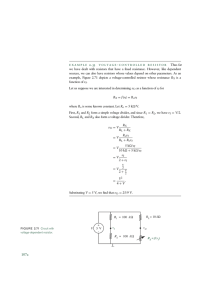
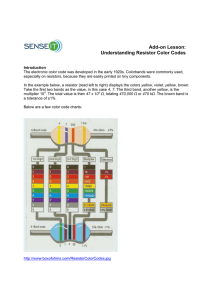
Supplementary Note 1A Basic Electronic Component: Resistor Resistor • A device to limit current in a circuit. • Unit: Ohm () • Ohm’s Law: 1 = 1V/1A 1A 1V 1 V-I Relationship • Recall Ohm’s Law 𝑉𝑅 = 𝐼𝑅 𝑅 V/V Slope = V/I = R I V I/A Assuming V is fixed, The current 𝐼 is unchanged. Power Dissipation • When current goes through a resistor, power dissipates at the resistor in a form of heat. • Calculation of Power 𝑉𝑅2 𝑃 = 𝑉𝑅 𝐼𝑅 = = 𝐼𝑅2 𝑅 𝑅 The unit of Power is Watt (W) Types of Resistors • Wirewound Higher power rating • Film (metal / metal oxide/ carbon) Types of Resistors (Cont’) • Surface Mount Resistor (Chip Resistor) – Very small – Limited power rating: 1/8W – 1/4W – Thin film / thick film process Resistance Value • Color code (usually for carbon/metal resistors) https://www.allaboutcircuits.com/tools/resistor-color-code-calculator Resistance Value • 3-digit or 4 digit (usually for surface mounted resistor) Available Resistors in Market • Not all resistance values are available • Use the closest (if design is allowed) Tolerance • Tolerance: All manufacturing processes have some degree of variations, which affect the accurate of the resistance. • Tolerance: 20%, 10%, 5%, 2%, 1%, 0.5%, 0.25%, 0.1%, 0.05%, 0.02% differ from the nominal value • Eg. A resistor with 10K and 10% tolerance, its value can be from 9K to 1.1K Variable Resistor (Potentiometer) • The two ends are fixed • No. of turns determines the precision of VR, eg. 10 turns, 20 turns