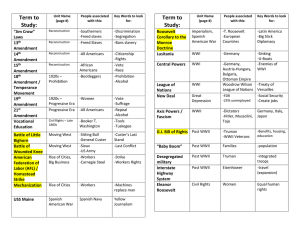
NAME: _____________________________________________________________________________________ PERIOD: ____________ #: ___________ U.S. History EOC Information Sheet SECTION #1: FOUNDING AMERICA Founding Fathers: 1. Benjamin Rush, John Hancock, John Jay, John Witherspoon, John Peter Muhlenburg, Charles Carroll and Jonathan Trumbull Sr. DOI (1776): 1. Thomas Jefferson, listed colonial grievances against the British King 2. America is ruled by the “Consent of the Governed”- People have the power 3. Unalienable Rights: Rights that no one can take away without due process (Life, Liberty and the Pursuit of Happiness) U.S. Constitution (1787): 1. Supreme Law of the Land, Representative Government (Republicanism) 2. Separation of Powers, Checks and Balances, Popular Sovereignty, Federalism 3. “E Pluribus Unum” served as the first national motto for the U.S. (out of many, comes one) Bill of Rights: 1. 1st 10 Amendments to the Constitution 2. 1st: RAPPS (Religion, Assemble, Press, Petition, Speech) 3. 2nd: Right to Bear Arms 4. 4th: Unreasonable Search and Seizure 5. 5th: Property Rights 6. 6th: Speedy and Public Trial SECTION #2: RECONSTRUCTION 1. Rebuilding the South following the Civil War 2. 13th: FREE, abolish slavery 3. 14th: CITIZENS, granted citizenship to former slaves (Cannot be challenged by the Supreme Court) 4. 15th: VOTE, granted voting rights to African American males (Jim Crow Laws kept them from voting) 5. The passage of the 15th Amendment led to disappointment among women suffragists SECTION #3: SETTLING THE WEST 1. Transcontinental Railroad united the East and West and allowed the settlement of the West 2. Settlers moved westward due to the Gold Rush and the Homestead Act (Free land provided by the govt.) 3. Settlers were forced to ADAPT to the land and create new technology 4. Native Americans were forced off their land and onto reservations (unproductive land) 5. Settlers slaughtered the buffalo (Native American source of food, shelter, clothing, etc.) 6. Dawes Act: banned all Native American tribal activities (assimilate into American culture) SECTION #4: POPULISM 1. Populist Party supported mainly by southern and western farmers 2. 3rd Parties represent a voice of the political minority, bring light to new ideas 3. 3rd Parties often split the vote of larger parties—larger parties are then forced to address the concerns of 3rd Parties 4. Populists Platform: Coinage of Silver (Bi-Metallism), Income Tax, Direct Election of Senators, etc. 5. William Jennings Bryan served as the Populist Party candidate (1896 Election) SECTION #5: THE GILDED AGE Immigration 1. After 1880, immigrants came from Southeast Europe (Spoke no English, Unskilled, Uneducated) 2. Immigrants sought a better life, jobs, opportunities, freedom 3. Mainly settled in large Northeast cities in tenements (run down, filthy apartments) 4. Formed ethnic enclaves (neighborhoods with the same ethnicity, felt more like home) 5. Immigrants were a source of cheap labor for industrialists 6. Political Machines, such as Tammany Hall, took advantage of immigrants by bribing them for votes in exchange for helping them to assimilate into American culture 7. Nativism (Nativists)-American hostility/resentment towards immigrants because they took low paying jobs 8. Americanization- the process to assimilate immigrants into American culture (language, religion, traditions, customs) 9. Eugenics was used to justify new restrictions on immigration throughout the 1920’s 10. Chinese Exclusion Act- banned all Chinese Immigration (mainly on the West Coast) for over 60 years (Nativism) Industrialization 1. Laissez-faire economy- very little govt. involvement in business activities, businesses took advantage (NO Regulations) 2. John D. Rockefeller- oil robber baron or captain of industry, 90% of the world’s oil (Monopoly) 3. Andrew Carnegie- Steel Monopolists, utilized the Bessemer Process (process to make cheap steel) 4. Monopolies- control an entire industry, eliminate competition and