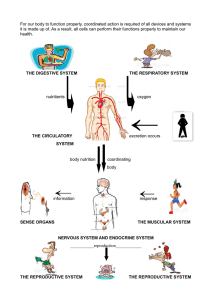
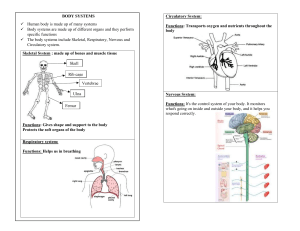
INTRODUCTION TO BODY SYSTEMS WHAT DO THE BODY SYSTEMS DO? Humans and other organisms need to get energy. Body systems, also called organ systems, help organisms to do all of these things. They also coordinate all the functions of a body. There are eleven body systems – 1. The muscular system: allows movement of body parts. Consist of skeletal, smooth and cardiac muscles. There are approximately 640 skeletal muscles within a typical human. BODY SYSTEMS 2. Skeletal system – is made up bones, ligaments, and cartilage. It supports the body and protects important organs. It also makes blood cells. The human skeleton has 206 bones. BODY SYSTEMS 3. Respiratory system – gathers oxygen from the environment and gets rid of carbon dioxide form the body. The primary organs of the respiratory system are lungs, which carry out this exchange of gases as we breathe. BODY SYSTEMS 4. Cardiovascular system – moves blood through the body. The heart is the pump for this system. Includes the veins, arteries, capillaries, heart, and blood. 5. Male reproductive system – produces sperm and delivers it to the female reproductive system. Female reproductive system – produces eggs and nourishes a developing fetus. BODY SYSTEMS 6. Lymphatic system – returns leaked fluid back to the blood. The primary function of the lymphatic system is to transport lymph, a fluid containing infectionfighting white blood cells, throughout the body. BODY SYSTEMS The spleen plays multiple supporting roles in the body. It acts as a filter for blood as part of the immune system. Old red blood cells are recycled in the spleen, and platelets and white blood cells are stored there. BODY SYSTEMS 7. Endocrine system – makes chemical messages. They also influence growth and development. Is made up of glands that produce and secrete hormones, chemical substances produced in the body that regulate the activity of cells or organs. BODY SYSTEMS 8. Integumentary system – is the protective covering of the body. It includes the skin, hair, and nails. The skin acts as a barrier that protects the body from infection. BODY SYSTEM 9. Excretory system – gets rid of the body’s wastes. The urinary system removes wastes from blood. The skin, lungs, and digestive system also remove wastes from the body. BODY SYSTEM 10. Digestive system – breaks down food into nutrients that can be used by the body. The stomach breaks down food into tiny pieces. Digestion begins in the mouth with chewing and ends in the small intestine. The gallbladder then stores the extra bile the liver makes. It releases bile when you eat a meal with fats that need to be digested. BODY SYSTEM 11. Nervous system – collects information and responds to it by sending electrical messages. The brain is the center of the nervous system. The nervous system of vertebrates (including humans) is divided into the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The (CNS) is the major division, and consists of the brain and the spinal cord. WHAT ARE THE BASIC NEEDS OF ALL CELLS? Cells need to get enough oxygen to carry out life processes and to have their wastes taken away. They also need an energy/food supply. HOW ARE STRUCTURES AND FUNCTION LINKED? oThe shapes and sizes of cells are related to their function. oFor example, sperm cells have long tails that are used to move. oNerve cells are long and thin to send messages long distances. oSkin is made up of different cells in many layer. The epidermis is the outer layer of skin. The dermis is the second layer of skin, and contains glands, hair follicles, and blood vessels. WHAT IS HOMEOSTASIS? oCells need certain conditions to work properly. oThey need food and oxygen and to have their wastes taken away. oIf body conditions were to change too much, cells would not be able to do their jobs. oHomeostasis – is the maintenance of a constant internal environment when outside conditions change. WHAT CAN GO WRONG WITH HOMEOSTASIS? oIf one body system do not work properly, other body systems can be affected. oFor example, body cells that do not get enough or nutrients cannot work properly. oThe presence of toxins or pathogens also can disrupt homeostasis. oToxins can prevent cell from carrying out life processes and pathogens can break down cells. COMPLETE THE FOLLOWING TABLE: Alcoholism is a disease that disrupts homeostasis. Below are three body systems that are affected by alcohol. The effects on the nervous system are filled in. In the space provided, make a claim about what might happen when the function of the two remaining systems is affected. Body systems affected What are the effects? Nervous system Disrupts proper functioning of the brain. The brain cannot respond properly to internal or external messages. Digestive system The liver and other organs of the digestive system can be harmed by alcohol, which will affect the ability of the digestive system to digest food and remove toxins. Reproductive system Affecting the reproductive system could harm the ability to produce healthy sex cells, or in the case of a woman, develop and nourish a healthy fetus or baby.