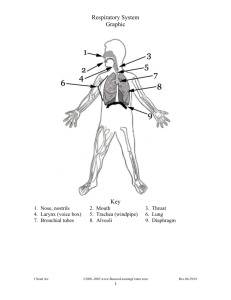
Upper and lower respiratory tract Clinical classification Paranasal sinuses Upper and lower respiratory tract Anatomical classification External nose: Bone and cartilage Tip of the nose skin Ala of the nose Nasal Cavity : Medial wall Lateral wall Choncae Meatus Roof :Ethmoid bone Floor: Palate Medial wall: Nasal septum Lateral wall: Conchae Opens in inferior meatus Function of paranasal sinuses: Lighten the weight of the skull Add resonance to the voice Insulator against cold air Transnasal hypophysectomy Nasopharynx contains : 1) Adenoids: Lymphoid tissue aggregation 2) Opening of Eustachian tube Oropharynx contains : 1) Palatine tonsils 2) Lingual tonsils Laryngeopharynx behind larynx Epiglottis Larynx The Larynx is a cartilaginous box in the neck : 1) Respiration passage 2) Role in voice production 3) Closed during deglutition Extends from C4---C6 vertebrae Larynx Epiglottis Thyroid Cricoid Larynx Laryngeal muscles: 1) Opening of the laryngeal inlet during respiration 2) Closing it during deglutition 3) Changing the tone of the vocal cords Trachea Length 11cm Width 2.5 cm C6---T4 Trachea 15—20 c shaped tracheal cartilages Trachea Trachea Oesophagus is posterior to trachea Main Bronchii Shorter Wider More Horizontal Narrower Longer More oblique Lungs Pleura