Complications of pediatric airway management for anesthesia
advertisement

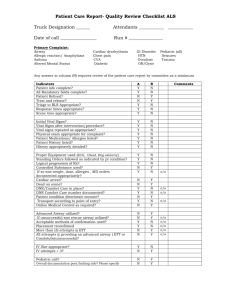
31/07/2018 Complications of pediatric airway management for anesthesia - UpToDate ® OfficialBy reprint from UpToDate This site uses cookies. continuing to browse this site you are agreeing to our use of cookies. www.uptodate.comContinue ©2018 UpToDate, and/or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. or find outInc. more. Complications of pediatric airway management for anesthesia Authors: Narasimhan Jagannathan, MD, MBA, Nicholas Burjek, MD Section Editors: Carin A Hagberg, MD, Lena S Sun, MD Deputy Editor: Marianna Crowley, MD All topics are updated as new evidence becomes available and our peer review process is complete. Literature review current through: Jun 2018. | This topic last updated: Mar 14, 2018. INTRODUCTION — Perioperative complications of airway management are more common in children than adults, and may result in critical events, including cardiac arrest. The incidence, prevention, and management of airway­related complications in children during anesthesia will be reviewed here. Basic principles of airway management for pediatric anesthesia are discussed separately. (See "Airway management for pediatric anesthesia".) INCIDENCE OF AIRWAY RELATED COMPLICATIONS — Airway and respiratory events are the most common perioperative complications in pediatric patients [1­3]. Several studies have reported on the incidence of pediatric airway­related complications. Consistently reported risk factors for serious airway complications include very young age and multiple intubation attempts. The Pediatric Perioperative Cardiac Arrest Registry found that respiratory events lead to 27 percent of all pediatric perioperative cardiac arrests. Laryngospasm was the most common cause of respiratory­related arrests; other etiologies included airway obstruction, difficult intubation, esophageal intubation, and aspiration [4]. A prospective observational multicenter cohort study of severe critical events in anesthesia (the Anaesthesia PRactice In Children Observational Trial [APRICOT] study) included 31,127 anesthetics in pediatric patients across 33 European countries [2]. Respiratory and airway events accounted for 60 percent of all anesthesia­related complications and occurred in 3.1 percent of all anesthetics; laryngospasm occurred in 1.2 percent, bronchospasm in 1.2 percent, postoperative stridor in 0.7 percent, and aspiration in 0.1 percent of all anesthetics. The highest rates of airway and respiratory events occurred in neonates (<1 month old) and infants (<1 year old). Other risk factors for respiratory complications included history of prematurity and reactive airway disease. A multicenter registry study of difficult intubations in 13 children's hospitals in the United States (the Pediatric Difficult Intubation [PeDI] study) found that among 1018 cases of difficult intubations, 20 percent had at least one complication [5]. The most common severe complication was cardiac arrest (2 percent of patients), and the most common nonsevere temporary complication was hypoxemia (oxygen saturation [SpO2] <85 percent). Risk factors for complications included weight <10 kg, more than two intubation attempts, short thyromental distance, and three or more attempts at direct laryngoscopy before switching to a more advanced intubation technique. The effect of the choice of airway device on the incidence of perioperative respiratory adverse events (laryngospasm, bronchospasm, and postoperative stridor) is discussed separately. (See "Airway management for pediatric anesthesia", section on 'Supraglottic airway versus endotracheal tube'.) https://www.uptodate.com/contents/complications-of-pediatric-airway-management-for-anesthesia/print?search=pulmonary%20aspiration%20anesthesia&sourc… 1/9 31/07/2018 Complications of pediatric airway management for anesthesia - UpToDate HYPOXEMIA — Infants and young children are particularly prone to rapid oxygen desaturation, hypoxemia, and This cardiovascular site uses cookies. decompensation By continuing when rendered to browse apneic this during site you anesthesia. are agreeing Hypoxemia to ourmay use occur of cookies. because of inability to ventilate by mask,Continue but can also or occur find out in the more. few seconds after the facemask is removed and before ventilation is reinstituted via a successfully placed airway device. Infants have high vagal tone compared with adults, and are likely to experience severe bradycardia and cardiac arrest in response to hypoxemia, particularly when combined with stimulation of the airway. Among 1018 children who were difficult to intubate, hypoxemia (>10 percent decrease from preintubation oxygen saturation [SpO2] for more than 45 seconds) occurred in 9 percent of patients, and cardiac arrest occurred in 16 percent of these patients who became hypoxemic [5]. All cardiac arrests were preceded