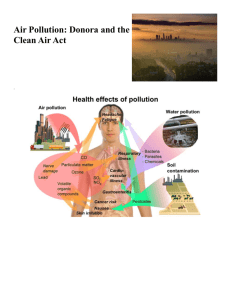
AIR POLLUTION EPISODES Air Pollution Episodes Meuse Valley-Belgium, 1930 • About 60 died (mostly elderly) • Sore throats, shortness of breath, cough, phlegm, nausea, vomiting • SO2, sulfur dioxide • H2O (water vapours) • SO4 , sulfuric acid mist • Cattle, birds and rats died • Got little news coverage Cont……. Fumigation of a valley floor caused by an inversion layer that restricts diffusion from a stack Donora, Pennsylvania—Oct. 1948 • Monongahela River Valley • Industrial town—steel mill, sulfuric acid plant, freight yard, etc. • Population—14,000 • Steep hills surrounding the valley • Oct 26—temperature inversion (warm air trapping cold air near the ground) • Stable air, fog, lasted 4.5 days • 20 died and 7000 ill Environs of Donora, Pennsylvania. Horseshoe curve of Monongahela River is surrounded by mountains. Railroad tracks are located on both sides of the river. Low-lying stretch of Monongahela valley between railroad and river is natural trap for pollutants. Poza Rico, Mexico 1950 • • • • • • • Single source– high sulfur crude oil Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) Flare went out Inversion in valley 22 sudden deaths, 320 hospitalized All ages affected Forerunner of Bhopal • • • • • • • December 1952 Great London Smog Cold front, Londoners burned soft coal Factories, power plants Temperature inversion 5 days of worst smog city had ever seen Public transportation stopped Indoor concerts had to be cancelled because no one could see the stage, etc. 4000 died London smog repeats • Repeated in 1956 and 1962 respectively • 1000 and 700 dead respectively London smog pictures Weekly death registered from diseases of the lungs and heart in the London Administrative County around the time of the severe fog in December, 1952. Total death in Greater London and air pollutants levels measured during the fog of December 1952 Seveso, Italy --Dioxin • July 10, 1976, north of Milan • A valve broke at the Industry Chimichee Meda Societa Azionaria chemical plant • Cloud of 2,3,7,8 tetrachlorodibenzopara-dioxin (TCDD) traveled southwest through Seveso toward Milan • Contaminant of herbicide • 200 people suffered skin diseases and liver problems Bhopal, India Dec. 3, 1984 • Union Carbide pesticide plant leak kills up to 2,000 with up to 350,000 injured and 100,000 with permanent disabilities • Methyl isocyanate (MIC)—used as an intermediary in manufacture of Sevin (Carbaryl) • CO + Cl = phosgene • Phosgene + methylamine = MIC • MIC—irritant to the lungs---edema, fluid (cause of death, corneal opacity (blindness) • MIC is heavier than air • 25 km2 area covered • MIC is water soluble gas • Leak was stopped after 40 minutes by hosing down the tank with cold water. • Disaster management plan was not in existence Hundreds Troubled by 'World Trade Center Cough‘ NYC fire fighters, school workers have 9/11 breathing problems, new studies say Objective Questions Q1. ___________ is the killing or collapse of tissues. Q2. ____________is the loss or reduction of the green plant pigment, chlorophyll. Q3. _________________is dropping of tree leaves. Q4. ________________is a downward curvature of the leaf due to higher rate of growth on the upper surface. Q5. Solid particles with sufficient size and high velocity causes _________________. Q6. _____________ is electrochemical process. Q7. Toxic gas ___________ was responsible for Bhopal gas tragedy in 1984. Q8. MIC is formed by combination of ____________ and ______________. Q9._____________ causes cracking of rubber. Q 10.__________________ is affected by pollution because of refineries. Theory Questions Q1. Define 1. Epinasty 2. Abscission 3. Chlorosis 4. Necrosis Q2. Write Effects of following pollutants on plants 1. Aldehydes 2. Ozone 3. Particulates 4. NO2 Q3. Write short notes on 1. Mechanisms of deterioration in polluted atmosphere. 2. London smog 3. Bhopal gas tragedy 4. Air pollution episodes Q4. Give tabular format w r t • Pollutant • characteristics • Sources • Health Effects • Welfare Effects for SO2, CO and O3