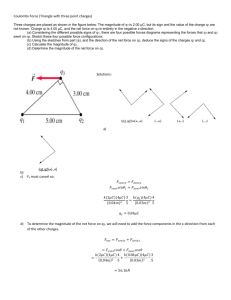
Ch. 16 and 17 Review Problems NAME_____________________________ 1) Is it possible for two negative charges to attract each other? A) Yes, they always attract. B) Yes, they will attract if they are close enough. C) Yes, they will attract if one carries a larger charge than the other. D) No, they will never attract. 2) A proton carries a A) positive charge. B) neutral charge. C) negative charge. D) variable charge. 3) A negatively charged rod is brought near one end of an uncharged metal bar. The end of the metal bar farthest from the charged rod will be charged A) positive. B) negative. C) neutral. D) none of the given answers 4) Two charged objects are separated by a distance d. The first charge is larger in magnitude than the second charge. A) The first charge exerts a larger force on the second charge. B) The second charge exerts a larger force on the first charge. C) The charges exert forces on each other equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. D) The charges exert forces on each other equal in magnitude and pointing in the same direction. 5) For an electron moving in a direction opposite to the electric field A) its potential energy increases and its electric potential decreases. B) its potential energy decreases and its electric potential increases. C) its potential energy increases and its electric potential increases. D) its potential energy decreases and its electric potential decreases. 6) The electron-volt is a unit of A) voltage. B) current. C) power. D) energy. 7) A dielectric material such as paper is placed between the plates of a capacitor. What happens to the capacitance? A) no change B) becomes larger C) becomes smaller D) becomes infinite 8) Electric dipoles always consist of two charges that are A) equal in magnitude; opposite in sign. B) equal in magnitude; both are negative. C) equal in magnitude; both are positive. D) unequal in magnitude; opposite in sign. 9) A piece of plastic has a net charge of +2.00 μC. How many more protons than electrons does this piece of plastic have? A) 1.25 × 1013 B) 1.25 × 1019 C) 2.50 × 1013 D) 2.50 × 1019 10) Two 1.0-C charges have a force between them of 1.0 N. How far apart are they? A) 95 km B) 9.5 m C) 4.0 m D) 4.0 mm 11) What are the magnitude and direction of the electric field at a distance of 1.50 m from a 50.0-nC charge? A) 20 N/C away from the charge B) 20 N/C toward the charge C) 200 N/C away from the charge D) 200 N/C toward the charge 12) Two point charges of +3.0 μC and -7.0 μC are placed at x = 0 and x = 0.20 m. What is the magnitude of the electric field at the point midway between them? A) 1.8 × 106 N/C B) 3.6 × 106 N/C C) 4.5 × 106 N/C D) 9.0 × 106 N/C 13) A Styrofoam ball of mass 0.120 g is placed in an electric field of 6000 N/C pointing downward. What charge must be placed on the ball for it to be suspended? A) -16.0 nC B) -57.2 nC C) -125 nC D) -196 nC 14) A copper penny has a mass of 3.0 g. A total of 4.0 × 10 12 electrons are transferred from one neutral penny to another. If the electrostatic force of attraction between the pennies is equal to the weight of a penny, what is the separation between them? A) 31 cm B) 33 cm C) 35 cm D) 37 cm 15) Three identical charges of 3.0 μC are placed at the vertices of an equilateral triangle which measures 30 cm on a side. What is the magnitude of the electrostatic force which acts on any one of the charges? A) 1.6 N B) 1.8 N C) 2.0 N D) 2.2 N 16) The force between a 30-μC charge and a -90-μC charge is 1.8 N. How far apart are they? A) 1.9 m B) 2.3 m C) 3.7 m 17) It takes 50 J of energy to move 10 C of charge from point A to point B. What is the potential difference between points A and B? A) 500 V B) 50 V C) 5.0 V D) 0.50 V 18) A proton, initially at rest, is accelerated through an electric potential difference of 500 V. What is the speed of the proton? A) 2.2 × 105 m/s B) 3.1 × 105 m/s C) 9.6 × 1010 m/s D) zero 19) A 6.0-V battery maintains the electrical potential difference between two parallel metal plates separated by 1.0 mm. What is the electric field between the plates? A) 6.0 V/m B) 600 V/m C) 6000 V/m D) zero 20) Consider a uniform electric field of 50 N/C directed toward the east. If the voltage measured relative to ground at a given point is 80 V, what is the voltage at a point 1.0 m directly west of that point? A) 30 V B) 50 V C) 80 V D) 130 V 21) Two parallel plates, separated by 0.20 m, are connected to a 12-V battery. An electron released from rest at a location 0.10 m from the negative plate. When the electron arrives at a distance 0.050 m from the positive plate, what is the speed of the electron? A) 5.0 × 105 m/s B) 1.0 × 106 m/s C) 5.0 × 106 m/s D) 1.0 × 107 m/s 22) What charge appears on the plates of a 2.0-μF capacitor when it is charged to 100 V? A) 50 μC B) 100 μC C) 150 μC D) 200 μC 23) A parallel-plate capacitor is filled with air, and the plates are separated by 0.050 mm. If the capacitance is 17.3 pF, what is the plate area? A) 4.9 × 19-5 m2 B) 9.8 × 10-5 m2 C) 2.4 × 10-4 m2 24) A charge of 60 μC is placed on a 15 μF capacitor. How much energy is stored in the capacitor? A) 120 J B) 240 μJ C) 120 μJ