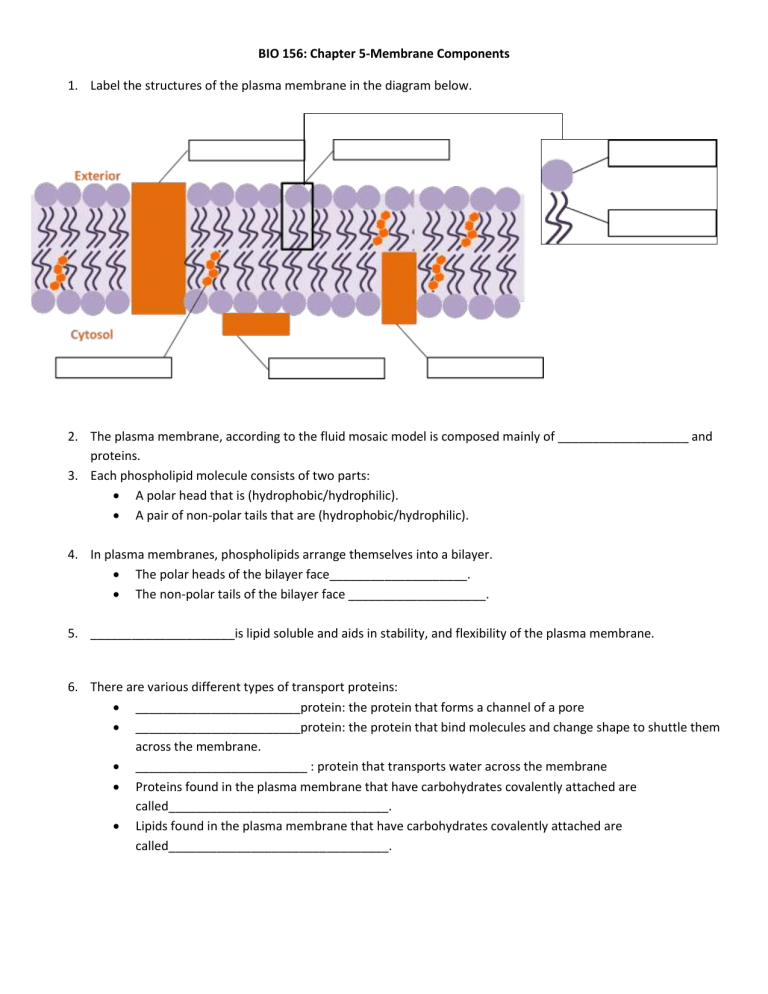
BIO 156: Chapter 5-Membrane Components 1. Label the structures of the plasma membrane in the diagram below. 2. The plasma membrane, according to the fluid mosaic model is composed mainly of ___________________ and proteins. 3. Each phospholipid molecule consists of two parts: A polar head that is (hydrophobic/hydrophilic). A pair of non-polar tails that are (hydrophobic/hydrophilic). 4. In plasma membranes, phospholipids arrange themselves into a bilayer. The polar heads of the bilayer face____________________. The non-polar tails of the bilayer face ____________________. 5. _____________________is lipid soluble and aids in stability, and flexibility of the plasma membrane. 6. There are various different types of transport proteins: ________________________protein: the protein that forms a channel of a pore ________________________protein: the protein that bind molecules and change shape to shuttle them across the membrane. _________________________ : protein that transports water across the membrane Proteins found in the plasma membrane that have carbohydrates covalently attached are called________________________________. Lipids found in the plasma membrane that have carbohydrates covalently attached are called________________________________. BIO 181: Chapter 7: Transport 1. Complete the table by checking the correct column for each statement: Statement Hypotonic Solution Isotonic Solution Hypertonic Solution High solute concentration inside the cell. Solute concentration is the same inside and outside the cell. Solute concentration is higher outside the cell Results in Osmosis 2. Plant cells have specific vocabulary terms depending on the tonicity of the solution. List those terms below. Hypotonic:____________________ Isotonic:____________________ Hypertonic:____________________ 3. Match the term with its correct description: a. ATP (cellular energy) b. Facilitated diffusion c. Endocytosis d. Passive transport e. f. g. h. Active transport Exocytosis Carrier protein Channel protein _____Transport protein that provides a tube-like opening in the plasma membrane through which particles can diffuse _____Is used during active transport but not passive transport _____Process by which a cell takes in material by forming a vacuole around it _____Particle movement from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration _____Process by which a cell expels waste from a vacuole _____A form of passive transport that uses transport proteins _____Particle movement from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration _____Transport protein that changes shapes when a particle binds with it Match the term with its correct description: a. Transport protein d. Passive transport b. Active transport e. Osmosis c. Diffusion f. Endocytosis _____The diffusion of water through a cell membrane g. Exocytosis h. Equilibrium _____The movement of substances through the cell membrane without the use of cellular energy _____Used to help substances enter or exit the cell membrane _____When energy is required to move materials through a cell membrane _____When the molecules of one substance are spread evenly throughout another substance to be balanced _____A vacuole membrane fuses (becomes a part of) the cell membrane and the contents are released inside the cell.
