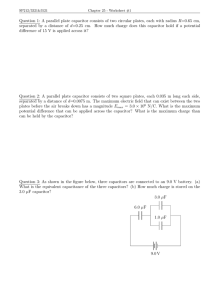
Physics 12 2015-2016 ACADEMIC YEAR GRADE 12 / PHYSICS Capacitors Worksheet : Capacitors (Problems) CAPACITORS (Problems) 1. 1. 2. 2. 3. A capacitor is connected to the terminals of a battery as shown in the figure. A Two capacitor is charged and disconnected batteryC1 capacitors are arranged as shown.from The the capacitor ashas shown in theof figure. a charge 20µC and the capacitor C2 is uncharged. The switches S1 and S2 are closed at the same time. After a dielectric is inserted between the plates of capacitor; After a dielectric is inserted between the plates of capacitor; increases a) The capacitance of capacitor ______________. remains the same b) Potential difference across the plates _____________. increases c) Charge of capacitor ______________. increases a)Calculate; The capacitance of capacitor ______________.. a) final charges of each capacitor. b) the potential difference across the plates of each decreases b) Potential difference across the plates _____________. capacitor. c) the energy stored in the capacitor C1. remains the same c) Charge of capacitor ________________. decreases d) The electric field between the plates _____________. 1 remains the same d) The electric field between the plates ____________. 4. c) Charge of capacitor ______________. DEMIC YEAR PHYSICS Capacitors S (Problems) d) The electric field between the plates ____________. Physics 12 3. 3. Worksheet : Capacitors (Problems) 4. Two capacitors are arranged as shown. The capacitor C1 has a charge of 20µC and the capacitor C2 is uncharged. The switches S1 and S2 are closed at the same time. 2. 4. A capacitor is charged and disconnected from the battery as shown in the figure. For the circuit given calculate a) Equivalent capacitance of the system b) Total charge of the system c) The charge of the each capacitor d) Potential difference across the plates of each capacitor. After a dielectric is inserted between the plates of Calculate; capacitor; a) final charges of each capacitor. b) the potential difference across the plates of each a) The capacitance of capacitor ______________.. capacitor. c) the energy stored in the capacitor C1. a) Ceq=2 µF difference across the plates _____________. a) b)QPotential total=20 µC b) Qtotal=24 µC Q/1=5 µC and Q/2=15 µC c) Charge of capacitor ________________. The electric b) d)V=5/3 voltsfield between the plates _____________. 4. c) E=(CV2)/2=(3.(5/3)2)/2=25/6 µJ 1 c) Q1= Q2=24 µC d) V1=8 V and V2=4 V Physics 12 Worksheet : Capacitors (Problems) Capacitors 5. 5. 6. 6. 7. The potential difference across the plates of C1 is 40 volts. After the capacitors are fully charged an insulator with K=2 is inserted between the plates of C1 and the system is again fully charged. Calculate; a) The potential difference of C2 b) The potential difference of battery c) The total charge of system For the given circuit, calculate a) The equivalent capacitance and the total charge of the system. a) What is change in the charge of C1? c)What The potential across b) is changedifference in the potential ofeach C1? capacitor. d) The charge stored on each capacitor. e) The electric potential energy of the system. a) Ceq= 2 F a) Q1= Q2=120 C then V2=(120)/(6)=20 V Q1= Q2=12 C then After dielectric is inserted; C/1=6 F then C/eq= 3 F b) V=40+20=60 V c) Ceq= 2 F and V=60 V Qtotal=2.60=120 C 6. After the capacitors are fully charged an insulator with Q/1= Q/2=18 C b) V1=4 V and V2=8 V After dielectric is inserted; 8. V/1=3 V and V/2=3 V After the capacitors are fully charged an insulator having Physics 12 Worksheet : Capacitors (Problems) Capacitors 7. 7. 6. 8. 