by hypoxemia. Strategies for avoiding hypoxemia during airway management in children are discussed separately. (See "Airway management for pediatric anesthesia", section on 'Maintenance of oxygenation'.) LARYNGOSPASM — Laryngospasm can occur during induction, maintenance, or emergence from anesthesia, and most commonly occurs during light levels of anesthesia. Laryngospasm must be recognized and treated rapidly to prevent complications. In most cases, laryngospasm responds to treatment without sequelae, but oxygen desaturation, bradycardia, negative pressure pulmonary edema, aspiration, and cardiac arrest can occur. Laryngospasm is the reflex closure of the false and true vocal cords, accompanied by the descent of the epiglottis over the laryngeal orifice. Laryngospasm may progress from inspiratory stridor, retractions, and rocking chest wall movement with inspiration, to complete cessation of air movement despite inspiratory effort. Risk factors for laryngospasm — The incidence of laryngospasm during anesthesia is higher in children than in adults, and ranges from 1.7 to 25 percent [6­8]. Factors that increase the risk of laryngospasm during anesthesia include the following: Airway instrumentation during light anesthesia. Vocal cord irritation by inhalation anesthetics, secretions, mucus, or blood. Young age, with infants at highest risk [6]. Recent or current upper respiratory infection [9,10]. Passive smoke exposure [11]. Obstructive sleep apnea. Airway anomaly. Airway procedures (eg, tonsillectomy) [12]. Prevention of laryngospasm — Strategies that may be used to prevent laryngospasm during induction of anesthesia include the following: Delay elective surgery for children with current or recent upper respiratory infection. (See "Anesthesia for the child with a recent upper respiratory infection", section on 'Timing of elective procedures'.) Suction nasal and oropharyngeal secretions, if present. Perform laryngoscopy, intubation, or insertion of a supraglottic airway (SGA) during deep plane of anesthesia (ie, sevoflurane with or without propofol). For children over the age of one year, use an SGA rather than an endotracheal tube (ETT) when either would be appropriate. (See "Airway management for pediatric anesthesia", section on 'Supraglottic https://www.uptodate.com/contents/complications-of-pediatric-airway-management-for-anesthesia/print?search=pulmonary%20aspiration%20anesthesia&sourc… 2/9 31/07/2018 Complications of pediatric airway management for anesthesia - UpToDate airway versus endotracheal tube'.) This site uses cookies. By continuing to browse this site you are agreeing to our use of cookies. Administer muscle relaxant for intubation. Continue or find out more. Management of laryngospasm — Treatment for laryngospasm should commence as soon as it is recognized. Steps for management are described here and appear in an algorithm (algorithm 1) [13]. Administer 100 percent oxygen by facemask. Obtain tight mask seal, and deliver continuous positive airway pressure with jaw thrust, neck extension, and mouth open. If necessary, place oral airway, particularly if the nasal airway is obstructed (eg, by nasal secretions, adenoids, anatomic factors). Deepen anesthesia with sevoflurane or propofol. If no improvement, administer medications as follows: • Succinylcholine 0.25 to 0.5 mg/kg intravenous (IV), if bradycardia occurs, atropine 0.02 mg/kg IV; OR succinylcholine 3 to 4 mg/kg IM, if bradycardia occurs, atropine 0.02 mg/kg IM. • Ventilate by mask, SGA, or endotracheal intubation until neuromuscular block resolves. BRONCHOSPASM — Bronchospasm can occur during anesthesia as a result of stimulation from an airway device, aspiration of gastric contents, anaphylaxis, or underlying reactive airway disease. Prevention and treatment of bronchospasm during anesthesia are discussed separately. (See "Anesthesia for the child with asthma or recurrent wheezing", section on 'Intraoperative bronchospasm'.) ASPIRATION — Aspiration of gastric contents is a rare complication of pediatric airway management, with reported incidences ranging from 0.02 to 0.1 percent of all anesthetics in children. Patients are instructed to fast preoperatively to empty the stomach and reduce the risk of aspiration and the severity of pulmonary effects if aspiration occurs. (See "Preoperative fasting guidelines", section on 'Pediatric patients' and "Preoperative fasting in children and infants".) Risk factors for aspiration — Risk factors for aspiration in children include American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) physical status of III or IV and emergency procedures [2,14­16]. While most studies find the highest rates of aspiration at induction and laryngoscopy, up to one­half of these events may occur during maintenance of anesthesia or at extubation [2,14]. Light anesthesia and high intra­abdominal pressure (eg, due to lithotomy positioning) are additional risk factors for aspiration