DEVELOPMENT OF A NEW PRODUCT FOR THE OPTIMIZATION OF THE GEOTECHNIC CHARACTERISTICS OF THE BASE COURSE IN THE ROADS CONSTRUCTION IN SOUDANO-SAHALIAN AREA: CASE STUDY OF THE MAROUA AGGLOMERATION
advertisement

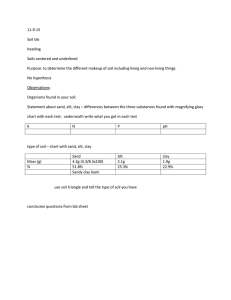
International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 10, Issue 04, April 2019, pp. 1192–1202, Article ID: IJCIET_10_04_125 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?JType=IJCIET&VType=10&IType=4 ISSN Print: 0976-6308 and ISSN Online: 0976-6316 © IAEME Publication Scopus Indexed DEVELOPMENT OF A NEW PRODUCT FOR THE OPTIMIZATION OF THE GEOTECHNIC CHARACTERISTICS OF THE BASE COURSE IN THE ROADS CONSTRUCTION IN SOUDANOSAHALIAN AREA: CASE STUDY OF THE MAROUA AGGLOMERATION Flavien Guetsa Kamanou* Ecole Polytechnique, University of Yaoundé I, PO Box 8390 Yaoundé Cameroon LE COMPETING BET, Centre A. EINSTEIN. PO Box: 7214 Yaoundé. Denis Ntamack, Thomas Tamo Tatietse Ecole Polytechnique, University of Yaoundé I, PO Box 8390 Yaoundé Cameroon *Corresponding Author ABSTRACT Road infrastructure is expensive for developing countries. Indeed, on the one hand the outdated implementation techniques, and the unavailability of standards materials such as crushed gravels in some project areas, attest to and accentuate this difficulty. The northern part of Cameroon is part of the Sudano-Sahelian area of the African continent. Which is characterized by the scarcity and remoteness of rocky deposits as well as the delicacy of extraction conditions, illustrative of areas where road construction generates the most prohibitive expenditures. The work carried out, which is based on the mixture techniques commonly used in soil concretes, aims to implement locally in abundance available materials, by associating them a minimum fraction of hydraulic binders, in order to obtain a new constituent for the base course of road construction, according to the universal standards. After a comprehensive documentary compilation and experimental approach in the laboratory with samples taken in the extreme north of Cameroon, the results are convincing: the constituent of the mixture comprising 70% of sand, 25% of soil and 5% of hydraulic binder, meets the eligibility criteria prescribed in the implementation of the base course in road construction, in particular the bearing index or stability (CBR) and the hardness of skeleton’s (Rc, Rc ‘) product. This mixture would be recommended for road construction in the Sudano-Sahelian areas, alternating with crushed gravels which is scarce. Its implementation according to the prescribed optimal conditions, generally reduce considerably the expenses for an efficient development of road network in the Sudano-Sahelian area, and precisely in the north of Cameroon . http://www.iaeme.com/IJCIET/index.asp 1192 editor@iaeme.com Development of a New Product for the Optimization of the Geotechnic Characteristics of the Base Course in the Roads Construction in Soudano-Sahalian Area: Case Study of the Maroua Agglomeration Key words: Aggregates, soil concrete, skeleton, stability, crushed gravels, SudanoSahelian zone, and road construction. Cite this Article: Flavien GUETSA KAMANOU, Denis NTAMACK, Thomas TAMO TATIETSE, Development of a New Product for the Optimization of the Geotechnic Characteristics of the Base Course in the Roads Construction in SoudanoSahalian Area: Case Study of the Maroua Agglomeration, International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology 10(4), 2019, pp. 1192–1202. http://www.iaeme.com/IJCIET/issues.asp?JType=IJCIET&VType=10&IType=4 1. INTRODUCTION Road construction is very important in country’s development plans. If the mastering of concepts and implementation of road construction programs is widespread in industrialized countries, it is not the case of developing countries [1], where the adoption of stereotyped model quite often confront to many difficulties among which the scarcity of usual materials on the site, the problems of implementation and the insufficiencies material, human and financial resources. In this universe of concerns, where large investments are made often to achieve poor results, it is necessary to multiply processes likely to reverse the trend, both the absolute necessity of roads networks and more extensive roads in the cities and the countryside arises acutely [2]. The subject treated finds its material relevance for the materials taken of experimentation from a specific area, with the Sudano-Sahelian characteristics domain, and their implementation which is conform within the normative context, from which important savings in time and resources could be released. The region of the far north of Cameroon since it is the case study, is a striking illustration of this constraining environment from an infrastructural point of view, but conducive to the experimentation of innovative techniques of improvement of the construction and maintenance of road. The objective in this Sahelian part of the continent remains to provide constructive solutions adapted to the road network, prioritizing the materials it abounds in