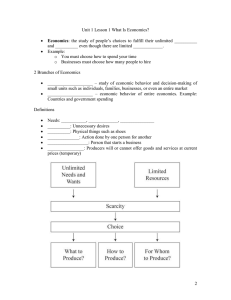
Kamla Nehru Institute of Technology, Sultanpur Engineering & Managerial Economics Professor: Respectfully Mr. Pradeep Kumar Sir, MBA, M.Phil Assignment submission by Akshay Kumar Rahul Roll NO: 16503 Mechanical Engineering Semester 5th 2018-2019 ASSIGNMENT OF ENGINEERING & MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS (B.Tech. Sem. V) UNIT 1 1. Explain the definition of economics. Answer-: The term economics has its root from the Greek word Oikonomia . Adam Smith called Fathr of e]\Economics proposed economics as All money is a matter of belief. For the definition many contributors form the basis of the definition as Economics is a science which studies human behaviour as a relationship between ends and scarce means which have alternative uses. Economics is the science of analyzing the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. In other words, what choices people make and how and why they make them when making purchases. Economic analysis often progresses through deductive processes, much like mathematical logic, where the implications of specific human activities are considered in a "means-ends" framework. Various contributors to the definition are● James Steuart ● Adam Smith ● J.B. Say ● William Stanley Jevons ● Alfred Marshall ● Lionel Robbins 2. Is economics science or art? Give your views and reasons for it. Answer- Economics is a science (whether positive or normative) in its methodology and an art in its application, because it has theoretical as well as practical aspects.Economics is both science and art. #Economics is a sciece because: Many laws of economics are based on assumption a person choses the best available option this hints towards economics being art. Economics has laws like science e.g., law of demand : As price increase demand decreases. It reflects human buying behavior. Science is a study based on observation and experiment. As science economics answers questions related to micro or macro economic units based on data and economics laws. Which crop a farmer should produce economics answers. How to increase crop produce other science answers. . #Economics is an art because: Art means physical & mental ability by which an activity may be performed in a best way so economics is an art because formation of economics policy is a measure function of art. Economists suggest policies along with their application and procedures to solve the economic problem. 3. Explain the nature of economics as a positive science and normative science. Answer: In 1906, Irving Fisher argued that economics is no less scientific than physics or biology. Economics does have both theories and facts. When supply greatly exceeds demand, prices usually drop. When taxes become crushing, personal incentive declines. When interest rates drop, home sales increase and retiree's income drops. It's wrong to think of it as not a serious field of study because it doesn't produce exact results in every situation. #Economics is a positive science because: • Firstly, economists collect the facts. • Secondly, they analyze them and derive result. • Thirdly, they determine the relationship between facts and results. • Finally, they give a title to the bosomed relationship #Economics is normative science because: • Economists points out different economic problems. • They analyse them in the light of statistics or facts and figures. • Finally, they advise policies, laws, theories to solve the problems 4. Differentiate between micro- economics and macro-economics. Answer: The main differences are: #DefinitionMacroeconomics is a branch of economics dealing with the performance, structure, behavior, and decision-making of an economy as a whole. Microeconomics is the branch of economy which is concerned with the behavior of individual entities such as market, firms and households. #FoundationThe foundation of macroeconomics is microeconomics. Microeconomics consists of individual entities. #ideologyOutput and income, unemployment, inflation and deflation. Preference relations, supply and demand, opportunity cost. #ApplicationsUsed to determine an economy's overall health, standard of living, and needs for improvement. Used to determine methods of improvement for individual business entities. #Time NatureMicroeconomics is a static analysis. It does not take into account the time element. macroeconomics is a dynamic analysis. It is based on time-lags, the rates of change and past and expected values of the variables. 5. Define managerial economics and discuss its scope. Answer: Managerial Economics is concerned with the economic decisions of business managers. It is a branch of Economics which uses microeconomic analysis to specific business decisions (i.e. Economics applied in business decision-making). Managerial Economics may be viewed as Economics applied to problem solving at the level of the firm, company, organisation . The problems of course relate to choices and allocation of resources, which are basically economic in nature and are faced by managers all the time. It is that branch of Economics, which serves as a link between abstract theory and managerial practice Example: In the movie “Batman Begins”, the hierarchical owner BRUCE WAYNE o f Wayne Enterprises, was abandoned due personal reasons. After learning management and martial arts. He decided to fight against the corruption ridden Gotham City despite of having no friend and supporters. He has having very decent resources and ideas and a few believable people. But he manages to all level of superiority and good beliefs and in the end he wins making Gotham a happy place. #Scope of Mangerial economics: ● ● ● ● ● Theory of demand Theory of productiok Theory of exchange or price Theory of profit Theory of capital and investment ● Demand analysis and forecasting : A firm's performance and profitability depends upon accurate estimates of demand. The firm will prepare its production schedule on the basis of demand forecast. Demand analysis helps to identify the factors influencing the demand for a firm's product and thus helps a manager in business planning. ● Cost and production analysis: . ● Recognizing the factors, which are causing cost to firm. ● Suggests cost should be reduced for making good profits. ● Production analysis deals with, Minimum cost should be spend on raw materials and maximum production should be obtained ● Pricing decisions, policies and practices: The topics covered under this area are: price determination in various market forms such as perfect market, monopoly, oligopoly, etc., pricing methods such as differential pricing and product-line pricing, and price forecasting. ● Profit management l ike nature and measurement of profit, profit policies, and techniques of profit planning ● Capital Management ● Competition 6. “Managerial economics is applied micro economics”. Elucidate. Answer: Since managerial economics is basically concerned with economic decision making within the firm, it is more close to microeconomics than to macroeconomics. Some writers have ventured to call it applied microeconomics or price theory in the service of business executives. Managerial economics is slightly broader than microeconomic theory. It also necessitates the application and integration of practices, principles, and techniques from the areas of accounting, finance, marketing, production, personnel, and other functions or disciplines associated with economics. Because the survival, growth and prosperity of the firm are often linked to what is happening to the gross national product, the general level of employment, and the general price level, there is a need to relate the economics of the firm with the economic system. 7. What do you understand by the term engineering and how it is dependent on managerial economics to achieve objectives? Answer: Engineering: Engineering is a scientific field and job that involves taking our scientific understanding, concepts of the natural world and using it to invent, design, and build things to solve problems and achieve practical goals for the betterment of humans and surroundings. It helps in the following domains or objectives of managerial economics: ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● Value Analysis Linear Programming Critical Path Economy Interest and Money - Time Relationships Depreciation and Valuation Capital Budgeting Risk, Uncertainty, and Sensitivity Analysis Fixed, Incremental, and Sunk Costs Replacement Studies Minimum Cost Formulas Various Economic Studies in relation to both Public and Private Ventures It has wide scope in manufacturing, construction, mining and other engineering industries. Examples of economic application are as follows: – Selection of location and site for a new plant. – Production planning and control. – Selection of equipment and their replacement analysis. – Selection of a material handling system. Better decision making on the part of engineers. Managerial economics is profounded in the engineering economics as folows: 1. Engineering is closely aligned with Conventional Micro-Economics. 2. Engineering is devoted to the problem solving and decision making at the operations level. 3. Engineering can lead to sub-optimisation of conditions in which a solution satisfies tactical objectives at the expense of strategic effectiveness. 4. Engineering is useful to identify alternative uses of limited resources and to select the preferred course of action. 5. Engineering Economics is pragmatic in nature. It removes complicated abstract issues of economic theory. 6. Engineering Economics mainly uses the body of economic concepts and principles. 7. Engineering Economics integrates economic theory with engineering practice.