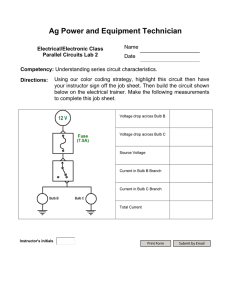
Electricity What is Electricity??? Definition: Electricity is a form of energy that can be easily changed to other forms. Where does Electricity come from? Mainly 2 sources: 1) Power Stations -Supply a lot of electricity -Used in many electrical appliances 2) Electric Cells (batteries) - Supply a little electricity - Portable - Safe How does anElectrical Appliance Work? • To make an electrical appliance work, electricity must flow through it. • The flow of electricity is called an electric current. • The path along which the electric current moves is called the electric circuit. Current??? electric cell connecting wire filament flow of electrons Definition: An electric current is the rate of flow of electric charges in a circuit. Electric Charges • Electric charges are made up of positive charges (protons) and negative charges (electrons). • When these charges flow in a circuit, a current is produced. How does electricity flow? • The battery in a circuit gives energy to the electrons and pushes them around a circuit, from the negative terminal of the cell, round the circuit and back to the positive terminal of the cell. How to Measure Current? • The SI unit for electric current is ampere (A). • Smaller currents are measured in milliamperes (mA). 1 A = 1,000 mA 1 mA = 0.001 A • Different electrical components and appliances require different sizes of current to turn them on. Instrument to Measure Current • An ammeter is an instrument used for measuring electric current. What is Electric Current? Electric current is a measure of the rate of flow of electric charge in a circuit. current = charge time I = q Coulomb, C t seconds, s Andre-Marie Ampere Image credit: https://scientibulous.wordpress.com/2012/06/07/poster-on-andre-marie-ampere/ Unit of current I = q Coulomb, C t seconds, s 1A=1C s A current of 1 A is 1 coulomb of charge flowing every second. So, a current of 5 A is 5 coulombs of charge flowing every second. Electric Circuits connecting wires •electric Electric circuits are made up cell electrical components light bulb • These components must be joined together without any in between to form a closed circuit board circuit. Note: Components refer to the light bulb, wires, battery Electric Circuits • Incomplete circuits are called open circuits. connecting wire is missing no source of electrical energy Both the circuits in the diagram are incomplete, hence they are known as “open circuits”. • a source of electrical energy and • a closed circuit connecting wires electric cell light bulb circuit board How to draw Circuit Diagrams Component Symbol Component + An electric cell Symbol + Battery Switch (open) Light bulb (lamp) Switch Connecting wires (not joined) Connecting wires (joined) Switch (closed) Symbols are used to represent the various electrical components in circuits. Examples of circuit diagrams: Switches A switch is used to open or close a circuit. Main switch used in buildings Switches used on circuit Circuit diagrams for open and closed circuits Open circuit. Bulb does not light up when the switch is Close circuit. Bulb w ill light up when the switch is Series andP a r a l l e l There are 2 ways in which an electric circuit can be arranged: 1. Series 2.Parallel Series Circuit • A series circuit connects the components one after the other • A single loop is formed • A break in any part of a series circuit stops the flow of current in the whole circuit. P a r a l l e l Circuit • A parallel circuit divides into two or more branches. • The current divides and flows through each parallel branch. • If a component breaks or is removed, the other components remain on. Which of the following is a series circuit? Which is a parallel circuit? Which is brighter? What is Voltage? Voltage (also known as Potential difference) is the work done (or energy transferred) between two points in a circuit, per coulomb of charge. It is the “push” to the charges in the circuit. Voltage is measured in volts (V). work done charge 1V=1 J C A 1 V cell gives 1 joule (J) of energy to each coulomb of charge. voltage = So, a 12 V battery gives 12 J of energy to each coulomb of charge. Alessandro Volta Image credit: https://pbs.twimg.com/media/C6HwLIrWUAEiev6.jpg Voltage • An electric cell gives energy to the electrons and pushes them round a circuit. Voltage is a measure of how much energy the electrons receive. • Different voltages are supplied by different cells and batteries. 