set prices 5. Monopolists exploited workers (long hours, unsafe conditions, little pay) 6. Children were a source of cheap labor 7. Assembly Lines (H. Ford) were utilized to speed up production and allowed the use of unskilled workers 8. Sherman Anti-Trust Act- prevented the growth of monopolies (poorly regulated) 9. Labor Unions formed to fight for better pay, hours, and conditions (Knights of Labor & AFL) Inventions and Urbanization 1. Thomas Edison: light bulb/electricity, increased production and improved the standard of living 2. Alexander Graham Bell: telephone, improved long-distance communication 3. Many technological innovations led to an increase in industrialization 4. Rural (farm) populations decreased as many Americans moved to urban (city) areas for industrial jobs 5. Growing urban areas led to overcrowding, poor sanitation, and the spreading of diseases SECTION #6: PROGRESSIVISM 1. People work for a more democratic process in society 2. Reform- to change, improve (Businesses and industry begin to be regulated by the govt.) 3. 16th: BY TAXING, Graduated federal income tax 4. 17th: SENATORS, Direct election of U.S. Senators 5. 18th: TO DRINK, Banned the sale, transportation, and possession of alcohol (Prohibition) 6. 19th: WITH WOMEN, Women’s Suffrage, the right to vote (1920) (led by Susan B. Anthony) 7. Temperance Movement- led by Christian women to ban alcohol (Frances Willard) 8. Settlement House Movement- Jane Addams (Hull Houses) provided the poor with housing and an education, helped to assimilate immigrants 9. Pendleton Civil Service Act ended the spoils system 10. Muckrakers- journalists who exposed the corruption of the Gilded Age which led to change -Upton Sinclair wrote “The Jungle” exposing the unsanitary conditions in the meat packing industry -Ida Tarbell wrote about the corruption of J.D. Rockefeller’s oil monopoly -Jacob Riis- exposed poor living conditions in tenements through photography 11. Initiative, Referendum, Recall- provided citizens a more direct voice in the American government 12. Lobbying serves as a way for citizens to influence representatives to speak on their behalf 13. Booker T. Washington- believed education was the key to equality for African Americans 14. W.E.B. Du Bois- founded the NAACP, fights for equality for all minority groups 15. Ida B. Wells- led an anti-lynching campaign (hanging) 16. Theodore Roosevelt- Square Deal, Trust-Buster, Health Reform, Conservation -Meat Inspection Act and the Pure Food and Drug Act (as a result of “The Jungle”) 17. Child labor was BANNED during the Progressive Era 18. Triangular Shirtwaist Factory Fire led to the passage of safety laws and regulations to ensure employee safety 19. Social Gospel Movement- church provided aid to the American people SECTION #7: EXPANSIONISM AND THE SPANISH-AMERICAN WAR 1. U.S. becomes expansionistic in search of new markets and raw materials (TRADE), International Affairs 2. Annexed Hawaii (Stanford B. Dole) and bought Alaska 3. Spanish-American War (1898)-splendid little war; America emerged as a world power (Puerto Rico, Guam, and the Philippines) and was able to expand commercial trade 4. Conservation- to conserve or save, specifically the environment (Teddy Roosevelt) 5. De Lome Letter- Spanish Diplomat wrote a letter criticizing American President McKinley for being weak 6. U.S.S. Maine- exploded in Cuba killing 258 sailors, Americans blamed Spain due to Yellow Journalism 7. Yellow Journalism- unbalanced or exaggerated reporting in an effort to make a story more exciting 8. Alfred T. Mahan- built up the U.S. Navy and argued for making America a world power 9. Theodore Roosevelt- Spanish-American War, Rough Rider, Panama Canal, Big Stick Policy (U.S. Military serves as the police force in Latin America) 10. Panama Canal- Roosevelt sends military support to help Panama gain independence from Columbia in order to build the canal (shortened the distance for the U.S. Navy, as well as trade routes) 11. Open Door Policy- protect U.S. trade in China SECTION #8: WWI 1914-1918 (U.S. enters in 1917) 1. Causes of WWI- Militarism, Alliances/Agreements, Imperialism, Nationalism (MAIN) 2. Assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand sparks the start of WWI 3. US remains neutral (Isolationists) 4. Causes of U.S. entry- Unrestricted Submarine Warfare (Lusitania), Sussex Pledge, and Zimmerman Telegram 5. Selective Service Act- conscription or military draft 6. John J. Pershing- leader of the American Expeditionary Forces in WWI, trained inexperienced troops 7. Battle of Argonne Forest- ended the military stalemate in WWI 8. Military Technology- Tanks, Planes, Machine Gun, and Poison Gas (increased casualties) 9. Trench Warfare- increased the death toll and length of WWI (Stalemate) 10. Treaty of Versailles ends the war (U.S. does not sign)-Treaty of revenge against Germany 11. Wilson’s Fourteen Points- plan to end all warLeague of Nations-U.S. Senate rejects the League of Nations in fear of being forced into future wars (Collective Security) Henry Cabot Lodge was the strongest opponent to the League of Nations 12. Great Migration- African Americans move to the north to take the vacant jobs 13. Women go to work in the factories, rationing, and war bonds used to support the war effort 14. Espionage Act of 1917 and Sedition Act of 1918 created constitutional questions regarding freedom of speech 15. Alvin York received the Congressional Medal for Valor 16. President Wilson supports Eugenics as a way to continue to restrict immigration 17. Federal Reserve Act of 1913 (Wilson): set up Federal Reserve & National Banking System, all banks must leave a percentage of their deposits on reserve SECTION #9: 1920’s 1. Growth and Prosperity following a slight recession following WWI 2. Improved transportation=automobiles=new industries 3. Henry Ford revolutionized the industry with the assembly line, affordable automobiles 4. Harlem Renaissance- celebration of African American culture (Jazz, Art, Literature) 5. Tin Pan Alley- music publishing district in New York (popular music sold to ordinary people) 6. Red Scare- fear of Communism which led to the Palmer Raids (Sacco & Vanzetti Trial) 7. 1920s is known for high consumer spending, buying on credit 8. Scopes Monkey Trial- evolution vs. creationism (Bible vs. Science) Lawyers: William Jennings Bryan (Bible) & Clarence Darrow (Science) 9. Eugenics led to limitation or bans on immigration 10. Teapot Dome Scandal (selling American oil reserves)-led to mistrust in the govt. 11. Marcus Garvey-led the Back-to-Africa Movement 12. Charles Lindbergh-1st man to fly solo across the Atlantic Ocean, American hero for his bravery and courage 13. Glenn Curtiss- aviation pioneer who invented airplanes that landed on water 14. Prohibition Movement (18th Amendment) led to a rise in organized crime (bootlegging, speakeasies) 15. Flappers- young women who rejected the traditional roles of women SECTION #10: GREAT DEPRESSION AND THE NEW DEAL 1. American economy collapsed and millions of Americans became unemployed 2. Causes: buying on credit, buying on margin, poor regulation and over-speculation of the stock market 3. Stock Market Crash “Black Tuesday” (October 29, 1929) 4. Dust Bowl- dry, flat, overproduced land led to dust storms (Farmers migrated to California) 5. President Hoover provided little to no direct relief to the American people 6. Hoover is replaced with President FDR and the New Deal (plan to get America out of the depression) 7. Fireside Chats- FDR delivered a series of radio speeches in an effort to keep Americans well-informed 8. FDR provided the America people with DIRECT RELIEF, including: employment opportunities 9. FDIC (Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation)-insures $ in the bank 10. SSA (Social Security Administration)-pension, elderly, retire, disabled 11. SEC (Securities and Exchange Commission)-regulated the Stock Market 12. FDR’s “Court Packing” Scheme to increase the # of Supreme Court justices was rejected as it violates separation of powers 13. Monetary Policy- tightened the money supply which led to a rise in interest rates until the Stock Market Crash SECTION #11: WWII1939-1945 (U.S. enters in 1941) 1. Depression in Europe leads to the Rise of Dictators (Hitler, Mussolini, Tojo, and Stalin) 2. 