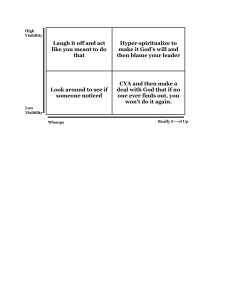
CLASS A blueprint of an object Collection of methods and variables OBJECT Everything we see around us in object Instance of a class Just like a capsule, where all things remain encapsulated Hiding unnecessary details from the user Showcasing only the required things to the outside world while hiding the details Focus on “what an object does”, instead of how an object is presented or “how it works” Sharing some functionality and properties from one class to another Allows code reusability Allows you to redefine the way something works, by changing how it is done or by changing the parts used to get it done 2 ways Overloading overriding Parent Class Base class Super class Child Class Subclass or derived class Visibility/Access Modifier PHP 3 types of visibility Private Protected Public Property Class variables Method function, or behavior Static keyword Giving access to any property or method without any instance of object, or accessing property or method directly by class “::” Scope Resolution Operator Used to indicate static and constant “$this” pseudo-variable Pseudo-variable originally contained the object of the current class If you want to use any non-static property in PHP and non-static method within the class, use “$this” pseudo-variable https://medium.com/@yannmjl/object-oriented-programming-concepts-in- simple-english-3db22065d7d0 http://www.w3programmers.com/php-oop-basics/ http://www.tonymarston.co.uk/php-mysql/abstraction.txt