1.5VDry Cell 12VCar Battery 9 VDry Cell How t o Measure Voltage? • The SIunit for voltage is volt (V). • Avoltmeter is an instrument used for measuringvoltages. Voltmeter • Voltmeters must be connected in parallel to thecircuit. • The positive side of voltmeter is connected to th e positive terminal of the ce l l , andvice versa. Recall: Ammeter!!! • It must be connected in series in the circuit. • Positive side of ammeter mustbe connected nearest to the positive t erminal of the battery (electr ic cell), and vice versa. Electromotive Force (e.m.f) • Electromotive force is the same as voltage. • E.m.f refers to the amount of energy supplied by the electric source (eg. battery) to each unit of electric charge. • E.m.f is also measured by a Vm Electromotive Force (e.m.f) Potential Difference (P. ) d . Potential Difference • (p.d) Remember Diffusion? • High Low • Similarly, electric charges will flow from a point of higher potential (energy) to lower potential electric cell connecting wire filament flow of electrons •This difference in electric potential between 2 points in a circuit is known as the potential difference. It is the same as VOLTAGE also. What is Resistance? Resistance (R) is a property of a material that prevents the flow of charges. Resistance is measured in ohms (Ω). resistance = 1Ω=1 voltage current V A Resistance is measured using an ohmmeter. Resistance • When an electric current f l o w s through a circuit, there w i l l be some resistance that opposes it. (similar to friction) • It can be measured by voltage over current Resistance • Good conductors o f electricity have LOWRESISTANCE. (Eg. Metal objects) –Electricity is able to f l o w through them very easily • Poor conductors o f electricity have HIGH RESISTANCE. (Eg. Wood, cloth) –Electricity is not able toflow Resistance • The SI unit f o r resistance is ohm () • Different electrical components have different resistance • For example, nichrome wires have a higher resistance than copper wires. So should we use nichrome o r copper to make wires? Example 1 • An electric rice cooker operates at 240 V and uses a current o f 8 A. What is the Vroelstiasgtean(Vc)eo f the rice cooker? =240 V Current (I) =8 A R= V I 240 R= 8 = 30 Resistor A resistor is a component designed to reduce the current. Resistors are often used with components that require less current than is being supplied to the whole circuit. Most electronic circuits need to have resistors to work properly. Resistors can be produced that reduce the current by different amounts. Describe how does this system works? How will you vary the flow of water? Describe how does this system works? https://www.google.com.ph/search?q=current+voltage+resistance+analogy&source=lnms&tbm=isch&sa=X&ved=0ahU KEwjEiMKdk7_aAhWGqo8KHalDAyIQ_AUICigB&biw=1350&bih=643#imgrc=6lM9OM8HVr9P0M: The Unfortunate Siblings of Benjamin Ohm’s law Ohm’s law is a formula that links voltage, current and resistance. Resistance is measured in ohms (Ω). voltage = current × resistance V=I×R Depending on the values given, the formula can be used to calculate voltage, current and resistance in a circuit. What two other equations could you write from this Ohm’s law formula triangle? What does Ohm’s law mean? These three equations can be derived from the Ohm’s law formula triangle. But what do they actually mean? • • • V=I×R If the voltage increases, then either the current flowing through a material or the resistance will also be increased. R = V/I The resistance of a material is constant for a given temperature, which means that current and voltage must be proportional. I = V/R For a low resistance material, more current is allowed to flow for a given voltage. For a high resistance material, less current will flow at the same voltage. A bulb has a current of 20 A and a voltage of 100 V What is the resistance? R = V I = 100 V 20 A = 5Ω Resistors • An electrical component that is specially made to have a certain resistance is called a resistor. • They can be connected in a circuit to resist the current flow. Fixed Resistors and Variable Resistors • Fixed resistors have only one resistance value • Variable resistors can be adjusted to change the resistance. fixed resistor symbol •Variable resistors are useful in light dimmers and variable resistor symbol S/E:Resistors • Resistors can be connected in series or parallel extra resistor in series results in dimmer bulb Resistors connected in SERIES single resistor extra resistor in parallel results in brighter bulb Resistors connected in PARALLEL S/E: Resistors in Series • When resistors are connected in series, the resistance w i l l add up and increase. 2 3 • R = RT1 h+eRt2ot+alRr3e…sistance for this circuit is: 2+3=5 S/E: Resistors in P a r a l l e l • When resistors are connected in parallel, the resistance will decrease • This is because they will provide alternate routes for the current to flow. S/E: Resistors in P a r a l l e l 1 = 1 + 1 R2 R1 R + 1 R3 What is the resistance of the cir1cuit1? + 1 R = 6 6 6 2 1 = 6 R 6 = 1 3 R = 3 The final resistance is WhatElectrical is Electrical Power? Power (also known as Wattage) • is the rate at which an electric appliance converts electrical energy to other forms. (rate of energy transfer) • is expressed in terms of “watts”. Watt is equivalent to Joule per second. • is a product of the voltage and current passing through the component. power (W) = voltage (V) × current (A) P = IV We can express the relationship between current, voltage and power mathematically using the equation: Power = Current x Voltage P=IV Voltage measured in Volts (V) Current measured in Amps (A) Power measured in Watts (W) Electrical Power power (W) = voltage (V) × current (A) What is the power of a bulb which uses a 230 V mains supply and has