Introduction to Matter: Properties, Mass, Volume, Density
advertisement

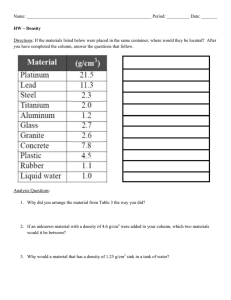
Big Idea Matter is described by its properties and may undergo changes Unit 1 Lesson 1 Introduction to Matter Essential Question: What properties define matter? P6 What’s the Matter? What is matter? • Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. • Matter makes up the materials around you. • Everything is made up of matter. • Light, sound, and energy are not matter because they do not have mass or takes up space. P7 What is mass? • Mass describes the amount of matter in an object. • A gram (g) is a common measurement of mass. • Objects of the same size can be made up of different amounts of matter. • Weight is a measure of the gravitational force on an object. • The greater the mass of an object, the greater the gravitational force on the object and the greater the weight will be. P7 How does mass differ from weight? • You would weigh less on the moon because gravity on the moon 1/6 as strong as it is on Earth. • Mass stays the same for an object even when increased or decreased gravitational forces change the weight of the object. 7) Weight is the downward pull of an object due to gravity. Because gravity on the moon is less than Earth, an astronaut weighs less on the moon. MASS STAYS THE SAME Measuring Mass – Triple-Beam Balance 1st – Place the object on the scale. 2nd – Slide the large weight (100g) to the right until the arm drops below the line. Move the rider back one groove. Make sure it “clicks” into place. 3rd – Repeat this process with the top weight (10g). When the arm moves below the line, back it up one groove. 4th – Slide the small weight (1g) on the front beam until the lines match up. 5th – Add the amounts on each beam to find the total mass to the nearest tenth of a gram. P8 How are mass and weight measured? Visualize It #8) Yes – this is a balance, so both sides need to balance. It would balance the same way on the moon or on Earth. MEASURES MASS • A triple-beam balance can be used to determine mass. The balance compares an object’s mass to countermasses. • Weight is measured with a spring scale. • The standard scientific unit for weight is the newton (N). • A 100-g mass weighs approximately 1 N on Earth. Mass vs Weight 3) As mass increases, weight also increases. 4) The Spring inside the spring scale P9 Measuring Space How is the amount of space occupied by matter measured? • Volume is the amount of space that an object takes up, or occupies. • Two objects may have similar volumes do not always have the same mass. Active Reading #9) Volume measure the amount of space that an object takes up, or occupies P10 How can volume be determined? • An object’s volume can be determined by a formula if the object has a well-defined shape. • For rectangular solids: • volume equals the object’s length times width times height V = lwh • To calculate volume, all measurements must be in the same units. Do the Math (p11) A. What do you know? A. B. What do you want to find? B. C. Draw and label a C. sketch D. write the formula E. substitute the given D. values E. F. Solve (multiply) F. G. Check your units G. Length = 30cm; Width = 40cm; height = 200cm Volume V=lwh V = 30cm x 40cm x 200cm 240,000 cm3 The given units are centimeters, and the measure found is volume. Therefore, the units should be cm3 P12 How can volume be determined? • Liquid volume is measured with a beaker or graduated cylinder in liters (L) or milliliters (mL). • 1 mL = 1 cm3 • Displacement of water in a graduated cylinder can be used to find the volume of irregular-shaped solid objects. • How many milliliters of fluid does this object displace? 40 mL Volume of rock = 5 mL or 5 cm3 180 mL 60 cm3 C What causes the meniscus? A concave meniscus occurs when the molecules of the liquid attract those of the container. The glass attracts the water on the sides. Packing It In! • Density is a measure of the amount of mass in a given volume. • The density of a substance remains the same no matter how much of the substance you have. • Density is mass divided by volume, D = m/V. • Common units for expressing density are grams per cubic centimeter, or g/cm3. • Water has a density of 1 g/mL. • objects with density greater than 1 g/mL sink in water. Objects with density less than 1 g/mL float in water. P13 What is density? P13 How is density determined? • Density is mass divided by volume, or D = m/V. • Common units for expressing density are grams per cubic centimeter, or g/cm3. •Water has a density of 1 g/mL. Thus, objects with density greater than 1 g/mL sink in water. Objects with density less than 1 g/mL float in water. Visual Summary P16 17)An objects' weight is the amount of space it occupies. 18)The mass of an object is equal to its weight. 19)The volume of a solid can be expressed in units of cm3. 20)An object that floats in water is less dense than water. First you find mass of the object Then you find the volume of the object by water displacement for something that is irregularly shaped. For a regular shape object multiply lwh Density is a calculation dividing mass by volume Eureka! Density 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 9) 10) 11) 12) 13) 14) 15) Simply Measure Volume Concept Scratch Equal Method Equivalent Legend Discovery Buoyancy Total Iceberg Based basis 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) Archimedes 2,260 yrs ago Greece Both B & C He put two crowns in water and saw which one displaced more water 6) I have found it! 7) Float 8) sink Measuring Mass – Triple-Beam Balance 1st – Place the object on the scale. 2nd – Slide the large weight (100g) to the right until the arm drops below the line. Move the rider back one groove. Make sure it “clicks” into place. 3rd – Repeat this process with the top weight (10g). When the arm moves below the line, back it up one groove. 4th – Slide the small weight (1g) on the front beam until the lines match up. 5th – Add the amounts on each beam to find the total mass to the nearest tenth of a gram.