Krugman ‘International Economics: Theory and Policy’ Chapter 14 Presentation
advertisement

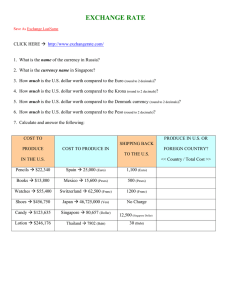
ASSIGNMENT 1-CHAPTERS 13, 14, 15 DUE IN CLASS ON FEB 5th, TUESDAY. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Government purchases are defined as A) all goods and services purchased by the federal, state, or local government. B) goods and services purchased from the government. C) all goods and services purchased by the federal government. D) only goods purchased by federal, state, or local governments. E) all goods and services purchased by the federal or state government. p 2) In an open economy, private saving,S , is equal to A) B) C) D) I - CA - (G - T). I + CA + (G - T). I + CA + (G + T). I - CA + (G - T). E) I + CA - (G - T) 3) For open economies A) S = I. B) S < I + CA. C) S > I + CA. D) S = I – CA E) S = I + CA. 4) Which one of the following statements is the MOST accurate? A) GDP less depreciation is called net national product (NNP). B) GNP less depreciation is called net factor product (NFP). C) GDP plus depreciation is called net national product (NNP). D) GNP less depreciation is called net national product (NNP). E) GNP plus depreciation is called net national product (NNP). 5) Movements in GDP A) are not allowed to differ at all from movements in GNP by definition. B) differ greatly from movements in GNP. C) are not relevant to an examination of national income. D) do not differ greatly from movements in GNP. E) need to be inflation adjusted in order to match movements in GNP. 6) A country's gross national product (GNP) is A) the value of all intermediate goods and services produced by its factors of production and sold on the market in a given time period. 1 B) the value of all final goods and services produced by its factors of production, excluding land, and sold on the market in a given time period. C) the value of all final goods and services produced by its factors of production and sold on the market within the domestic country. D) the value of all final goods and services produced by its factors of production and sold on the market in a given time period. E) the value of all final and intermediate goods produced by its factors of production and sold on the market in a given time period. 7) In the United States over the past fifty years, the fraction of GNP devoted to consumption has fluctuated in a range of about A) 32 to 39 percent. B) 22 to 29 percent. C) 62 to 70 percent. D) 42 to 49 percent. E) 82 to 89 percent. 8) If the dollar interest rate is 10 percent and the euro interest rate is 6 percent, then an investor should A) invest only in dollars. B) invest only in dollars if the exchange rate is expected to remain constant. C) invest only in euros if the exchange rate is expected to remain constant. D) invest only in euros. E) be indifferent between dollars and euros. 9) The covered interest rate parity condition can be stated as follows: The interest rate on dollar deposits equals the interest rate on euro deposits ________ the forward ________ on euros against dollars. A) plus; discount B) minus; discount C) plus; premium D) times; premium E) minus; premium 10) What is the expected dollar rate of return on euro deposits if today's exchange rate is $1.10 per euro, next year's expected exchange rate is $1.166 per euro, the dollar interest rate is 10%, and the euro interest rate is 5%? A) -1% B) 10% C) 15% D) 11% E) 0% 11) If the goods' money prices do not change, a depreciation of the dollar against the pound A) makes American jeans more expensive in terms of British sweaters. B) makes British sweaters cheaper in terms of American jeans. C) makes British jeans more expensive in Britain. D) doesn't change the relative price of sweaters and jeans. 2 E) makes British sweaters more expensive in terms of American jeans. 12) Given PUS and YUS A) An increase in the European money supply causes the euro to appreciate against the dollar, but it does not disturb the U.S. money market equilibrium. B) An increase in the European money supply causes the euro to depreciate against the dollar, and disturbing the U.S. money market equilibrium. C) An increase in the European money supply causes the euro to appreciate against the dollar, and it creates excess demand for dollars in the U.S. money market. D) An increase in the European money supply causes the euro to depreciate against the dollar, but it does not disturb the U.S. money market equilibrium. E) An increase in the European money supply causes the euro to depreciate against the dollar, and it creates excess demand for dollars in the U.S. money market. 13) The aggregate real money demand schedule L(R,Y) A) slopes downward because a fall in the interest rate raises the desired real money holdings of each household and firm in the economy. B) slopes downward because a rise in the interest rate makes consumers less focused on the liquidity of their assets. C) has a zero slope because a fall in the interest rate keeps constant the desired real money holdings of each household and firm in the economy. D) slopes downward because a fall in the interest rate reduces the desired real money holdings of each household and firm in the economy. E) slopes upward because a fall in the interest rate raises the desired real money holdings of each household and firm in the economy. 14) A reduction in a country's money supply causes A) its currency to appreciate in the foreign exchange market. B) affects other countries currency in the foreign market. C) does affect its currency in the foreign market in an ambiguous manor. D) does not affect its currency in the foreign market. E) its currency to depreciate in the foreign exchange market. 15) A foreign exchange swap A) make up a negligible proportion of all foreign exchange trading. B) is a spot sale of a currency. C) is a forward repurchase of the currency. D) is a spot sale of a currency combined with a forward sale of the currency. E) is a spot sale of a currency combined with a forward repurchase of the currency. 3 SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS. 1) Calculate the Expected Dollar Depreciation Rate against the euro and the expected dollar return on euro deposits if the expected exchange rate is $1.10 per euro. Expected Dollar Expected Dollar Today's Dollar/Euro Interest Rate on Depreciation Rate Return on Euro Exchange Rate Euro Deposits Against Euro Deposits E$/€ R€ (1.10 - E$/€)/E$/€ R€ + (1.10 - E$/€)/E$/€ 1.10 0.03 1.08 0.03 1.06 0.03 1.04 0.03 1.02 0.03 2) Using a figure describing both the U.S. money market and the foreign exchange market, analyze the effects of a temporary increase in the European money supply on the dollar/euro exchange rate. 3) Combine a graph showing the interest parity condition and one showing money demand and supply to demonstrate simultaneous equilibrium in the money market and the foreign exchange market. How would an increase in the U.S. money supply affect the Dollar/Euro exchange rate and the U.S. interest rate? Illustrate your answer graphically and explain. 4) Using an identity, discuss the different uses of private saving in open economies. 5) You are provided with the following information about a country's international transactions during a given year: 4 Service exports Service imports Merchandise exports Merchandise imports Income flows received, net Unilateral transfers made, net Increase in the country’s holding of foreign assets, net (excluding official reserves assets) Increase in foreign holdings of the country’s assets, net (excluding official reserve assets) Statistical discrepancy, net a. b. $346 $354 $480 $348 $153 $142 $352 $252 $154 Calculate the current account and the financial account balance of this country. Show your work. Is the country increasing or decreasing its net holdings of official reserve assets? Show your work. 5