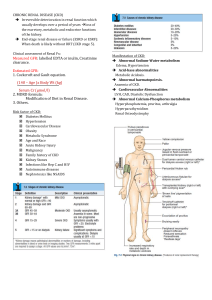
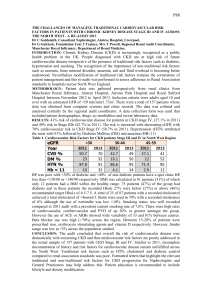
CHRONIC RENAL DISEASE (CKD) Irreversible deterioration in renal function which usually develops over a period of years loss of the excretory, metabolic and endocrine functions of the kidney. End-stage renal disease or failure (ESRD or ESRF): When death is likely without RRT (CKD stage 5). Clinical assessment of Renal Fx: Measured GFR: labelled EDTA or inulin, Creatinine clearance. Estimated GFR: 1. Cockcroft and Gault equation. (140 – Age )x Body Wt (kg) Serum Cr (µmol/l) 2. MDRD formula: Modification of Diet in Renal Disease. 3. Others. Risk factor of CKD: Diabetes Mellitus Hypertension Cardiovascular Disease Obesity Metabolic Syndrome Age and Race Acute Kidney Injury Malignancy Family history of CKD Kidney Stones Infections like Hep C and HIV Autoimmune diseases Nephrotoxics like NSAIDS Manifestation of CKD: Abnormal Sodium-Water metabolism Edema, Hypertension Acid-base abnormalities Metabolic Acidosis. Abnormal haematopoiesis. Anaemia of CKD. Cardiovascular Abnormalities LVH, CAD, Diastolic Dysfunction Abnormal Calcium-Phosphorus metabolism Hyperphosphatemia, pruritus, arthralgia Hyperparathyroidism Renal Osteodystrophy Causes of anemia in CKD: Why atherosclerosis is very common in CKD?? Investigation: refer AKI investigation Complication: Cardiovascular Cx: IHD, Pericarditis, HTN, LVH, Vascular calcification. Anemia. Renal bone disease. Fluid overload. Hyper K, acidosis. Pathogenesis of renal osteodystrophy: Referral Criteria of CKD pt to a nephrologist: 1. Age < 40 years 2. Stage 4 CKD or worse (eGFR < 30 mL/min/1.73 m2) 3. Rapid deterioration in renal function. (Fall in eGFR > 5 ml/min/1.73 m2/yr or > 10 mL/min/1.73 m2 over 5 yrs) 4. Significant proteinuria (PCR > 100 mg/mmol or ACR > 70 mg/mmol) 5. Significant haematuria. Aims of management in CKD: to prevent or slow further renal damage. to limit the adverse physiological effects of renal impairment on the skeleton and on haematopoiesis. to treat risk factors for cardiovascular disease. to prepare for RRT. Management: Diagnostic work up to decide underlying etiology Treatment of Hypertension and Dyslipidemia (atorvastatin, statin) Treatment of Anemia(recombinant human erythropoietin) Treatment of Hyperphosphatemia (CaCO3, aluminium hydroxide, carbonate, sevelamer) Avoidance of Dehydration & Nephrotoxic agents Proper Dosing of Drugs Preparation for Renal Replacement Therapy