during maintenance with a supraglottic airway (SGA) in place [14]. Aspiration events during maintenance of anesthesia are more common in patients managed with an SGA, mask anesthetic, or natural airway rather than an endotracheal tube (ETT). (See "Airway management for pediatric anesthesia", section on 'Supraglottic airway versus endotracheal tube'.) Management of aspiration — If an aspiration event is suspected, the patient should be placed in head down position. Immediate management should include the following steps: Remove an SGA, if used, as it can trap gastric contents at the glottic opening. Suction the mouth and pharynx, and administer 100 percent oxygen by face mask. Evaluate for laryngospasm and bronchospasm, and treat as necessary. (See 'Laryngospasm' above and 'Bronchospasm' above.) For large particle aspiration, summon assistance to evaluate for possible rigid bronchoscopy. Subsequent management depends on the severity of signs and symptoms, the timing of the aspiration, the perceived cause of aspiration, and the urgency of the procedure. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/complications-of-pediatric-airway-management-for-anesthesia/print?search=pulmonary%20aspiration%20anesthesia&sourc… 3/9 31/07/2018 Complications of pediatric airway management for anesthesia - UpToDate Outcome and disposition after aspiration — Morbidity from pulmonary aspiration varies widely, ranging from Thisnosite observable uses cookies. sequelae Bytocontinuing severe hypoxemia to browse andthis acute site respiratory you are distress agreeing syndrome. to our use Based of cookies. on large prospective observational studies of anesthesia­related Continue or find aspiration out more. in pediatric patients, pulmonary sequelae occur in one­third to three­fifths of patients who aspirate [14,16]. If pulmonary sequelae occur, they do so within two hours of aspiration. Therefore, patients may be discharged from the hospital two hours after suspected aspiration if they have no new pulmonary symptoms (eg, cough or wheeze) and have normal oxygen saturation on room air. Children with mild symptoms who maintain oxygen saturation (SpO2) >90 percent with low level oxygen supplementation via nasal cannula can be observed on a patient ward. Children who require mechanical ventilation or high fraction of inspired oxygen should be admitted to the intensive care unit. Recovery in severe cases may take days to weeks, though death due to aspiration in otherwise healthy children is extremely rare [15,16]. POSTINTUBATION CROUP — Postintubation croup may occur in the post­anesthesia care unit (PACU) in recently extubated children. This occurs due to local edema and inflammation caused by pressure of the endotracheal tube (ETT) on laryngeal or subglottic structures. Even a small amount of edema can cause a significant increase in airway resistance because of the small internal diameter of the trachea in young children. Symptoms may include barking cough, inspiratory stridor, suprasternal or subcostal retractions, respiratory distress, and cyanosis. Risk factors for postintubation croup — Risk factors include those related to the patient, airway management, and procedure [17]. Age one to four years old More than one intubation attempt Coughing with an ETT in place Lack of an airway leak with >25 cm H2O airway pressure Non­supine position or changes in patient position during surgery Intubation longer than one hour Prevention of postintubation croup — In all children, an appropriately­sized cuffed ETT should be used to minimize the need for reintubation for an incorrectly­sized tube. (See "Airway management for pediatric anesthesia", section on 'Endotracheal tube'.) The goal for all children should be to achieve a smooth, controlled emergence from anesthesia without laryngospasm or bronchospasm, oxygen desaturation, coughing, or vomiting. Techniques for emergence and extubation are discussed separately. (See "Airway management for pediatric anesthesia", section on 'Emergence and extubation'.) For children who undergo oropharyngeal or neck surgery, or have other risk factors for postintubation croup (multiple intubation attempts, absence of an airway leak), dexamethasone 0.5 to 0.6 mg intravenous (IV) is routinely administered intraoperatively. Dexamethasone may also decrease postoperative nausea and vomiting and pain. (See "Anesthesia for tonsillectomy with or without adenoidectomy in children", section on 'Dexamethasone'.) Treatment of postintubation croup — Treatment of postoperative croup is primarily based on clinical experience and the treatment of infectious croup. Dexamethasone: 0.6 mg/kg IV to a maximum 10 mg, if not given intraoperatively [18]. