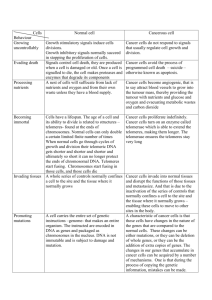
Cell Division Going Wrong: Cancer When cells divide, their DNA is almost always duplicated errorfree. The genetic information in the daughter cells is identical to the parent cell. Sometimes random changes occur in the cell’s DNA. These changes are called mutations. Mutations may result in the death of the cell or allow it to survive and continue to grow and divide. Cancerous cells are formed when there is a mutation in the portion of the DNA controlling the cell cycle. This change prevents the cell from staying in interphase for the normal period of time. When the normal checkpoints fail, the cell and its daughter cells will divide uncontrollably. When cells grow and divide out of control, they cause a group of diseases called cancer. Telomerase The telomeres (ends of the chromosomes) in most cells shorten after each division, eventually causing cell death Shortening telomeres also cause aging Cancer cells have unique features that make them "immortal" They have an enzyme called telomerase, which extends the cancer cell's life span. This is a major reason that cancer cells can accumulate over time creating tumors. Causes of Cancer Carcinogens o Tobacco smoke o Radiation (X-rays, UV rays) o Viruses such as HPV and hepatitis B o Certain chemicals in plastics o Many organic solvents o Hereditary links (breast, colon) - it is very difficult to predict who will develop cancer Cancer Screening Breast / testicular self-examinations Regular Pap tests PSA tests Blood tests ABCD for moles Reducing Cancer Risks – Lifestyle Choices Diagnosing Cancer Discomfort Swelling Tiredness Loss of weight Endoscopy – colon X-ray – lung / breast Ultrasound –heart / liver CT scanning MRI Biopsies Cancer Treatments Surgery Chemotherapy Radiation (ionizing) Biophotonics – beams of light to detect / treat