affluence, in order to substantially reduce the costs of achieving the infrastructure, while remaining in conformity with the requirements, and respond effectively to the priority needs of the communities that reside there [3]. Road construction emphasizes, in addition to the sub base course and the surface course, on the base course which forms the essential structure, and the level at which various technical solutions more or less conclusive are implemented according to the case, to the ranks of which the lateritic gravels, crushed gravels, soil concretes, or their respective derivatives stabilized with cement or bitumen, for the more standard ones [4]. The principle of composition of soil concretes, which generally results from an input of crushed gravels to a lateritic soil of insufficient mechanical characteristics, inspires our approach which in the interest region is implemented with local materials available in quasi unlimited quantities. Namely sand and soils. If soil concretes are limited to the mixtures techniques of natural materials for the improvement of the mechanical performances of the pavement layers, the experimentation carried out within the context of our works associates a minimum fraction of hydraulic binder, to dope mixtures obtained and bring its characteristics to the values required by the road construction standards. So we call this approach using the term "outsourcing of concrete soil" which in its base, on the one hand contextualizes a concept recognized already in a specific environment, and on the other hand seeks to expand it. This widening consists essentially in exploring the specific materials of the study area in alternation with those that are usually used for similar purposes, like 0 / 31.5 crushed gravels, the scarcity of which is established: it is the neo-productive nature of the environment in which the study takes place. http://www.iaeme.com/IJCIET/index.asp 1193 editor@iaeme.com Flavien GUETSA KAMANOU, Denis NTAMACK, Thomas TAMO TATIETSE The use as a base course of 0 / 31.5 crushed gravels recommended in road projects carried out generally in the Sudano-Sahelian zone and precisely in Far-North Cameroon in particular generates very high costs, in view of the origin of this material and the conditions of its implementation, hence the need to seek for economic solutions integrating the use of local materials. The abundance of sand in this region and particularly in the Maroua’s town and its neighbouring localities, precisely in the beds of Mayo (rivers) militate in favor of the usage of this material in the pavement layers design. The objective is to find the proportion of the constituents of a sand-soil mixture stabilized with cement and according to the criteria of eligibility of materials use as base course for pavement with moderate traffic in zones according to the characteristics described above: 2. MATERIAL AND METHODOLOGICAL APPROACH In practice, the design of the structure of a road is based on the knowledge of its essential components such as the formation layer, the sub base, the base course and the Surface course (Figure 1). Figure 1 Drawing of the concept of pavement structure Of these different parameters, the base course is one of the most constraining, due to the severity of its mechanical characteristics, its key role in the durability of the road structure, and the costs it generates. The methodological approach developed to achieve the goal is to vary the percentage of sand and soil by maintaining the percentage of cement at 5% and appreciate the geotechnical characteristics of the mixture. The geotechnical characteristics evaluated are the simple compressive strength after 7 days exposure to the air (Rc), the simple compressive strength after 3 days exposure to the air and 4 days of immersion (Rc'), the CBR (California Bearing Ratio) index after 3 days exposure to the air and 4 days of immersion. 2.1. Materials and Equipment The experimental material is divided into two main classes, described below: The specimen making equipment: It includes the CBR mold, rammer and the normal and modified Proctor compaction equipment with the set of accessories (extension collar , annular surcharge disc, spatula or palette knife, small tools), and the material of common use comprising a balance, trays, an oven and a hot plate. A cylindrical metal plunger, the lower end of which shall be of hardened steel and have a nominal cross-sectional area of 19.35 cm², corresponding to a specified diameter of 60 mm. A convenient size would be approximately 20 cm long. http://www.iaeme.com/IJCIET/index.asp 1194 editor@iaeme.com Development of a New Product for the Optimization of the Geotechnic Characteristics of the Base Course in the Roads Construction in Soudano-Sahalian Area: Case Study of the Maroua Agglomeration A machine for applying the test force through the plunger, having a means for applying the force at a controlled rate. The machine shall be capable of applying at least 50 kN at a rate of penetration of the plunger of 1.27 mm/min to and a dynamometric device for measuring the punching forces. 