Human Traits Lab
advertisement

Create a Baby Lab
THE HEAD OF THE COIN = THE DOMINANT FORM OF A TRAIT…THE CAPITAL LETTER
*THE FIRST PART OF THE LAB, YOU HAVE TO DETERMINE THE SEX OF THE CHILD….ONLY
THE PERSON REPRESENTING THE MALE FLIPS THE COIN AS THE ONE WHO REPRESENTS THE
FEMALE ALREADY IS AN X.
IF THIS PERSON FLIPS HEADS, THE CHILD IS XX – A GIRL
IF THIS PERSON FLIPS TAILS, THE CHILD IS XY- A BOY
AT THE END OF THIS LAB, HAND IN THE ANSWERS TO THE TERMS, THE CHARTS FILLED IN
WITH YOUR ALLELES, GENOTYPE AND PHENOTYPE AND A COLORED DRAWING OF YOUR
“BABY.”
Purpose: To demonstrate the principles of Mendelian genetics and sex determination, including the concepts of
allele, phenotype, genotype, dominant, recessive, codominant, homozygous and heterozygous by creating a
simulated baby.
Materials: Two pennies, art supplies, paper.
Procedure:
1) Working with a partner, determine the genotype of the baby by flipping pennies. "Mom" flips one penny to
choose an allele for her egg and "Dad" flips the other to choose an allele for his sperm. (Note that the gender of
the baby is a special case and is determined by dad alone. Boys are XY and girls are XX. Mom can give only an
X but dad can give either an X or a Y.)
2) Record the alleles which resulted from the coin flips, and put "sperm and egg" together. (You cannot pick the
traits you want; life doesn't work that way!) Write down baby's genotype for each trait in Table 1. Heads
represents allele #1 and tails represents allele #2.
3) Record the baby's phenotype in Table 1. Note: Dominant alleles are written with an uppercase letter and
recessive alleles are written as lowercase letters. Dominant alleles mask the expression of recessive ones. Codominant alleles are written as uppercase letters with a subscript. Co-dominant alleles result in a phenotype that
is blended.
4) Repeat steps 1, 2, and 3 for all traits and then draw, color, and name your creation. Remember that you are
drawing a baby's face - not a child's or an adult's (no tattoos, no mustaches, no pierced ears, noses, etc., and not
too much hair!)
Name of people in group
:_______________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
Period:___________________________
Questions:
1. Why is the coin flip used to represent the selection of alleles?
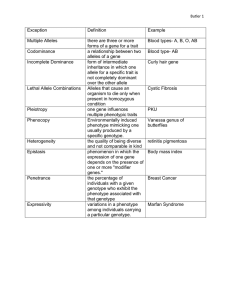
2. Define the following terms:
allele-
phenotype-
genotype-
dominant-
recessive-
codominant-
homozygous-
heterozygous-
chromosomelocusgeneResults: Keep track of the toss of each coin; if the person representing the female gets tails, the trait letter is
lower case; heads, it would be the upper case letter. The other person flips their coin and lets’ say they get
heads.
TRAIT for face shape uses the letters R for round shape and r for square shape.
If the first person got tails, the letter in the allele from mom would be “r”
If the second person get heads, the letter in the allele from dad would be R
The genotype would be Rr.
The phenotype would be R
Table 1: Check here indicating whether you are the mom
or the dad
and fill in the data below.