a current of 0.44 A passing through it? P = V × I = 230 × 0.44 = 101.2 W What is the voltage across a microchip if it has a normal operating power of 0.5 W and draws a current of 0.1 A? V = P ÷ I = 0.5 ÷ 0.1 = 5 V Other equations for Power Electrical power can also be calculated using resistance. The equations linking power to resistance are found by substituting the equation V = I × R into the power equation: P=V×I P=V×I and… V=I×R and… I=V÷R Therefore, using substitution: Therefore, using substitution: P=I×R×I P=V×V÷R P = I2 × R P = V2 ÷ R Power calculations If you have a filament bulb and it has a potential difference of 200V across it and a current of 0.2A running through it. At what power is the bulb operating at? P = IV P = 0.2A x 200V P = 40W Power calculations If you have a filament bulb and it operates at a power of 60W and it has a potential difference of 240V across it, what is the current running through the bulb? P I I I = IV = P/V = 60W / 240V = 0.25A Concept Check Suppose you are buying a refrigerator and you have a choice between two models with labels shown below. Which will you take? Why? Refrigerator A 220 V 0.82 A 60 cycles Refrigerator B 220 V 0.75 A 60 cycles What is Electrical Energy Electrical Energy • The amount of electrical energy consumed by a certain appliance can be calculated as the product of it power rating and the duration of usage. Electrical Energy = Power x time • is expressed in terms of “Joules” • It can also be expressed in Watt.hour (Wh) or kiloWatthour (kWh) Prove that Wh is a unit of Energy 1 Wh = (1 W) (1 hr) = (1 J/s)(3600 s) 1 Wh = 3600 J 1 kWh = 3, 600, 000 J Sample Problem 1)A 20 w table lamp is used for 10hrs. How much energy is consumed in kWh? Given: P = 20 w t = 10 hrs E = Pt = (20 w) (10 hrs) = 200 Wh 200 Wh x 1 kWh 1000 Wh = 0.20 kWh Sample Problem 2) The power rating of a light bulb when use at 220 v is 50 W a) How much current passes through it ? b) How much energy is consumed in 10s ? Given: A.) B) P= 50 w P= IV E= Pt V= 220 v I= _P_ = (50 W)(0.0028 hrs) t = 10 s = 0.14 Wh = 0.0028 hrs I= 50 w V = 0.00014 kWh 220 v I= 0. 227 A Electrical Power and Electrical Energy What do we pay for in our Electric Bill – is it Electrical Power or Electrical Energy? Heating Effect o f Electric Current • When an electric current f l o w s through a wire, the wire heats up. Electrical energy has been converted into heat energy. • The greater the resistance o f the wire, the greater the amount o f heat produced. This heating effect is used in common electrical appliances. Iron Kettle Hair Dryer A kettle uses both copper and nichrome wires. Copper has low resistance while nichrome has high resistance. Which material, copper or nichrome, should be used for the heating element, and for the external wire? Use copper wire for the external wire as it has low resistance & produces less heat Use nichrome wire for the heating element as it has high resistance& produces a lot of heat Heating Effect o f Electric Current ARGON (inert/unreactive gas) filament wire produces heat and light In a light bulb, the heated filament which is also a resistance wire, becomes so hot that light is also emitted. Chemical Effect o f Electric Current What is ELECTROLYSIS? Definition: • Electrolysis is the chemical change that occurs when an electric current passes through solutions or molten compounds. Electrolysis There are 2 uses o f electrolysis: 1)Electroplating 2)Extraction o f Metals 1.E lectroplating • Inelectroplating, a key is covered with a thin layer of copper when electricity is passed through the sol- ution.+ copper wire key start copper sulphate solution copper on the key after a few minutes Uses o f Electroplating Metal objects canbe plated with a thin layer of another 2. Extraction of metals • Some metals (eg. sodium, aluminium) are obtained by electrolysis. • To extract the metal – heat the solid compound of the metal until it melts – pass an electric current through the molten compound Magnetic Effect o f a Current • Astraight wire is placed neara compass. When an electric current flows through the wire, the compass needle is deflected. This shows that an electric current has a magnetic effect. current in wire compass needle is deflected Electromagnet • An electromagnet is a magnet that is made by using electricity • It consist o f a wire coiled around a metal metal r o d (eg. Iron) coil of wire iron core to battery compass needle is strongly attracted to iron core Electromagnet The magnetic effect of the electromagnet can be increased by: 1. increasing the current (by using more batteries) 2. increasing the number of turns of wire in the coil 3. Using an iron rod Differences between an electromagnet and a magnet: Electromagnet Magnet A temporary magnet which can be turned on and o f f using electric current. A permanent magnet which retains magnetism until it is purposely demagnetised (spoilt). Magnet can be made stronger o r weaker Magnet remains the same strength Uses o f Electromagnets • Cranes that l i f t iron/steel • Iron/steel separ ators • Electric bells • Magnetically crane Electric bell Electric motor in fans