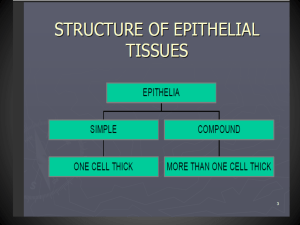
Histology Introduction & Epithelium By Rahat Anarbekov HISTOLOGY HISTOLOGY: the study of tissues - the branch of anatomy that deals with the microscopic structure of tissues HISTOLOGY tissues: groups of cells that are similar in structure & function 4 main types of tissue 1) Epithelial 2) Connective 3) Muscle 4) Nervous All tissues are interconnected! Epithelial Tissue EPITHELIAL TISSUE Also known as EPITHELIUM Is the lining, covering, and glandular tissue of the body FUNCTIONS OF EPITHELIUM 1) 2) 3) 4) Protection Absorption Filtration Secretion Characteristics of Epithelium 1) Cells fit closely together to form continuous sheets 2) Always one unattached (free) surface or edge * called the apical surface Characteristics of Epithelium 3) Lower surface of epithelial tissue rests on a basement membrane * thin layer of extracellular material to which epithelial cells are attached Characteristics of Epithelium 4) Epithelium is avascular = no blood supply of own blood gets to these cells by diffusion from capillaries 5) Epithelial cells can regenerate easily (if well nourished) Classification of Epithelium: Each type of epithelium has 2 names: First part of name = # of CELL LAYERS Second part of name = SHAPE Classification of Epithelium: First name: Simple = one layer of cells, very thin Functions: absorption, secretion, filtration Stratified = two or more layers of cells, more durable Functions: protection Classification of Epithelium: First name: Pseudostratified = “false” stratified, cells are different heights but still one layer Classification of Epithelium: Second name: Squamous = flattened, like fish scales or floor tiles Cuboidal = cube-shaped, like dice Columnar = column-shaped, thinner Classification of Epithelium: Simple vs. Stratified Stratified epithelia named for the cells at the free surface of the epithelial membrane Simple Squamous Epithelium Single layer of flat cells resting on a basement membrane Location: lines air sacs of lungs, blood vessels, lines ventral body cavity Function: exchange of substances by rapid diffusion, filtration, secretion Simple Squamous Epithelium Simple Cuboidal Epithelium Single layer of cube-shaped cells resting on a basement membrane Location: salivary glands; kidney; ovaries Functions: Secretion and absorption Simple Cuboidal Epithelium Nonciliated Simple Columnar Epithelium Single layer of nonciliated rectangular cells resting on a basement membrane Location: lines digestive, respiratory, urinary tracts Function: Secretion and absorption Nonciliated Simple Columnar Epithelium Contain absorptive and goblet cells Absorptive cells- columnar epithelial cells with microvilli (fingerlike projections that increase surface area, therefore increasing the rate of absorption) Goblet cells- modified columnar cells that secrete mucus Before mucus is released, it accumulates in the upper portion of the cell, causing that area to bulge out and resemble a goblet or wine glass Simple Columnar Epithelium Epithelial membranes that line body cavities which open to the body exterior are called mucous membranes Ciliated Simple Columnar Epithelium Single layer of ciliated columnar cells resting on a basement membrane Location: Upper respiratory tract Function: Moves mucus and other substances by ciliary action Ciliated Simple Columnar Epithelium Stratified Squamous Epithelium Multiple layers of cells, with squamous at the apical surface and cuboidal or columnar lining the basement membrane Location: Skin, mouth, throat Function: protection Stratified Squamous Epithelium Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium Two or more layers, with cube-shaped cells at the apical surface Location: large glands (sweat glands) Function: secretion Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium Stratified Columnar Epithelium Two or more layers of cells with columnar shaped cells at the apical surface Location: large glands Function: secretion Stratified Columnar Epithelium Transitional Epithelium Modified stratified squamous epithelium Basal layer: cuboidal/columnar Apical surface: vary in shape Location: urinary tract (bladder, ureters, urethra) Function: Cells can slide over each other to accommodate change in organ size Organs can stretch without rupturing Transitional Epithelium Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium Single layer of ciliated columnar cells of varying heights resting on a basement membrane Location: lines respiratory tract Function: Secretion and movement of mucus by ciliary action Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium 1: simple squamous 2: simple cuboidal - kidney 3: simple columnar – small intestine 4: ciliated pseudostratified columnar - trachea 5. Stratified squamous epithelium – tongue Glandular Epithelium Function: secretion Glandular cells often lie in clusters deep to the covering and lining epithelium A gland may consist of one cell, or a group of highly specialized cells They secrete substances into ducts, onto a surface, or into the blood Glandular Epithelium Endocrine glands Secretions enter extracellular fluid, then diffuse into the bloodstream without flowing through a duct Secretions are hormones (regulate metabolic and physiological activities to maintain homeostasis) Ex: pituitary, thyroid, adrenal glands Glandular epithelium Exocrine glands Secrete into ducts that empty at the surface of covering/lining epithelium or directly onto a free surface Skin or interior space (lumen) of a hollow organ Secrete mucus, sweat, oil, earwax, milk, saliva, digestive enzymes Ex: sweat glands, salivary glands Epithelium Review 1 2 3 4 5 6 Histology What is a tissue? Histology tissues: groups of cells that are similar in structure & function Epithelial Tissue Is the lining, covering, and glandular tissue of the body Functions of Epithelium 1) 2) 3) 4) Protection Absorption Filtration Secretion Pigeons Always Fly Straight Characteristics of Epithelium 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Abut Apical surface Basement membrane Avascular Regenerate Another Awesome Byrne Anatomy Review! Characteristics of Epithelium 1) Abut: Cells fit closely together to form continuous sheets 2) Apical Surface: Always one unattached (free) surface or edge Characteristics of Epithelium 3) Basement Membrane: Lower surface of epithelial tissue rests on * thin layer of extracellular material to which epithelial cells are attached Characteristics of Epithelium 4) Avascular: no blood supply of own blood gets to these cells by diffusion from capillaries 5) Regenerate: Epithelial cells can regenerate easily (if well nourished) Simple Squamous Specimen: artery Label: apical surface, nucleus of squamous cell Simple Cuboidal Specimen: Kidney Label: cuboidal cell, nucleus Simple Columnar Specimen: Small Intestine Label: goblet cells Pseudostrified ciliated columnar Specimen: Trachea Label: apical surface, cilia Stratified Squamous Specimen: Skin Label: squamous cell, apical surface Transitional Specimen: Urinary bladder Label: apical surface