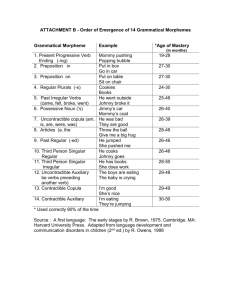
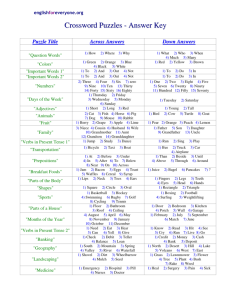
Brown’s Stages of Syntactic Development • We will be referring back to this chart as we start to look at more complex sentences. For now, let’s just practice reading the chart by age to see what we can expect at each stage as far as syntactic development goes. Stage: Early I • • • • • • • • • MLU=1 to 1.5 Age= 19-22 months No real morphemes used No is only way to signal negation No syntactic way of showing question formation; rising intonation is used instead Can say What _____? NP is mostly just a single N VP is mostly just a single V, possibly ending in -ing. No complex sentences used Stage: Late I-Early II • • • • • • • • • MLU=1.5 to 2 Age= 23-26 months No real morphemes used No or Not + noun or verb=negation Rising intonation for Questions Can say What _____? Where_____? NP is mostly just a single N VP is mostly just a single V, possibly ending in -ing. No complex sentences used Stage:II • • • • • • • • • MLU= 2 to 2.5 Age= 27-30 months Morphemes used are: -ing verbs, plural -s, preposition “in” No or Not + noun or verb=negation Rising intonation for Questions Can say What _____? Where_____? NP is mostly just a single N VP is mostly just a single V, possibly ending in -ing. No complex sentences used; constructions with gonna, gotta, wanna and hafta begin Stage:III • MLU= 2.5 to 2.99 • Age= 31-34 months • Morphemes used are: -ing verbs, plural -s, preposition “in”, preposition “on”, possessive -s • NP + negative word + VP • Rising intonation for Questions • Can say What /Where/Who/How_____? • NP is demonstratives and articles + adjectives + N • VP is the verb, with some past tense -ed, present tense -ing, and helping verbs can, will and be. • Complexities begin with the object NP Stage: Early IV • MLU=3.0 to 3.49 • Age= 35-38 months • Morphemes used are: -ing verbs, plural -s, preposition “in”, preposition “on”, possessive -s • NP + auxiliary word + negative word + VP • Subject-Verb Inversion for Yes-No Questions • Can say What /Where/Who/How/When_____? • NP is demonstratives and articles + adjectives + N • VP is the verb, with some past tense -ed, present tense -ing, and helping verbs can, will and be. • Simple infinitives, simple wh relative clauses, conjoined sentences with “and” Stage: Late IV-Early V • • • • • • • • • MLU=3.5 to 3.99 Age= 39-42 months Morphemes used are: -ing verbs, plural -s, preposition “in”, preposition “on”, possessive -s NP + auxiliary word + negative word + VP Subject-Verb Inversion for Yes-No Questions Can say What /Where/Who/How/When_____? NP elaboration looks like the adult form. Knows that a pronoun or a noun/elaborated NP must be used in each sentence VP is the verb, regular use of past tense -ed, and helping verbs can, will, could, would, should, must, might, be +ing progressive, Multiple embeddings in one sentence, conjoined and embedded clauses in same sentence. Stage: Late V • • • • • • • • • MLU=4.0 to 4.49 Age= 43-46 months Morphemes used are: -ing verbs, plural -s, preposition “in”, preposition “on”, possessive -s, regular past tense -ed, irregular -ed, regular 3rd person singular s, definite and indefinite articles, contractible copulas Negative is in the auxiliary and can now be contracted to “n’t” Subject-Verb Inversion for Yes-No Questions Can say What /Where/Who/How/When_____? NP elaboration looks like the adult form. Knows that a pronoun or a noun/elaborated NP must be used in each sentence. May struggle with number agreement. VP is the verb, regular use of past tense -ed, and helping verbs can, will, could, would, should, must, might, be +ing progressive, 3rd person singular in present tense -s Relative clauses appear, infinitive clauses with different subjects, If-then clauses. Stage: Late V+ and V++ • • • • • • • • • MLU=4.5 to 5.49 Age= 47-66 months Morphemes used are: -ing verbs, plural -s, preposition “in”, preposition “on”, possessive -s, regular past tense -ed, irregular -ed, regular 3rd person singular -s, definite and indefinite articles, contractible copulas, contractible aux, uncontractible cop, uncontractible aux, irregular 3rd person Negative is in the auxiliary and can now be contracted to “n’t” Subject-Verb Inversion for Yes-No Questions Can say What /Where/Who/How/When_____? NP elaboration looks like the adult form. Knows that a pronoun or a noun/elaborated NP must be used in each sentence. May struggle with number agreement. VP is the verb, regular use of past tense -ed, and helping verbs can, will, could, would, should, must, might, be +ing progressive, 3rd person singular in present tense -s, pst tense of be, some use of the perfect tense Relative clauses appear, infinitive clauses with different subjects, If-then clauses, gerunds, wh-infinitves, unmarked infinitives, conjunctions like “because, when and so” Verbs • There is a lot of verb terminology on the Brown’s Stages chart. • Look for detailed explanation of terms like auxiliary, copula, contractible and uncontractible in the next chapter on verbs. • The full charts are shown on the next two slides. Brown’s Stages, Part 1 Brown’s Stages, Part 2 Sample Language Analysis • On the next slide you will see a language sample from a child who is 4 years old. You should notice several things from this sample: • She is age appropriate for plural -s, “in”, possessive -s, and contractible copular. • She is delayed for regular past tense -ed, irregular past tense, articles • This sample needs more data before we can make any judgment on -ing, “on”, regular 3rd person, contractible aux, uncontractible cop, uncontractible aux, and irregular 3rd person. We would never want to make a definitive statemant about language development with no, 1 or even 2 samples. That is too low to know for sure what the child is doing. Grammatical Morhpeme Analysis Sheet Grammatical Morpheme Analysis • I use this sheet frequently when I want to know how advanced morpheme development is for a particular child. First I collect a free language sample of 100+ sentences. Then I look for morphemes in each sentence. • The numbers on the sheet refer to the sentence in the language sample. • If the child should have used the morpheme, the sentence number goes under Obligatory Context. That means an adult would use a morpheme there. • Then we check to see if the child really did use the morpheme. If he/she did, the sentence number goes under the Use column. If he/she did not, then a dash goes under Use. • The percentage is calculated from the number in the Use column divided by the number in the Obligatory Context column.