1939, Germany invades Poland starting WWII (US remains neutral but supplied Allied forces with weapons) 3. FDR persuades the US to enter WWII after Japan attacks Pearl Harbor (December 7, 1941) 4. US enters as an Allied country against the Axis Powers 5. Allies: US, GB, FR, USSR Axis: GR, IT, JP 6. “Rosie the Riveter”- embodies the role women played during WWII by filling vacant factory jobs left by soldiers 7. War Production Board- war-time production only, unemployment drops to less than 1% 8. Office of war Information- provided information to Americans through propaganda posters 9. Rationing- save or limit, all extra goes to the troops—goods became scarce (very limited) 10. Operation Torch (Patton)-N. Africa (Tanks) 11. Holocaust serves as an extreme example of eugenics 12. Operation Overlord “D-Day” (Eisenhower)- invasion of Normandy serves as the turning point of WWII in Europe because it opened a 2nd major front 13. WWII Pacific “Island Hopping” (MacArthur & Nimitz)-Battle of Midway=turning point because it crushed the Japanese Navy 14. Bataan Death March- (Philippines) one of the largest losses in American history, POW’s tortured and killed 15. WWII in the Pacific ended with President Truman’s approval to drop the Atomic Bomb on Japan in order to save American lives 16. Manhattan Project- Atomic Bomb Project led by Einstein, bomb made from uranium 17. Heroic Units: Flying Tigers, Navajo Code Talkers, and Tuskegee Airmen (led to integrated military units) 18. Vernon Baker-awarded the Congressional Medal of Honor for Battlefield Courage, displayed African Americans willingness to fight for the U.S. 19. Executive Order 9066- Sent Japanese Americans to internment/relocation camps, Americans feared they were spies 50+ years later viewed as unconstitutional, Japanese Americans given money to cover loses 20. G.I. Bill- $ for education to veterans SECTION #12: THE COLD WAR 1. A war of nerves between the Soviets and the US—neither country faces the other directly on the battle field 2. The Cold War and the arms race with the Soviets lead to increased defense spending in 1950-1960 3. Capitalism (Free Enterprise)-private citizens control economic activities, promotes competition 4. Communism (Command Economy)-government controls all economic activities 5. Truman Doctrine- main goal is to stop the spread of Communism and to spread democracy 6. Marshall Plan-helped war torn countries in Europe rebuild in order to stand firm against Communism 7. Containment- to control the spread of Communism 8. Berlin Wall-split Berlin into East & West, Communists and Free 9. Berlin Airlift- US supplied food and supplies to the people of W. Berlin due to a Soviet blockade (blockade is lifted) 10. HUAC (House Un-American Committee)-investigated Communism in Hollywood prior to Joseph McCarthy 11. McCarthyism (Joseph McCarthy)-witch-hunt of suspected communists (Red Scare) 12. Rock n’ Roll created a cultural divide between generations 13. NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization) established a military alliance between many free nations including the US 14. Warsaw Pact- military alliance between Communist countries including the Soviet Union SECTION #13: THE 1950’s (Foreign and Domestic) 1. Korean War, divided North (Communists) vs. South (Free) at the 38th Parallel-effort to contain communism, considered an American victory (fear of communism continues) 2. “The American Dream”- economic prosperity, suburban life, white collar workers 3. Baby Boom Generation- soldiers return from WWII, births dramatically increase 4. Television became increasingly popular during the 1950’s (I Love Lucy and Leave it to Beaver) 5. “In God We Trust” was adopted as our nation’s new motto in 1956 to separate ourselves from countries that restricted freedom of