HUMAN HEREDITY
advertisement

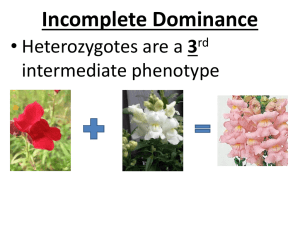
HUMAN HEREDITY Vocab • • • • • • • • • • • • Allele Codominance Dihybrid cross Dominant F1 generation F2 generation Genetic disorder Genetics Genotype Heredity Heterozygous Homozygous •Incomplete dominance •Law of Independent Assortment •Law of Segregation •Monohybrid cross •Multiple Alleles •Mutation •Pedigree •P generation •Phenotype •Probability •Recessive •Sex linked trait Mendel and Heredity R. GILBERT Why are you the way you are? What’s different about these people? • Have people ever said you look similar to your mom or dad? • Do you look exactly like either of your parents? • Why do you think this happens? Genetics is the study of how traits are inherited. Gregor Mendel • Considered the “Father of genetics” • Austrian monk who studied the plants in his garden; specifically the pea plant • The first to use the mathematics of probability to explain heredity Heredity The passing of traits from the parent to the offspring Genetics The study of heredity Genes and alleles • Genes on chromosomes control the traits that show up in an organism – Genes control traits like • • • • • Eye color Skin color Dimples Hair type Many more… • Alleles are different forms of a trait that a gene may have. – The gene for controlling dimples has two alleles: Dimples No dimples – The gene for controlling hair color has many alleles: • • • • • Blonde Black Red Brown Many, many others Mendel’s contribution • Hybrids – offspring that receive different genetic information for a trait from each parent…YOU ARE A HYBRID! • Dominant alleles – covers up or dominates the other trait (written as a capital letter) • Recessive alleles – the trait that seems to disappear (written as a lower case letter) Traits • For each trait, an individual has two factors: one from mom and one from dad – If the factors have the same information the individual is homozygous • Two dominant alleles or two recessive alleles – If the factors have different information the individual is heterozygous • One dominant and one recessive allele Parent Parent Dimples (d) No Dimples (D) (Recessive) (Dominant) Offspring (Dd) No dimples Laws of Heredity • Law of Segregation – members of each pair of alleles separate when gametes are formed (meiosis) Laws of Heredity • Law of Independent Assortment – pairs of alleles separate independently of one another during gamete formation Genotype- the genetic makeup of an organism (examples: TT, Tt, tt) • Homozygous- an organism with two alleles for one trait that are the same (TT) • Heterozygous- an organism with two alleles for one trait that are different (Tt) Phenotype- what an organism looks like because of its genotype Probability helps you predict the chance that something will happen. • Punnet Squares – Help you predict what an offspring will look like • Upper case lettersstand for dominant alleles • Lower case lettersstand for recessive alleles Monohybrid Cross A cross that provides data about one pair of contrasting traits Dihybrid Cross A cross that involves two pairs of contrasting traits Incomplete Dominance • An individual displays a trait that is intermediate between two parents – Example: red flower x white flower = pink flower Codominance • Two dominant alleles are expressed at the same time – Example: red coat horse x white coat horse = red and white coat horse Multiple Alleles • Traits that have genes with more than two alleles – Example: human blood types have three alleles – A, B, O Pedigrees • Family history of traits recorded over generations • Used to study human heredity and identify which relatives exhibit a trait