8. After the capacitors are fully charged an insulator with K=2 is inserted between the plates of C1 and the system is again fully charged. For the given circuit, calculate a) The equivalent capacitance and the total charge of the system. Theispotential difference across capacitor. a) c) What change in the charge of C1each ? Theischarge stored each capacitor. b)d) What change in theon potential of C1? e) The electric potential energy of the system. a) Ceq= 1+2=3 µF Qtotal= 12.3 =36 µC After the capacitors are fully charged an insulator having a dielectric constant K=2 is inserted between the plates of C1 and the system is again fully charged. a) What is change in the charge of C1? b) What is change in the potential of C1? c) How does the charge of C2 change? Why? a) Q1= 3.12=36 µC b) V1= V2=12 V C1= 3 µF then c) Q1= 1.12 =12 µC C/1= 6 µF (with dielectric) Q2= 2.12 =24 µC d) Etotal=CV2/2=(3.122)/2 8. Etotal=216 µJ After the capacitors are fully charged an insulator having Q/1= 6.12=72 µC b) V1= V/1=12 V c) Q2= Q/2=48 µC Physics 12 Worksheet : Capacitors (Problems) Capacitors 9.9. 10. 10. 11. When the switch is open the totalthe charge of the syste When the switches S1Sand S2 are open, equivalent is Q1. When switch closed the total charge of the capacitance of thethe circuit is 6isµF. system becomes Q2. For the circuit given, Calculate a) charge stored on each capacitor b) potential difference across each capacitor c) energy stored in C2 the ratio capacitance of Q1/ Q2? of the circuit WhatCalculate is the equivalent when both switches are closed? When both switches are open a) 2 F and 4 F are parallel : 6 F Ceq=C =6 µF 6 F and 12 F are series : Ceq= 4 µF then Qtotal=4.12=48 µC Q1=48 µC, Q2=16 µC and Q3=32 µC When both switches are closed b) V1=4 V and V2=V3=8 V Ceq=10C/3 c) E2=(2.82)/2=64 J 10. When the switches S1 and S2 are open, the equivalent 12. Ceq=(10.6)/3=20 µF Physics 12 Worksheet : Capacitors (Problems) Capacitors 11. 11. 10. When the switch S is open the total charge of the system When the switches S1 and S2 are open, the equivalent is Q1. When the switch is closed the total charge of the capacitance of the circuit is 6 µF. system becomes Q2. 12. 12. Calculate the equivalent capacitance between points K and L. Calculate the ratio of Q1/ Q2? What is the equivalent capacitance of the circuit when both switches are closed? S is open; 4 F and 4 F are series Ceq=2 F then Q1=2.V Q1/Q2=(2.V)/(8.v/3) Q1/Q2=3/4 S is closed; 4 F and 4 F are paralle:8 F Ceq=8/3 F then Q2=8.V/3 12. Ceq=4+4+12 Ceq=20 F Physics 12 Worksheet : Capacitors (Problems) Capacitors 13. 13. 15. 14. 14. A 40 µF capacitor is charged by connecting it to 16 V battery. The battery is then disconnected and the charged capacitor is next connected across a 120 µF that was initially uncharged. After steady state has been reached, what is the charge on each capacitor and the voltage across each? If the potential difference between the ends of 3µF capacitor is 24 V, what is the potential difference between points K and L? What is the equivalent capacitance between th points K and L? Initially; Qi=40.16=640 µC then Qtotal=640 µC Q1=160 µC and Q2=480 µC (Q is directly proportional to C when two capacitors are parallel.) 6.V=3.24 VKL=12+24 V=12 V VKL=36 V Vcommon=160/40=4 V 4 Physics 12 Worksheet : Capacitors (Problems) Capacitors 15. 15. . 16. 16. 40 µF capacitor is charged by connecting it to 16 V ttery. The battery is then disconnected and the arged capacitor is next connected across a 120 µF that as initially uncharged. ter steady state has been reached, what is the harge on each capacitor and the voltage across ch? The potential difference between the two ends of 12 µF capacitor is 40 V. What is the equivalent capacitance between the points K and L? What is the amount of charge stored in the 6µF capacitor, in µC? 12 µF and 3 µF : parallel: 15 µF 6 µF and 4 µF : parallel: 10 µF 10 µF and 15 µF : series 8 F and 24 F : series : 6 F 6 F and 18 : parallel : 24 F 24 F and 12 F : series : Ceq=8 F Their charges are the same. 40.15=V.10 then V=60 V The charge on 6 µF capacitor is Q=6.60=360 µC