religion 6. Introduction of vaccines limited the spread of infectious diseases dramatically in the United States 7. Beatniks- counterculture movement that made fun of mainstream America and strived to stand out SECTION #14: THE CIVIL RIGHTS MOVEMENT 1. Plessy v. Ferguson- “separate but equal”—made segregation legal 2. Brown v. Board of Education- banned all segregation in public schools (Thurgood Marshall served as the lawyer and was later appointed as the 1st African American Supreme Court Justice) 3. Martin Luther King, Jr. supported nonviolent resistance (sit-ins, protests, marches) “I Have a Dream Speech” and “Letter from Birmingham Jail” 4. Malcolm X was the opposite of MLK, urged African Americans to protect themselves 5. Little Rock Nine, first African American students integrated into Central HS in Arkansas 6. SNCC (Student Nonviolent Coordinating Committee) 7. SCLC (Southern Christian Leadership Conference)—formed by MLK 8. Jackie Robinson was the first to break the color barrier in Major League Baseball 9. Civil Rights Act of 1957 increased African American voting in the South by creating a Civil Rights Division in the U.S. Justice Department. 10. Civil Rights Act of 1964 ended discrimination in all public places 11. Voting Rights Act of 1965 ended poll taxes and literacy tests in all states 12. 22nd Amendment: limits the President to 2 terms (8 years) to ensure one person doesn’t acquire too much power 13. 24th Amendment: outlaw/prohibits poll taxes 14. Lester Maddox was elected Governor of Georgia in 1966; staunch segregationist. 15. Orval Faubus was the Governor of Arkansas (1955-1967) who stood against the Little Rock Nine and opposed desegregation. 16. George Wallace served as the Governor of Alabama, staunch segregationist (“Segregation Now, Segregation Tomorrow, Segregation Forever”) 17. Betty Friedan- wrote the Feminine Mystique which challenged the traditional role of women in the home. 18. Billy Graham- prominent supporter of Civil Rights, a Christian preacher and spiritual advisor to several Presidents. 19. Rosa Parks- her refusal to give up her seat on a bus started the Montgomery Bus Boycott, known as the “Mother of the Civil Rights Movement” 20. Freedom Rides- interracial groups rode buses throughout America to encourage people to vote 21. President Lyndon B. Johnson (LBJ) took over after Kennedy’s assassination and signed most of the Civil Rights Laws. SECTION #15: 1960’S AND THE VIETNAM WAR 1. Miranda v Arizona- Miranda Rights, all people accused of a crime must be read their rights 2. John F. Kennedy (JFK)-1st televised debate, Peace Corps, NASA, Cuban Missile Crisis 3. NASA was created by JFK after the Soviets launched Sputnik in 1957 (first man-made satellite)—need for technology 4. Cuban Missile Crisis-stand-off with the Soviet Union, on the verge of nuclear war, everyone backs down 5. Lyndon B. Johnson (LBJ)-War on Poverty, Medicare, Medicaid, HUD (Housing and Urban Development), Civil Rights, 24th Amendment, 26th Amendment, Vietnam 6. 26th: Voting age changed from 21 to 18 (2 + 6 = “18”) 7. Although LBJ achieved great things in regards to Civil Rights, the Vietnam War ruined his legacy The Vietnam War 1. Divided North (Communists) vs. South (Free), 17th Parallel 2. Contain the spread of communism 3. Ho Chi Minh= North (Vietcong and the Vietminh), Ngo Dinh Diem= South (selected by JFK) 4. Gulf of Tonkin- gave the President a blank check to fight 5. Fighting in the Jungle- Agent Orange, Napalm, Search and Destroy 6. Tet Offensive- attack launched by the Vietcong on New Year’s Day, using the Ho Chi Minh Trail 7. Creditability Gap- what Americans saw and heard did not match, Americans began to mistrust the govt. 8. Public support for the war diminished greatly 9. Anti-War demonstrations were common throughout Vietnam 10. College aged students actively spoke out against the military draft 11. Devastating American loss- Communism spreads 12. Vietnamization-American troops are removed from Vietnam and North Vietnam takes over South Vietnam 13. War