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/complications-of-pediatric-airway-management-for-anesthesia/print?search=pulmonary%20aspiration%20anesthesia&sourc… 4/9 31/07/2018 Complications of pediatric airway management for anesthesia - UpToDate Nebulized epinephrine administered over 15 minutes, as follows (see "Croup: Pharmacologic and This supportive site uses interventions", cookies. By section continuing on 'Nebulized to browse epinephrine'): this site you are agreeing to our use of cookies. Continue or find out more. • Racemic epinephrine 0.05 mL/kg per dose (maximum of 0.5 mL) of a 2.25 percent solution diluted to 3 mL total volume with normal saline OR • L­epinephrine 0.5 mL/kg per dose (maximum of 5 mL) of a 1:1000 dilution Racemic and L­epinephrine are equally effective. The treatment may be repeated every 15 to 20 minutes if necessary. Disposition after postintubation croup — The effects of racemic epinephrine typically last for two hours [19], after which symptoms may recur. Children who receive epinephrine should be observed in the hospital for at least three to four hours after administration. (See "Croup: Pharmacologic and supportive interventions", section on 'Precautions'.) Children who at three to four hours are breathing comfortably, without stridor, and have normal oxygen saturation (SpO2) on room air may be discharged home with instructions to return to the emergency department if symptoms recur [20,21]. Children who require repeated doses of epinephrine should be admitted to the hospital or intensive care unit, as indicated, for further monitoring and treatment. SUMMARY AND RECOMMENDATIONS Airway and respiratory events (eg, laryngospasm, bronchospasm, aspiration, and perioperative croup) are the most common perioperative complications in pediatric patients. (See 'Incidence of airway related complications' above.) Risk factors for serious airway complications include very young age and multiple intubation attempts. (See 'Incidence of airway related complications' above.) Hypoxemia can occur rapidly during airway management, and can lead to bradycardia and cardiac arrest, particularly in infants. (See 'Hypoxemia' above.) Laryngospasm occurs more commonly in children than in adults, and can occur during induction, maintenance, or emergence from anesthesia. (See 'Laryngospasm' above.) The most important preventive measure is avoidance of airway manipulation during light anesthesia. Treatment includes administration of 100 percent oxygen by continuous positive airway pressure, deepened anesthesia, and if necessary, administration of succinylcholine (algorithm 1). (See 'Management of laryngospasm' above.) Bronchospasm can occur during anesthesia as a result of stimulation from an airway device, aspiration of gastric contents, anaphylaxis, or underlying reactive airway disease. (See 'Bronchospasm' above.) Aspiration of gastric contents is a rare complication that can occur during any stage of anesthesia. If aspiration is suspected, initial management should include the following (see 'Management of aspiration' above): • Suction the oropharynx • Administer 100 percent oxygen by facemask • Evaluate for and treat bronchospasm and laryngospasm • For large particle aspiration, summon assistance for possible bronchoscopy https://www.uptodate.com/contents/complications-of-pediatric-airway-management-for-anesthesia/print?search=pulmonary%20aspiration%20anesthesia&sourc… 5/9 31/07/2018 Complications of pediatric airway management for anesthesia - UpToDate Subsequent management and disposition depend on the severity of signs and symptoms. (See 'Outcome This and site disposition uses cookies. after aspiration' By continuing above.)to browse this site you are agreeing to our use of cookies. Continue or find out more. Croup can occur after endotracheal intubation due to local edema and inflammation caused by pressure of the endotracheal tube (ETT) on laryngeal or subglottic structures. (See 'Prevention of postintubation croup' above.) The most important preventive measure is the use of an appropriately­sized ETT. Treatment for postintubation croup includes administration of dexamethasone 0.6 mg/kg intravenous (IV) to a maximum of 10 mg, if not administered intraoperatively, and if necessary, administration of nebulized epinephrine. (See 'Treatment of postintubation croup' above.) Children who receive nebulized epinephrine should be observed in the hospital for at least three to four hours after administration. Children who require repeat doses of epinephrine should be admitted to the hospital for further monitoring and treatment. (See 'Disposition after postintubation croup' above.) Use of UpToDate is subject to the Subscription and License Agreement. REFERENCES 1. Mir Ghassemi A, Neira V, Ufholz LA, et al. A systematic review and meta­analysis of acute severe complications of pediatric anesthesia. Paediatr Anaesth 2015; 25:1093. 2. Habre W, Disma N, Virag K, et al. Incidence of severe critical events in paediatric anaesthesia (APRICOT): a prospective multicentre observational study in 261 hospitals in Europe. Lancet Respir Med 2017; 5:412. 