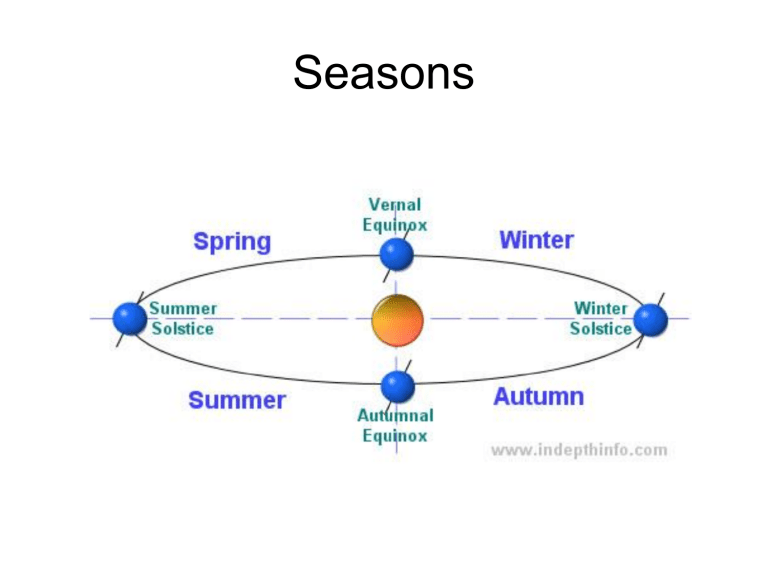
Seasons Seasons Vocabulary • • • • • • • • Altitude: the angle of a celestial body above the observer’s horizon. Azimuth: the distance in degrees measured clockwise from the due north position. Equinox: a time of year when the noon Sun is directly overhead at the equator, the hours of daylight and darkness are equal, and the entire Earth views sunrise directly in the east and sunset directly in the west. The vernal equinox occurs on/or about March 21 and marks the first day of spring in the Northern Hemisphere. The autumnal equinox occurs on/or about September 23 and marks the first day of autumn in the Northern Hemisphere. Horizon: the line around the edge of Earth where the celestial sphere meets Earth. Insolation: incoming solar radiation; that part of the Sun’s radiation that is received at Earth’s surface. Solar noon: the moment when the Sun crosses the meridian. Solstice: the two times of the year when the noon Sun is directly overhead at an angular distance of 23.5 degrees from the equator. In the Northern Hemisphere. The summer solstice occurs about June 21st and marks the first day of summer. The winter solstice occurs on about December 21st and marks the first day of winter. Zenith: the point on the celestial sphere that is directly above the observer’s position on Earth’s surface. Basic Info. for Seasons • Summer: – The first day of summer is June 21 (the Summer Solstice) – On 6/21 the sun at solar noon is shining directly on 23.5°N (Tropic of Cancer) • Winter: – The first day of winter is December 21 (the Winter Solstice) – On 12/21 the sun at solar noon is shining directly on 23.5°S (Tropic of Capricorn) • Spring/Fall: – The first day of fall is September 23 (the autumnal equinox) – The first day of spring is March 21 (the vernal equinox) – On 9/23 and 3/21 the sun at solar noon is shining directly on 0° (Equator) • Remember “EQU” words go together – EQUinox (3/21 & 9/23) EQUator (location of sun’s direct rays) EQUal (amounts of light and dark) Always ask yourself “Who is getting more sunlight?” • – – – North of the equator getting more sunlight = summer South of the equator getting more sunlight = winter North and south getting equal sunlight = spring and/or fall Seasons Diagrams – Type 1 • – When looking at this type of diagram, you should follow the following steps: 1. Locate the sun and shade the half of Earth that is in darkness. – When you are shading the Earth, the line separating dark from light is perpendicular to the sun. This line DOES NOT ALWAYS connect the north and south poles! 2. Now look at the North Pole. Is the North Pole in: – 100% light? This is summer. Earth diagram – 100% dark? Earth diagram 2 This is winter. Earth diagram 3 – 50% light and 50% dark? This is spring and/or fall. Shade the unlit portion of Earth and label the season for each diagram below: spring/fall 3/21 and 9/23 direct sunlight - 0° Equator summer 6/21 direct sunlight – 23.5°N Tropic of Cancer winter 12/21 direct sunlight – 23.5°S Tropic of Capricorn Seasons Diagrams – Type 2 • When determining the season and/or date using this type of diagram, you should focus on: 1. First, locating and labeling the compass directions (N,S,E,W) 2. Now locate the rising sun (positions D, E, F on the diagram). Is it… – Due (exactly) East? – This represents spring and/or fall. – North of East? – This represents summer. – South of East? – This represents winter. 3. Next, look at the altitude (height) of the sun at solar noon (positions A, B, C on diagram). Is it… 1. Lowest in the sky? – This represents winter. 2. Highest in the sky? – This represents summer. 3. In the middle? – This represents spring and/or fall. • For NY diagrams, the solar noon sun is always towards the south. 4. Also look at the length of the sun’s path on the diagram. – Shortest path (D-A-G) – represents winter – Medium path (E-B-H) – represents spring and/or fall – Longest path (F-C-I) – represents summer Season Diagrams – Type 3 • When this type of diagram is given for season determination, you should: 1. Look at the sun. Is it visibly closer to the left or right? If it is: – The Earth position that is closer to the sun (perihelion) – – The Earth position that is farther from the sun (aphelion) – 2. is winter. is summer. You can also look at the North Pole. Is it: – In 100% darkness (position C in diagram)? – – This is winter. In 100% light (position A in diagram)? – This is summer. Seasons Data DATE Location of sun at solar noon zenith Sunrise direction Sunset direction Total hours of daylight in N.Y. Total hours of daylight at North Pole 12/21 Winter Solstice Tropic of Capricorn 23.5°S South of East South of West 9 0 3/21 & 9/23 Spring & Fall Equinox Equator 0° due East due West 12 12 6/21 Summer Solstice Tropic of Cancer 23.5°N North of East North of West 15 24