Mom's Name: ________________ Dad's Name _________________ Baby's Name: ________________
Trait
Allele from Mom Allele from Dad
Genotype
Phenotype
Gender
______X______
_____________ _____________ _____________
Face Shape
_____________
_____________ _____________ _____________
Chin Shape
_____________
_____________ _____________ _____________
Chin Dimple
_____________
_____________ _____________ _____________
Freckles
_____________
_____________ _____________ _____________
Cheek Dimples
_____________
_____________ _____________ _____________
Lip Thickness
_____________
_____________ _____________ _____________
Eye Brows
_____________
_____________ _____________ _____________
Eye Shape
_____________
_____________ _____________ _____________
Eyelashes
_____________
_____________ _____________ _____________
Ear Shape
_____________
_____________ _____________ _____________
Ear Lobes
_____________
_____________ _____________ _____________
Widow's Peak
_____________
_____________ _____________ _____________
Hair Curliness
_____________
_____________ _____________ _____________
Eyebrow Color
_____________
_____________ _____________ _____________
Eye Width
_____________
_____________ _____________ _____________
Eye Size
_____________
_____________ _____________ _____________
Mouth Size
_____________
_____________ _____________ _____________
Nose Size
_____________
_____________ _____________ _____________
Birth Mark
_____________
_____________ _____________ _____________
Skin Tone
_____________
_____________ _____________ _____________
Polygenic Trait Alleles from Mom Alleles from Dad
Genotype
Phenotype
Hair Color
#1____ #2____
#1____ #2____
__ __ /__ __ _____________
Eye Color
#1____ #2____
#1____ #2____
__ __ /__ __ _____________
Genotype/Phenotype Reference Sheet
Trait
Face Shape
Chin Shape
Chin Dimple
Freckles
Cheek Dimples
Lip Thickness
Eye Brows
Genotype/Phenotype
(Homozygous for
Allele 1)
Ear Shape
Ear Lobes
Widow's Peak
Hair Curliness
Eyebrow Color
Genotype/Phenotype
(Homozygous for Allele
#2)
RR
Rr
rr
Round
Round
Square
NN
Nn
nn
Noticeable
Noticeable
Less Noticeable
AA
Aa
aa
Absent
Absent
Present
FF
Ff
ff
Present
Present
Absent
DD
Dd
dd
Present
Present
Absent
TT
Tt
tt
Thick
Thick
Thin
BB
Bb
bb
Bushy
Bushy
Fine
WW
Ww
ww
Wide
Wide
Round
LL
Ll
ll
Long
Long
Short
RR
Rr
rr
Long
Long
Round
FF
Ff
ff
Free
Free
Attached
Eye Shape
Eyelashes
Genotype/Phenotype
(Heterozygous)
WW
Ww
ww
Present
Present
Absent
C 1 C1
C 1 C2
C 2 C2
Curly
Wavy
Strait
D1D1
D1D2
D2D2
Darker than
hair
W1W1
Eye Width
Eye Size
Mouth Size
Nose Size
Birth Mark
(mole)
Skin Tone
Hair Color
Eye Color
Close
Together
Same as hair
Lighter than hair
W1W 2
W2W 2
Average
Far apart
S1S 1
S1S 2
S2 S2
Large
Medium
Small
M1 M 1
M1 M 2
M2 M 2
Wide
Medium
Narrow
P1P1
P 1P2
P 2P2
Small
Medium
Large
B1B1
B1B2
B2B2
Left cheek
Absent
Right cheek
S 1S1
S1 S2
S 2S2
Light
Medium
Dark
AABB=Black
AaBB=Dark Brown
aaBB=Blond
AABb=Black
AaBb=Light Brown
aaBb=Blond
AAbb=Red
Aabb=Dark Blond
aabb=white (albino)
AABB=Deep Brown
AaBB=Greenish Brown
aaBB=Green
AABb=Deep Brown
AaBb=Light Brown
aaBb=Light Blue
AAbb=Brown
Aabb=Gray-Blue
aabb=Pink
Human Trait Activity
Introduction:
When students practice Punnett squares, teachers often give them problems involving plants or small
mammals. Students may enjoy finding out about some of their traits.
For this exercise, all dominant traits will be heterozygous. This will make the results a little more
interesting, and will save time and paper.
After the students determine their traits and their genes, they will 'mate' with their partner. For each trait,
the partners will set up and complete a Punnett square and determine the phenotypic ration of the offspring.
If help is needed in determining what the traits look like, refer to the Create-A-Baby-Lab.
Objectives:
1. To practice Punnett squares.
2. To investigate genetic traits that affect themselves.
Materials:
1. Partner ('Mate')
2. Pens or pencils
Procedure:
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Mark off your traits in Table 1.
Determine and record your gene make up in Table 2.
Mark off your partner's traits in Table 1.
Determine your partner's genetic make up in Table 2.
Using the information in Table 2, set up and complete a Punnett square for each of the traits.
Determine the phenotypic ration for each trait.
Results:
Table 1:
Your phenotype and your partner's phenotype. (Remember: a dominant trait is automatically
heterozygous for this activity.)
Dominant Traits
You
Partner
Recessive Traits
Trait
You
Dark Hair
(Dd)
Widows' Peak
(Ww)
Free Ear
Lobes (Ee)
Partner
Freckles (Ff)
Right Handed
(Rr)
Straight
thumb (Ss)
Tongue Roller
(Tt)
Trait
Light Hair
(dd)
Straight Hair
(ww)
Attached Ear
Lobes
(ee)
No freckles
(ff)
Left Handed
(rr)
Hitch-hikers
thumb (ss)
Non-tongue
Roller (tt)
Table 2: Gene Make Up
Record genotypes in Table 2.
Trait
Your genes
Partner's genes
Hair color
Hair line
Ear lobes
Freckles
Hand Preference
Thumb
Tongue
Punnett Squares: For each trait above, cross you and your partner’s genotype. Record the
Phenotypic ratio.
Phenotypic Ratio:_________________________
Phenotypic Ratio:_________________________
Phenotypic Ratio:_________________________
Phenotypic Ratio:_________________________
Phenotypic Ratio:_________________________