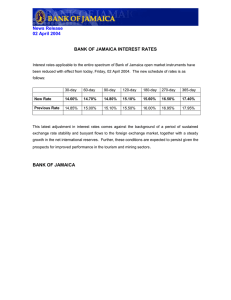
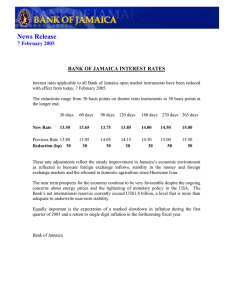
FIRST SPEAKER Introduction Panel of adjudicators, my fellow team mates, my worthy opponents, audience, a pleasant afternoon to you all. Today the affirmative team takes the stance that developing countries need more technology than developed countries. Technology is ubiquitous, simply put it is evident all around us; but what really is technology, what does it mean to be a developing country versus a developed one. Whilst there are numerous definitions for technology, according to the Oxford Dictionary, “technology is the use of methods, systems, and devices as a result of scientific knowledge for practical purposes, especially in industries.” Secondly, “a developed country otherwise known as a First World Country for example The United States of America is a country with a lot of industrial activity wherein people generally have high incomes, while a developing country, otherwise known as Third World Countries for example Jamaica is a country that has little industrial and economic activity wherein people generally have low incomes”, according to Cambridge Dictionary. The criterion used to differentiate between these countries would be per capita income which is the average income earned per person in a given region. We strongly agree with the moot because it allows for the growth and development of the Less Developed Countries through the countries’ governmental sectors. My task is to highlight how lack of technology impacts the health sector. The second speaker will focus on the manufacturing sector, the third speaker on the agricultural sector and the fourth speaker on the education sector. Healthcare Healthcare performance is strongly dependent on the economy. Investment in health is not only a desirable, but also an essential priority for societies. POINT – Less Developed Countries need more technology so as to improve the health systems for the country’s most valuable resources – us humans. EXPLANATION –With lack of healthcare comes low life expectancy which is one characteristic of developing countries. In many of the Less Developed Countries for example Bangladesh and parts of Africa, persons are faced with deplorable health infrastructure and as such these nations are unequipped with the necessary resources to fight diseases such as cancer, malaria, diabetes as well as HIV. EXAMPLE - According to Dr. Michael Rucker (2018), there are more cell phones on the planet than there are toilets or toothbrushes. Most of the world population now has access to a mobile phone and a mobile signal. In countries where access to health care is difficult and infrastructure is poor, development in health play an important role in bridging the divide between the developed and developing world. With the help of the mobile phone, diseases are now easier to diagnose and track, information can be disseminated quicker and reach more people, and online health education is more readily available to citizens in developing nations that are traditionally underserved. In her speech at the United Nations, Nancy Finn, a writer and thought leader on the impact of digital communication highlighted that Short Message Services (SMS) can be used to educate people and provide them with health information on best practices. Across Africa, text messages in local dialects can be sent to cellphone users to inform them about vaccination programs, malaria prevention, nutrition and basic hygiene. Furthermore, images of suspicious tissue can be taken with a cellphone and sent to an expert at a local hospital (or abroad) for inspection and treatment opinions, as seen in Botswana. Furthermore, for persons in need of medical supplies drones can be utilized to deliver these supplies, even in remote areas. Through the availability of technology, research can be conducted to develop treatments and possibly cures for diseases as seen in our very own country an Anti-Cancer drug developed by Professor Lawrence Williams of the University of Technology. LINK – These examples provided justifies why less developed countries need technology. If not for anything else, it can be used to save lives. SECOND SPEAKER Manufacturing If you always do what you always did, you will always get what you always got, famous quote by the American Industrialist Henry Ford. It is time for the countries deemed to be less developed to step it up a notch and become contenders among the more developed countries. With the aid of technology in the manufacturing sector such goal can be achieved. POINT – Therefore, without a doubt developing countries need more technology so as to improve the economic growth of one’s country. EXPLANATION - Economic Growth is the increase in the amount of goods and services produced in a country over time, according to the Cambridge Dictionary. With the use of technology, developing countries can benefit from economic growth to enable better living standards, lower unemployment, create higher tax revenues, and as such less money would be needed to spend on benefits such as subsidies, eg the Programme for Advancement Through Health and Education, the PATH program in Jamaica. Furthermore, with the utilization of technology in the manufacturing sector, the funds government have to borrow to maintain these countries will be significantly reduced. Also, it must be noted that with the implementation of technology in this sector, it allows for local companies to meet the demands of the crowded international market as well as compete globally. This allows for the country to earn foreign exchange, which then can be used to better the country. Moreover, adjustment of the manufacturing sector will create jobs for the people of its country through suitable training and provide goods and services to its own country, limiting importation of goods and services. EXAMPLES – In 1938, in Westmoreland, Jamaica, the Frome Sugar Factory had a high demand internationally for their quality sugar, but due to the lack of technology, they were unable to meet the demands of the market, losing most of the country’s revenue to countries in Europe whom manufactured sugar – beet through the use of technology. In this time period, sugar was one of Jamaica’s main export. Kenya, unlike Jamaica implemented technology into the manufacturing sector and as such as seen significant results. In a 2019 study of Supporting Economic Growth…of the African countries, Kenya has become the leader in economic growth as a developing country. Their increasing trend of economic growth is tracked to improvements in telecommunications, electricity, customs and regulations due to technology advancements. Similar to economic growth, labour productivity also increased in Kenya in the period 2001–2016, by 2% annually. Formal manufacturing employment also steadily increased, indicating the increased volume of high-productivity manufacturing activities taking place in Kenya. Kenyan firms with internet were found to be more productive and had a higher share of skilled