2.2. The Constituents of the Mixture The materials used in this study all come from the Maroua’s city, whose location map is illustrated in figure 2. We estimated the quantities of soil available in the site of Wourndé II, from where the analysis samples were taken. This calculation shows that the exploitable quantities are considerable. The minimum volume measured is estimated at nearly 2,800,000 m3, according to the identification map, shown in Figure 3. Figure 2: Site experiment: a portion of the Sudano-Sahelian influencing zone, part of Cameroon Figure 3 The city seat of experiment (Maroua) and its availability in sand and soil materials http://www.iaeme.com/IJCIET/index.asp 1195 editor@iaeme.com Flavien GUETSA KAMANOU, Denis NTAMACK, Thomas TAMO TATIETSE The table below shows the origin of materials exploited in this formulation Table 1 Origin of collected materials Material Origin The Mayos bed Borrow of Wourndé II Figuil Sand Soil Cement 2.3. Composition of the Mixtures In reference to experiments conducted by researchers in the field of material stabilization [4], we selected three compositions by varying only the percentage of sand and clay. In each composition, the percentage of cement is maintained at 5%. Table 2 below shows the different mixtures studied. Table 2 Proportion of materials content in each mixture Mixture Materials Proportion Sand 60% Soil 35% Cement 5% Sand 65% Soil 30% Cement 5% Sand 70% Soil 25% Cement 5% N°1 N°2 N°3 3. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION 3.1. Identification of materials before mixing The sand of Mayo Kaliao, a river running through the city of Maroua from west to east, and the soil of Wournde II quarry located in the northern peripheral districts of the same city are tested before mixing. The main results obtained are as follows: Table 3: Particle Size Analysis of the Wourndé II and Mayo kaliao Samples Boring Depth of sampling (m) P1 0,40 - 1,50 P4 On surface Nature of the materials Sandy-Clay (soil) Coarse sand Sieve analysis (sieve opening in mm) 25 20 Atterberg’s limits LL LP IP 0,5 0,08 ( %) (%) (%) 10 5 2 1 100 98,8 96 94 86 78 68 55,8 62 100 100 90 58 28 10 Not necessary 97 0,4 34 28 Observation: The plasticity index of the Wournde II soil material is greater than 25 and the percentage of fine elements greater than 50. The coarse sand of Mayo Kaliao has a fineness modulus of 3.87. http://www.iaeme.com/IJCIET/index.asp 1196 editor@iaeme.com Development of a New Product for the Optimization of the Geotechnic Characteristics of the Base Course in the Roads Construction in Soudano-Sahalian Area: Case Study of the Maroua Agglomeration 3.2. Results The characteristics of the different mixtures are given in the following table. Table 4 Characteristics of the different mixtures Sieve analysis (Sieve opening in mm) Mixture Composition 25 1 2 3 60% Sand 35% Soil 5% Cement 65% Sand 30% Soil 5% Cement 70% Sand 25% Soil 5% Cement 20 10 5 2 1 0,5 Atterberg’ Modified s limits Proctor LL LP Ɣd w 3 0,08 (%) (%) (T/m ( % ) ) 100 100 97,8 93,9 74,2 52,4 34,6 17,7 26 18 2,15 7,3 100 100 97,8 90,8 66,1 42,9 26,6 11,4 28 19 1,99 10,5 100 100 98,6 93,6 59,8 41,6 21,3 30 20 2,105 8,9 5,2 Thus, the experiment carried out on the samples of mixtures 1 and 2 gave the following graphical representations: http://www.iaeme.com/IJCIET/index.asp 1197 editor@iaeme.com Flavien GUETSA KAMANOU, Denis NTAMACK, Thomas TAMO TATIETSE http://www.iaeme.com/IJCIET/index.asp 1198 editor@iaeme.com Development of a New Product for the Optimization of the Geotechnic Characteristics of the Base Course in the Roads Construction in Soudano-Sahalian Area: Case Study of the Maroua Agglomeration On the samples compacted at 95% of the OPM density, the values of the CBR index and the simple compressive strength obtained are summarized in the table below. Table 5 Value of the CBR index, résistance to simple compression Mixture 1 2 3 𝑹𝒄 (bar) 18,7 19,3 21,4 CBR 162 193 215 𝑹𝒄′ (bar) 7,4 9,1 10,7 Observation: The bearing capacity index CBR (after 3 days of air treatment and 4 days of immersion) of the Sand-Soil-Cement mixture is greater than 160 which is the value required for an improved material intended for the base course implementation. 3.3. Discussion of Results Eligibility criteria of the materials : The principal criteria retained for the eligibility of materials at the base course are as follows : The stability or bearing index (CBR) and the hardness of the skeleton ( Rc, Rc’) : To meets these criteria, the bearing capacity index CBR must be at least equal to 80 for a dry density corresponding to 95% of the OPM. If the natural material does not reach this bearing capacity, a stabilization is necessary before its usage at the base course. Borrow materials from the city of Maroua (Soil from the mountains of Woundé II) have a bearing capacity Index CBR including between 25 and 35, sufficient to be used at the sub base course, but not at the base course. Interpretations of the results obtained: The bearing capacity index CBR increases progressively when the percentage of soil decreases in the mixture, until it