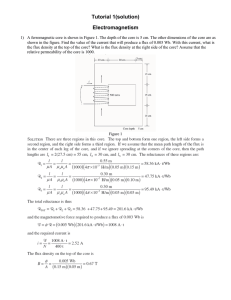
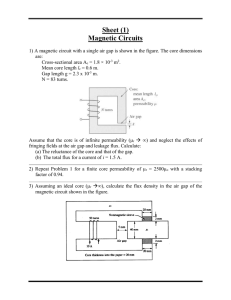
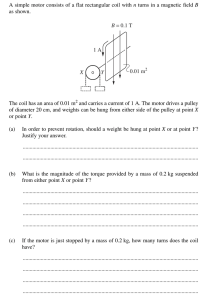
EEL1196 Instrumentation and Measurement Techniques Chapter 5 Tutorial 5: Magnetic Measurements 5.1 An iron ring of 3.5cm2 cross-sectional area with a mean length of 100cm is wound with a magnetising winding of 100 turns. A secondary coil of 200 turns of wire is connected to a ballistic galvanometer having a constant of 1 micro-coulomb per scale division, the total resistance of the secondary circuit being 2000 ohm. On reversing a current of 10A in the magnetising coil, the galvanometer gave a throw of 100 scale divisions. Calculate the flux density in the specimen and the value of the permeability at this flux density. (Answer: B = 1.43 wb/m2, µ = 1.43 × 10-3 H/m) 5.2 A magnetic circuit consists of an annular ring of mean diameter 15cm with a single narrow saw-cut through the ring. The width of the saw-cut is 0.1cm and the cross sectional area of the ring is 4cm2 with a magnetization curve given by the following table: H (At/m) 40 80 120 160 800 1600 3200 2 B (Wb/m ) 0.37 0.72 0.92 1.04 1.4 1.47 1.55 A coil 0f 400 turns is uniformly wound on the ring. Estimate the current in the coil required causing a flux of 0.28 mWb in the air gap formed by the saw-cut. (Answer: I = 1.49 A) 5.3. A fluxmeter with a single turn search coil and an area of 50cm2 shows a 100 divisions difference between two successive deflections. Assuming that the air damping effect and the resistance, both are small: i) calculate the change of flux linkages of the search coil, when the produced flux density is 1 Wb/m2. ii) It is proposed to extend the range of fluxmeter to measure flux densities 5 times the above using the same search coil and method of reversals. If the resistance of search coil is 1, find the resistance of the shunt to be connected in parallel with the fluxmeter. (Answer: i) Δ = 0.5 wb, ii) Rs = 0.25Ω) 5.4 An iron ring has a mean diameter of 0.1 m and a cross section of 33.5 × 10-6 m2. It is wound with a magnetizing winding of 340 turns and the secondary winding of 220 turns. On reversing a current of 10 A in the magnetizing winding, a ballistic galvanometer gives a throw of 272 scale divisions, while a Hilbert Magnetic Standard 1/2 EEL1196 Instrumentation and Measurement Techniques Chapter 5 (Bar Sample) with 10 turns and a flux of 2.5 × 10-4 gives a reading of 102 scale divisions, other conditions remaining the same. Find the relative permeability of the specimens. (Answer: µr = 33.089) 5.5 A fluxmeter with 5 turns of search coil and an area of 40 cm2, is showing a 20 divisions difference between two successive deflections. Calculate the change of flux linkages of the search coil if the produced flux density is 0.1 Wb/m2. Assume that the air damping effect and the resistance, both are small. [Final Exam 2014] (Answer: Δ = 8 mwb) 5.6 A current of 10 A is flowing through the magnetizing winding of 314 turns that wound on an iron ring specimen. The specimen has a mean diameter of 10 mm and a cross section of 40 mm2. If the flux is 16 × 10-6 wb, find the relative permeability of the specimen. (µo=4 × 10-7). [Final Exam 2015] (Answer: µr = 10) Self-Test Question 5.7 A magnetizing winding of 60-turns wound uniformly on an iron ring having a mean diameter of 0.1m and a cross-sectional area of 1cm2. A secondary winding of 20-turns is connected to a fluxmeter having a constant of 0.1×10-3 weber turn per division. When a current of 2A is reversed in the primary winding, a deflection of 33 divisions is observed. Determine: (i) the applied magnetizing force, H. (ii) the flux density, B. (iii) total flux linkages in the iron ring, . (iv) the relative permeability of the specimen, µr. [Final Exam Trimester 2, 2016/2017] (Answer : i) H = 381.92 A-turns/m, ii) B= 0.825 wb/m2, iii) =8.25×10-5 Wb, iv) µr = 1719) 2/2