workers than firms without access to internet. As firms became more tech - savvy, the share of skilled workers in total employment increased, suggesting the importance of targeted skill-development in coordination with public and private sector needs. LINK – Through the evidence provided, it can be clearly seen that without technology in the manufacturing sector there will be a damper in the country’s economic growth. Thus, developing countries need more technology than the developed. THIRD SPEAKER Agriculture According to the World Bank (2018), nearly 11% of the 7.42 billion world population is extremely poor, 78% of whom rely on agriculture for their livelihoods. POINT - Adoption of new agricultural technologies is core for agricultural development in developing countries which leads to sustainable development and reducing poverty. EXPLANATION – Sustainable development is development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs, according to Oxford Dictionary. With developing countries receiving more technology, agricultural productivity will increase, reducing poverty. In fact, agricultural growth is at least twice as effective in reducing poverty as in other sectors, according to the World Economic Forum (2018). Sustainable growth of the agricultural sector critically depends on the adoption of improved, scaleappropriate and eco-friendly technologies such as temperature and moisture sensors, aerial images, and GPS technology. With agricultural technology, farmers of developing countries will no longer have to apply water, fertilizers, and pesticides uniformly across entire fields. Instead, they can use the minimum quantities required and target very specific areas, or even treat individual plants differently. With agricultural technology comes higher crop productivity, decreased use of water, fertilizer, and pesticides, which in turn keeps food prices down, less runoff of chemicals into rivers and groundwater and safer foods being produced. EXAMPLES – In Pakistan agriculture is the main source of living. 48% of labour force is engaged directly with agriculture. About 70% of population is relates to agriculture directly or indirectly. Its contribution towards economic growth is about 25% which is higher than contribution by any other sector. It also provides employment to the public, wherein employment directly affects per capita income. With increase in per capita income living standards increase, higher hygiene facilities & better education facilities also increase. With technology being utilized, the money earned from the export of wheat, rice and cotton is used to import other technological equipment such as machinery or automobiles to improve the infrastructure of the country’s economy or for improving other sectors of the economy such as education and health. Digital technologies such as drones play an important role in transforming large-scale farming in Latin America and elsewhere. In our very own country, in St. Elizabeth, St. Ann and Trelawny, as well as other parts of the island, drone technology is currently being utilized by farmers. According to the Jamaica Information Service (2018), “The drones’ thermal imaging and multispectral cameras enable them to validate and count animals in a herd and identify those that have a higher than normal temperature, as well as identify disease stress of plants not readily seen with the naked eyes. In the event that theft has occurred of livestock, drones can be used to track their location via GPS. Furthermore, with Jamaica being prone to natural disasters, assessing damage to crops and livestock following natural disasters such as a flood or hurricane, will be easier, especially in remote areas and can better assist farmers to put measures in place to boost crop yield. These improvements raise farm productivity and facilitate diversification into non-traditional crops with higher returns. LINK – From the examples provided, adoption of new technology in agriculture is of high importance for poverty alleviation, longevity of sustainable development and furthermore the economic growth and development of developing countries. FOURTH SPEAKER Education According to Technical Education and Career Educator, Jenny Arledge, technology is the “wings” that will allow the educational world to fly farther and faster than ever before, if we will allow it. In the 21st century, technology knows no bounds. POINT – Therefore, less developed countries need more technology than the developed so as to improve human development and in turn the economic growth and development. EXPLANATION – Human Development, according to Oxford Dictionary, is the process of expanding people's freedoms and opportunities and improving their well-being. As such, the Human Development Index was created to emphasize that people and their capabilities should be the ultimate criteria for assessing the development of a country, not economic growth alone. With low literacy rates associated with the developing nations, according to Cambridge Dictionary, this is the percentage of people who are able to read and write. India’s literacy rate is currently at 69% while Canada’s literacy rate is currently at 99%. The education and training of a country's workers is a major factor in determining just how well the country's economy will do. A country's economy becomes more productive as the proportion of educated workers increases since educated workers can more efficiently carry out tasks that require literacy and critical thinking. However, obtaining a higher level of education also carries a cost, and this is where technology becomes useful. EXAMPLES - In the developing countries that incorporate education technology, for example Jamaica, they have seen improved literacy rates and have contributed to researches and innovated different products which allowed for boost in the country’s economy through revenues earned and companies being able to compete in the global market. Through implementation of technological devices, such as smartphones, tablets and laptops, persons can be enrolled in online courses to possibly learn a new language or even to receive training. The Massachusetts Institute of Technology Mathematician, Computer Scientist and Education Visionary Seymour Papert (2016) recognized that connected electronic devices improve the educational experience of students even for those who face poverty and geographical isolation. Papert who did extensive work on this matter in Kenya prior to his death was the first person to see that computers could be used to support children’s learning and development which later led to him developing The One Laptop per Child Initiative. This initiative was intended to provide low cost, low power and connected laptops to disadvantaged students around the world. LINK – From the examples provided, it is clearly seen that less developed countries need more technology so as to improve education and in turn improve the economic growth and development of countries through increase in human development.