Student practical B1.4.2
Name ..................................................................... Class ................. Date .....................
Testing for starch
Specification references:
B1.4d Investigating photosynthesis
WS1.1h, WS1.2c, WS1.3a, WS1.3e
Aims
You should be able to follow a method and understand the justification for the steps in that method. You should work safely and have an appreciation of the risk factors.
Learning outcomes
After completing this activity, you should be able to:
use a given method to carry out the starch test on a leaf
describe the ways plants makes use of glucose.
Background
Biologists need to be able to test for a range of biological molecules. It is possible to test leaves for starch. If photosynthesis has occurred, sugar will be produced in leaves and converted to starch.
Safety
Ethanol (alcohol) is highly flammable and harmful. Ensure that all naked flames are extinguished before using it.
Container for waste ethanol – NOT to be disposed of in sink
Iodine will stain hands and clothing.
Use of glassware – beware of breakages.
Wear eye protection.
Equipment and materials
tripod
gauze
Bunsen burner
heatproof mat
250 cm³ beaker
boiling tube
forceps
glass rod
© Oxford University Press 2016: www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original.
1
Student practical B1.4.2
Name ..................................................................... Class ................. Date .....................
ethanol
eye protection
white tile
iodine solution.
Method
1 De-starch the leaves of the plant before the experiment by leaving in a dark cupboard for 24 hours.
2 Set up the leaves by partially covering them as shown below, then expose the plant to sunlight for 3 days.
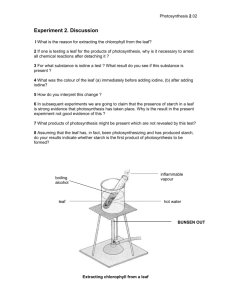
3 Boil 150 cm 3 of water in a beaker or collect boiling water from a kettle.
4 Place the leaf to be tested in the water for 2 minutes: this kills the leaf, stopping further photosynthesis.
© Oxford University Press 2016: www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original.
2
Student practical B1.4.2
Name ..................................................................... Class ................. Date .....................
5 Remove the leaf from the water and place in a boiling tube.
6 Turn off the Bunsen burner .
7 Add ethanol to the boiling tube to cover the leaf. Your teacher may choose to handle the alcohol/ethanol here.
8 Place the boiling tube in the hot water for 10 –15 minutes; the ethanol should boil and remove the chlorophyll from the leaf.
© Oxford University Press 2016: www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original.
3
Student practical B1.4.2
Name ..................................................................... Class ................. Date .....................
9 Now remove the leaf from the ethanol.
10 Dip the leaf into the hot water to soften the leaf (see diagram at point 4 above).
11 Spread the leaf out on a white tile.
12 Cover the leaf with iodine solution.
13 Areas that turn black contain starch, whereas areas of the leaf that stay brown do not contain starch.
Results
Draw a diagram of your leaf.
Questions
1 Name the zone of your leaf that produced starch.
( 1 mark )
2 Name the process that produced the starch.
( 1 mark )
3 Some of the glucose produced in photosynthesis is converted to starch. a Name three other products that glucose can be converted into in a plant. b Explain why the plant stores glucose as starch.
( 3 marks )
( 2 marks )
© Oxford University Press 2016: www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original.
4
Student practical B1.4.2
Name ..................................................................... Class ................. Date .....................
4 Describe one step taken in the experiment as a safety precaution.
( 1 mark )
5 Explain why the plant needed to be de-starched prior to the experiment being set up.
( 2 marks )
Student follow-up
There are a number of complex steps in the method for testing a leaf for starch.
1 Explain why each of the following steps is carried out: a boiling the leaf in water b boiling the leaf in ethanol.
2 Explain why you can’t simply add iodine to an untreated leaf to test for starch.
( 1 mark )
( 1 mark )
( 2 marks )
© Oxford University Press 2016: www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original.
5