAN Year 8 SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY Digital Technologies SUBJECT TOPIC VERSION DATE 8 STZ Digital Technologies 21 March 2018 YEAR DURATION 2018 2 weeks MACRO GOAL Students will apply the processes of computational thinking to decompose and generate solutions to a range of problems, to understand how computational thinking can be applied to coding and programming activities. 1 – Computational Thinking (4 lessons) We are learning to (WALT) What I’m looking for (WILF) Analyse information to draw conclusions I can name and define the steps in computational thinking Understand and follow the computational thinking process I can use pattern matching and abstraction to produce my own algorithms Declarative Knowledge (KNOW) This is because (TIB) Computational thinking helps us to break down complex tasks and solve problems It will be helpful when writing codes and programs Procedural Knowledge (DO) Computational thinking – decomposition, abstraction, pattern matching and algorithms Apply processes of decomposition, abstraction, pattern matching to develop simple algorithms in a range of contexts. 2 – Algorithms (4 lessons) We are learning to (WALT) What I’m looking for (WILF) Organise processes into a sequence of steps I can sort steps into order for everyday activities Clearly communicate steps so that someone else can follow them I can write a series of steps for an everyday activity that someone else can follow Use flowcharts to represent the steps in an algorithm I can represent my algorithm using a flowchart Declarative Knowledge (KNOW) Inputs, Outputs, processes, decisions and flows 1 Unit Planner | Cleveland DSHS This is because (TIB) Algorithms help us to make sure that instructions are clear and easy to follow Computer programs need algorithms to ensure that the computer completes a task correctly Procedural Knowledge (DO) Write a series of steps in words; translate a series of steps into a flowchart using correct symbols and MS Office tools. CLEVELAND STATE HIGH SCHOOL - UNIT PLAN Year 8 SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY Digital Technologies 3 – Codes (4 lessons) We are learning to (WALT) What I’m looking for (WILF) This is because (TIB) Represent information using numbers and symbols I can write an algorithm using symbols Codes allow complex messages and algorithms to be transmitted using a simple system of symbols or numbers Write and interpret on-off numerical code I can understand and follow an algorithm using symbols I can read and write information using on-off numerical code Declarative Knowledge (KNOW) Code, symbol, on-and-off code Data in computers is stored and transmitted using a form of on-off code called binary Procedural Knowledge (DO) Generating algorithms; representing algorithms; generating code; interpreting code 4 – Introduction to Robotics (4 lessons) We are learning to (WALT) What I’m looking for (WILF) This is because (TIB) Observe behaviour of an Ozobot to determine the meaning of colour codes I can relate changes in an Ozobot’s motor outputs (speed or direction) to colour codes Program an Ozobot using pen-andpaper colour codes I can use colour codes to control an Ozobot’s movement and complete a task Declarative Knowledge (KNOW) Inputs and outputs, sensor, motor, codes ASSESSMENT TYPE None TECHNIQUE CRITERIA 2 Unit Planner | Cleveland DSHS Ozobts are simple robots which allow us to see the outputs produced in response to simple coded programs Procedural Knowledge (DO) Interpret robot actions; define codes; use codes to control robot actions CLEVELAND STATE HIGH SCHOOL - UNIT PLAN Year 8 SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY Digital Technologies GLOBAL EDUCATION PILLAR N/A HABITS OF MIND Managing Impulsivity – students need to apply the steps of computational thinking to plan a solution before they create an algorithm Thinking about your Thinking – by thinking about computational thinking, we need to understand how our own thought processes work and can be communicated clearly EXTEND & REFINE KNOWLEDGE Abstracting – Students will use abstracting to match the decomposed parts of a complex problem to develop an algorithm or solution. USE KNOWLEDGE MEANINGFULLY N/A ACARA / CULLICULUM CODES ACTDIK023 TEACHING & LEARNING SEQUENCE TOPIC Computational Thinking SUB-TOPIC TIME ALLOCATION Components of Computational Thinking 2 lessons Applying Computational Thinking process (unplugged activity) 2 lessons Articulating steps (unplugged activity) 2 lessons Algorithms Introduction to 3 Computational Thinking PPT Plicker quiz Computational Thinking PPT The Game with No Instructions (prac) Computational Thinking Homework sheet Algorithms PPT Designing Algorithms (prac resources) Algorithms PPT Flowcharts Codes PRACS & RESOURCES 2 lessons Communicating in Code (unplugged activity) 2 lessons On-off Codes (unplugged activity) 2 lessons Introduction to Ozobots (unplugged 1 lesson Unit Planner | Cleveland DSHS Code PPT Grid Paper Programming sheet Grid Paper Programming Images sheet Grid Paper Programming homework sheet Code PPT On-off drawing sheet Ozobots and pens CLEVELAND STATE HIGH SCHOOL - UNIT PLAN Year 8 SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY Digital Technologies Robots activity) Bowling Challenge (unplugged activity) 4 Unit Planner | Cleveland DSHS 3 lessons Ozobot Sheet 1 Coding Challenge Ozobots, pens and code sheets Ozobot Sheet 2 Bowling Challenge Bowling pin sets