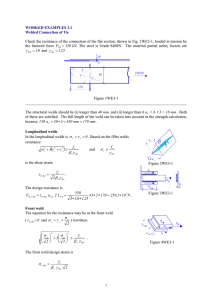
FILLET WELD INTRODUCTION Efficient and direct way of connecting is by welding Metallurgical bond by heat or pressure or both Advantages of welding • Direct transfer of stress - minimum weight , efficiency • Less fabrication • Economy - 15% saving in weight in bridges,less labor • Neat appearance • More rigid WELDING PROCEDURE • Environment • Welding position • Current : controls heat input • Shrinkage • Preheating Weldability of steels Economic welds, good , crack free TYPES OF JOINTS OR WELDS • • • • Joints:Lap,Tee,Butt and Corner Welds: Groove, fillet, plug and slot Welded joint description - Type of joint and weld Position of welding (a) Butt joint (b) Lap joint (c) Tee joint (d) Corner joint COMMON TYPES OF WELDS (b) Fillet welds (a) Groove welds Ends shall be semi circular A A A A Section A-A (d) Plug weld Section A-A (c) Slot weld • Fillet welds • Ease of fabrication and adaptability • Less precision • No special edge preparation • Throat of a weld • Concave and convex surfaces Weld and leg size s t Root of weld Te Face of weld Theoretical throat (t=0.707s) QUALITY OF WELDED CONNECTIONS • Proper electrodes , welding apparatus and procedures • Welding sequence Doubling up method Planned wandering method Step back method SEQUENCE OF WELDING OF FILLET WELDS Doubling - up method for vertical member 13 12 7 5 1 6 8 17 18 11 10 9 3 2 4 14 15 16 RESIDUAL STRESSES • Residual stresses - due to rapid heating and cooling • Yield strength of material is upper limit for residual stresses Tension LONGITUDINAL RESIDUAL STRESS DUE TO WELD - - WELD DISTORTION a)Transverse shrinkage (b) Angular change (c) Rotational distortion (e) Longitudinal bending distortion (d) Longitudinal shrinkage (f) Buckling distortion DEFECTS IN WELDS • • • • • Incomplete fusion Porosity Inadequate preparation Undercutting - Excessive current or long arc Slag inclusion - Failure to remove slag between runs • Cracks - Breaks in the weld metal • Lamellar tearing - Occurs in the base metal beneath the weld WELD DEFECT TOLERANCE For joints welded from both sides • Incomplete penetration - 5% of parent metal thickness < 2mm • Length of flaw < 200 mm / meter length Welded on one side • Incomplete penetration - 15% of thickness < 3mm • Slag inclusion < 200 mm / meter weld length • Total gas pores < 5 per square centimeter of weld • Thickness upto 10mm , undercut < 0.5mm • For thickness > 10mm undercut < 1mm • WELD INSPECTION Visual inspection Liquid penetrants Magnetic particles Ultrasonic testing Radiography CONNECTION DESIGN Static strength of welded joint • Type and size of the weld • Manner of welding • Type of electrode used • • • • • • • • • DESIGN Direct tension or compression Design strength same as parent metal strength Effective area equals effective length times throat size For full penetration,thickness of weld ,equals thickness of thinner part of connection Partial penetration welds are avoided Throat thickness - 5/8 thickness of thinner part Average stress concept Permissible stresses - Parent metal values Site welds – lower design strengths FILLET WELDS 11 1 1 1 1 11 Behaviour • Lap joints splices • Shear is the main design consideration • Side fillets and end fillets • End fillet loaded in tension - high strength and low ductility • Side fillet loaded - Limited to weld shear strength (50% tensile strength) Improved ductility • Average stress in weld throat • Fillet weld shape is important for end fillets. (A) CONNECTIONS WITH SIMPLE WELD DESIGN, (B) CONNECTIONS WITH DIRECTION- DEPENDENT WELD DESIGN Tension Shear P P (a) P (b) DESIGN Simple approach - Uniform strength Size of fillet weld 3mm or thickness of thinner part Effective throat thickness 3 mm < 0.7t and 1.0t = k fillet size Size Size (Min. Leg size) Fillets of unequal leg length Penetration Size Fillets of equal leg length Leg length Size = leg length * 2.4 mm (a) WELDS SUBJECTED TO SHEAR AND TORSION, (b) WELDS SUBJECTED TO SHEAR AND BENDING y M e P x x c.g of welds (a) y e P P e (b) 18 SUMMARY • Fundamentals of welding , details of fillet welding process, types fillet weld design, common weld defects and weld inspection have been presented. • Advantages of fillet welding are mentioned. • Behaviour and design of fillet-welded connections in steel structures are explained . • Truss connections and beam connections are discussed. 19