art-appreciation-report
advertisement

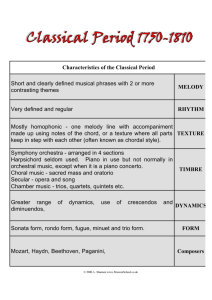
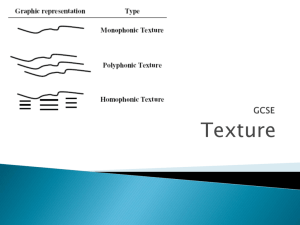
Tempo • An Italian word which literally means “time”. In Music it refers to Speed. Music may move at a fast, Moderate, or slow speed and varying degrees. • Tempo is more accurately indicated in musical scores by metronome designations, which show the number of beats per minute. Basic Tempo Markings • Allegro(Fast)(120-156 bpm) • Vivace(Lively)(156-176 bpm) • Moderato(Moderate Spped)(108-120 bpm) • Andante(Moderately slow)(76-108 bpm) • Adagio(slower than andante)(66-76 bpm) • Lento(Slow)(45-60 bpm) • Largo(Very Slow)40-60 bpm) Melody is that element of music which makes the most direct appeal. It is generally what we remember and whistle or hum. By melody we mean an ordely succession of tones or musical sounds. Melody divides itself into two halves, each half is called Phrase. In music, as in language, a phrase denotes a unit of meaning within a larger structure. Motif is the smallest melodic unit which expands into a phrase, a tones easily encompassed in one breath. Cadence in music means a closing phrase. An entire melody is formed out of repeated and contrasting phrases. Characteristic of Melody Dimension Melody has two dimensions. Length and Range. Length of the melody is relatively to the number of measurement which compose it. Generally speaking, popular songs consist of one, two or more melodies which are repeated several times. Range is the pitch distance from its lowest to its highest tone. Register is the relatively highness or lowness of the aggregate tones of a melody.It may have a high, medium or low register. Direction – Melody moves in two direction of pitch, upward and downward.A melody may move rapidly or gradually in either direction: rapidly ascending, rapidly descending, gradually ascending and gradually descending. A melody which remains at a given pitch, moving neither up nor down any appreciable distance is called a static melody. Progression refers to the intervals(pitch distance) between the tones as melody move from one tone to the next. Tone as distinguished from common noise, is a sound produced by regular vibrations of air. Sounds made by wind, traffic, clapping of hands, or creaking of the doors are merely noise because vibrations are irregular. Components of tone Pitch refers to the highness or lowness of a tonal sound. It is a physical principle that the faster the vibration are, the higher the pitch will be and the slower the vibrations, the lower the pitch. Duration is determined by the length of time the vibration is sustained. Intensity of Volumes Tones may vary in their degree of loudness and softness. Intensity is fundamental to musical rhythm(as accent), and it provides the basis for a separate musical element(dynamics). Timbre or quality This property enables one to distinguish one sound from another, one instrument from another. HARMONY Simultaneous sounding of two or more tones. Chord progression Chords not only are constructed in a variety ways, but also progress from one to another according to many different plans. - The scheme by which chords change. Consonance and dissonance Consonance certain combinations of tones produce a quality of repose or relaxation. Dissonance certain other combinations of tones produce a quality of unrest or tension. Tonality • is the arrangement of pitches and/or chords of a musical work in a hierarchy of perceived relations, stabilities, attractions and directionality. In this hierarchy, the individual pitch or triadic chord with the greatest stability is called the tonic. • The most common use of the term "is to designate the arrangement of musical phenomena around a referential tonic in European music from about 1600 to about 1910" (Hyer 2001). Contemporary classical music from 1910 to the 2000s may practice or avoid any sort of tonality—but harmony in almost all Western popular music remains tonal.[vague] Harmony in jazz includes many but not all tonal characteristics of the European common practice period, sometimes known as "classical music". Polytonality Music which two or more keys are combines simultaneously in a single composition,. - Is used to bring out the different levels or planes of the harmony. Multitonality Displaced tonality. Atonal It is music that rejects the framework of key. Dynamics • Forte- loud • Piano- soft • Fortissimo- very loud Pianissimo- very soft • Mezzo forte- moderately loud • Mezzo piano-moderately soft To the direction of dynamics: Crescendo- becoming louder Diminuendo- becoming soft Sudden stress forzando(accent on a single note or chord). The number of terms embraces both tempo and dynamics. Andante fairly slow and majestic - Implies a stately pace and full sonority Timbre Is tone of quality. Every musical medium has its own distinctive quality of tone.The tone quality of each of the following instruments – a piano, an organ, an orchestra, a band, a voice, and the like- can be easily identified by anyone who has heard this instruments. Texture In music, texture refers to the melodic and harmonic relationship of musical factor. Types of Texture • Monophonic Texture • Homophonic Texture • Polyphhonic Texture • Nonmelodic Texture Monophonic Texture Is the simplest of musical textures, consisting of a melody, typically sung by a single singer or played by a single instrument player without accompanying harmony or chords. Homophonic Texture Here, we have a single melody with chords. We here homophonic texture when the pianist plays the melody with his right hand while the left sounds the chords, or when the singer carries the tune against a harmonic accompaniment on the piano. A folk song with guitar accompaniment is homophonic music. Polyphonic Texture Or many voice texture. this is the combination of two or more melodies of more or less equal prominence. The terms “polyphonic” and “contrapuntal” are nearly synonymous. To create polyphonic texture, there should be at least be two melody sounded simultaneously. Nonmelodic Texture Is created for sound effects in which harmonic sounds obscure or partly exclude the melodic content of a composition. This occurs in contemporary and modern music. Sonority Is an attribute of texture which is based more on harmonic than melodic consideration. This refers to quality of richness or thinness of texture.it is determined by: 1. The number of parts 2. Spacing of tones 3. Register of tones 4. timbre 1. The Number of Parts Refers to the number of voices 2. Spacing of Tones Refers to the musical intervals between the parts. 3. Register of Tones Refers whether the tones are high, medium or low. 4. Timbre Refers to the tone quality .