reaches an empirical point of the composition. As a result, the mixture containing 25% of soil against 70% of sand and 5% of cement present the best CBR. Indeed, the increase in soil’s percentages aims at ameliorating the cohesion of the whole. The sand used has a fineness modulus in the order of 3.8 describing the poverty of this soil in fine elements. Following the Practical Guide of Dimensioning road of tropical areas, the stabilized materials are satisfactory when they respond to the criteria presented in the following table: Table 6: Eligibility criteria of the materials Criteria CBR at 95% of OPM after 3 days air treatment and 4 days of immersion The simple compressive strength after 7 days of air treatment Rc The simple compressive strength after 3 days of air treatment and 4 days of immersion Rc’. Required value >160 >18 bars >5 bars The three mixtures submitted to the study are all satisfactory, each meeting the eligibility criteria presented in the table above. One of the objectives of this study being encouraging the use of sand which will allow to eradicate the stream of the Mayo Kaliao, we recommend the adoption of mixture 3 which integrates the use of 70% of sand. 4. CONCLUSIONS This study aims at adapting roads structures in Soudano-Salelian areas, case of the region of the far North Cameroun, according to local materials available. At the end of this experiment, to meet the needs of the implementation of the base course in the roads construction in areas http://www.iaeme.com/IJCIET/index.asp 1199 editor@iaeme.com Flavien GUETSA KAMANOU, Denis NTAMACK, Thomas TAMO TATIETSE described above: Mixture III made up of 70% of sand, 25% of soil and 5% of cement could be definitely adopted for the construction of base course of roads in substitution to standard methods that appeals to the use of lateritic gravels or crushed gravels, almost inexistent in the interest region. This mixture has the advantage of incorporation up to 70% of sand, which is present in abundance in this part of the territory, and could also contribute in curing the Mayos’stream, which is full, and can reduce the hydraulic power. We can easily realize that the adoption of this new technic helps on the one hand in ameliorating the development of road’s insfrastructures in the Far Nord of Cameroon at reduced cost on one hand, and on the other hand limit flooding sites exposed to the overflow of Mayos by curing their stream. REFERENCES [1] Organisation des Nations Unies pour l’éducation, la science et la culture. Routes dans les pays en voie de développement – Construction et entretien – Conditions économiques et techniques (2009) p.2. [2] MINEPAT. Vision Cameroun 2035. 2009 p.v. [3] Direction de la statistique et de la comptabilité nationale. Conditions de vie des ménages et profil de pauvreté à l’extrême-nord Cameroun (Décembre 2002) p.18. [4] LCPC/SETRA. Traitement des sols à la chaux et/ou aux liants hydrauliques Application à la réalisation des remblais et des couches de forme, Guide technique (janvier 2000). [5] Modou Diop (2002), Conception des structures routières sur Marnes et argiles gonflantes. Projet de fin d’étude en vue de l’obtention du diplôme d’ingénieur de conception, Thiès.133P [6] Tidiane Ibrahim Doucoure et Mamadou Doudou Ndiaye (2009), Etude de matériaux de substitution à la latérite en couche de base : Sable –bitume et Banco-coquillage. Projet de fin d’études en vue de l’obtention du diplôme de conception, Thiès 168P. [7] Bakaiyang Lemankreo (2013), Contribution à l’entretien des routes revêtues en zone tropicale : cas des régions du Grand-Nord Cameroun. Mémoire de fin d’études en vue de l’obtention du diplôme d’ingénieur de conception, ENSP Yaoundé. [8] Symkiewicz Fabien, Evaluation des propriétés mécaniques d’un sol traité au ciment. Thèse de doctorat en vue de l’obtention du diplôme de docteur de l’université de ParisEst. Option Géotechnique.245P [9] BCEOM-CEBTP (1984), Guide pratique de dimensionnement des chaussées pour les zones tropicales, 155p. [10] MINDHU (Août 2014), Etude Technique en vue de la protection des berges du Mayos Kaliao-Maroua, Rapport d’APD –LE COMPETING-BET.142P [11] NB: The laboratory LE COMPETING-MAT, approved category B, served within the context of all the tests carried out, as part of the experiment conducted. May he find here the expression of our sincere gratitude. http://www.iaeme.com/IJCIET/index.asp 1200 editor@iaeme.com Development of a New Product for the Optimization of the Geotechnic Characteristics of the Base Course in the Roads Construction in Soudano-Sahalian Area: Case Study of the Maroua Agglomeration ANNEX A1-Summary sheet of geotechnic test ; A2- Some graphical illustrations ANNEX A1 : SUMMARY SHEET OF GEOTECHNIC TEST Result of the Sieve Size analysis Curve of the material Sand and Soil http://www.iaeme.com/IJCIET/index.asp 1201 editor@iaeme.com Flavien GUETSA KAMANOU, Denis NTAMACK, Thomas TAMO TATIETSE ANNEX A2 : SOME GRAPHICAL ILLUSTRATIONS Soil sampling at the bottom of Mount Wourndé … Avaibility of soil materials (Mountain range) http://www.iaeme.com/IJCIET/index.asp 1202 editor@iaeme.com