Powers Act- President must inform Congress within 48 hours of sending troops anywhere, within 90 days Congress must declare war or troops are removed 14. Roy Benavidez won the Congressional Medal of Honor during the Vietnam War SECTION #16: MODERN AMERICA 1970’S 1. Chicano Movement- Mexican Americans who fought for civil rights (protests) 2. Cesar Chavez and Delores Huerta created the United Farm Workers Association to protect the rights of migrant workers (farmers) 3. Hector P. Garcia- Hispanic Veteran that founded the American G.I. Forum 4. Environmental Protection Agency- govt. agency which sets pollution standards and conducts research 5. Title IX- requires gender equality for boys in girls in every educational program that receives federal funding 6. Affirmative Action- Policy of taking race, color, religion, gender, or national origin into account when making decisions to hire or accept people 7. Iran Hostage Crisis- Shah of Iran was admitted into the U.S. for medical treatment after being exiled from Iran— in response, Iran revolutionaries took a group of U.S. citizens hostage 8. OPEC- Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (controlled oil prices) 9. Watergate Scandal- President Nixon assisted in covering up a break in at the Democratic National Committee Headquarters—Nixon is impeached by the Senate then resigns 10. GATT eliminated trade barriers between varying nations, eventually replaced by the WTO, World Trade Organization 11. Camp David Accords- 1st Peace Treaty between Israel and an Arab state (negotiated by President Carter) 1980’S 1. Reaganomics, President Reagan’s economic policies—cut govt. spending on social programs, tax cuts, and increase military spending 2. Reagan pushed for deregulation of the federal government (reduces the federal governments power) 3. “Peace through Strength”- military strength through peaceful international relations 4. Iran – Contra Affair- was a political scandal in which officials secretly facilitated the sale of arms to Iran 5. Phyllis Schlafly- conservative activist known for her opposition to feministic ideas and for her ongoing campaign against the proposed Equal Rights Amendment (ERA) 6. Moral Majority- political organization which had an agenda of evangelical Christian-oriented political lobbying 7. National Rifle Association (NRA) - organization which goals include the protection of the Second Amendment and the promotion of firearm ownership rights (endorsed by President Reagan) 1990’S and Beyond 1. Gorbachev becomes the leader of the Soviet Union marking the end of the Cold War 2. Persian Gulf War (1991)- Iraq (Saddam Hussein) invaded Kuwait for oil—in response, President Bush launches Operation Desert Storm, Kuwait is freed 3. Balkans Crisis- Serbian rebels killed Bosnians (ethnic cleansing), US gets involved through NATO 4. Contract with America- Republican plan for political reform (President Clinton) 5. Rust Belt to Sun Belt Migration- as a result of factory jobs being cut in the north in the early 1990s, people began to migrate to the South and West (Sunbelt) 6. NAFTA (North American Free Trade Agreement) - Free trade between the US, Canada, and Mexico (Clinton) 7. President Clinton’s Impeachment- lied under oath (perjury and obstruction of justice), remained in office 8. Election of 2000- Gore vs. Bush, Florida Controversy led to a manual recount (Bush won) 9. September 11, 2001- US attacked by Al Qaeda terrorists— troops deployed to Afghanistan (War on Terror) 10. USA Patriot Act of 2001- Permitted extensive telephone and e-mail surveillance of suspected terrorists 11. Hurricane Katrina (2005)-50 levy failures, flooding in 85% of New Orleans, anger in regard to federal government action and response 12. Presidential Election of 2008-President Obama elected first African American president 13. American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 (ARRA)-known as “The Stimulus” or “The Recovery” Act, worked to create jobs, promote investment, and increase consumer spending during the recession