3. Morray JP, Geiduschek JM, Caplan RA, et al. A comparison of pediatric and adult anesthesia closed malpractice claims. Anesthesiology 1993; 78:461. 4. Bhananker SM, Ramamoorthy C, Geiduschek JM, et al. Anesthesia­related cardiac arrest in children: update from the Pediatric Perioperative Cardiac Arrest Registry. Anesth Analg 2007; 105:344. 5. Fiadjoe JE, Nishisaki A, Jagannathan N, et al. Airway management complications in children with difficult tracheal intubation from the Pediatric Difficult Intubation (PeDI) registry: a prospective cohort analysis. Lancet Respir Med 2016; 4:37. 6. Olsson GL, Hallen B. Laryngospasm during anaesthesia. A computer­aided incidence study in 136,929 patients. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 1984; 28:567. 7. Burgoyne LL, Anghelescu DL. Intervention steps for treating laryngospasm in pediatric patients. Paediatr Anaesth 2008; 18:297. 8. Cravero JP, Beach ML, Blike GT, et al. The incidence and nature of adverse events during pediatric sedation/anesthesia with propofol for procedures outside the operating room: a report from the Pediatric Sedation Research Consortium. Anesth Analg 2009; 108:795. 9. von Ungern­Sternberg BS, Boda K, Chambers NA, et al. Risk assessment for respiratory complications in paediatric anaesthesia: a prospective cohort study. Lancet 2010; 376:773. 10. Flick RP, Wilder RT, Pieper SF, et al. Risk factors for laryngospasm in children during general anesthesia. Paediatr Anaesth 2008; 18:289. 11. Lakshmipathy N, Bokesch PM, Cowen DE, et al. Environmental tobacco smoke: a risk factor for pediatric laryngospasm. Anesth Analg 1996; 82:724. 12. Mamie C, Habre W, Delhumeau C, et al. Incidence and risk factors of perioperative respiratory adverse events in children undergoing elective surgery. Paediatr Anaesth 2004; 14:218. 13. Orliaguet GA, Gall O, Savoldelli GL, Couloigner V. Case scenario: perianesthetic management of laryngospasm in children. Anesthesiology 2012; 116:458. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/complications-of-pediatric-airway-management-for-anesthesia/print?search=pulmonary%20aspiration%20anesthesia&sourc… 6/9 31/07/2018 Complications of pediatric airway management for anesthesia - UpToDate 14. Walker RW. Pulmonary aspiration in pediatric anesthetic practice in the UK: a prospective survey of Thisspecialist site uses cookies. By continuing to browse site you are agreeing to our use of cookies. pediatric centers over a one­year period.this Paediatr Anaesth 2013; 23:702. Continue or find out more. 15. Borland LM, Sereika SM, Woelfel SK, et al. Pulmonary aspiration in pediatric patients during general anesthesia: incidence and outcome. J Clin Anesth 1998; 10:95. 16. Warner MA, Warner ME, Warner DO, et al. Perioperative pulmonary aspiration in infants and children. Anesthesiology 1999; 90:66. 17. Koka BV, Jeon IS, Andre JM, et al. Postintubation croup in children. Anesth Analg 1977; 56:501. 18. Russell KF, Liang Y, O'Gorman K, et al. Glucocorticoids for croup. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2011; :CD001955. 19. Bjornson C, Russell K, Vandermeer B, et al. Nebulized epinephrine for croup in children. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2013; :CD006619. 20. Rizos JD, DiGravio BE, Sehl MJ, Tallon JM. The disposition of children with croup treated with racemic epinephrine and dexamethasone in the emergency department. J Emerg Med 1998; 16:535. 21. Kunkel NC, Baker MD. Use of racemic epinephrine, dexamethasone, and mist in the outpatient management of croup. Pediatr Emerg Care 1996; 12:156. Topic 117125 Version 1.0 https://www.uptodate.com/contents/complications-of-pediatric-airway-management-for-anesthesia/print?search=pulmonary%20aspiration%20anesthesia&sourc… 7/9 31/07/2018 Complications of pediatric airway management for anesthesia - UpToDate GRAPHICS This site uses cookies. By continuing to browse this site you are agreeing to our use of cookies. Continue or find out more. Management of laryngospasm in children CPAP: continuous positive airway pressure; IV: intravenous; IM: intramuscular. * If succinylcholine is contraindicated, administer rocuronium 1.2 mg/kg IV, or if no IV access, 1 mg/kg IM in children <1 yr of age, 1.8 mg/kg IM in children >1 year of age; expect prolonged duration of paralysis. Adapted from: Orliaguet GA, Gall O, Savoldelli GL, Couloigner V. Case scenario: perianesthetic management of laryngospasm in children. Anesthesiology 2012; 116:458. Graphic 113030 Version 1.0 https://www.uptodate.com/contents/complications-of-pediatric-airway-management-for-anesthesia/print?search=pulmonary%20aspiration%20anesthesia&sourc… 8/9 31/07/2018 Complications of pediatric airway management for anesthesia - UpToDate Contributor Disclosures This site uses cookies. By continuing to browse this site you are agreeing to our use of cookies. or find out more. Narasimhan Jagannathan, MD, MBA Continue Travel support: Mercury Medical [Airway (Air-Q)]. Consultant/Advisory Boards: Teleflex [Airway (LMA)]; Vyaire Medical [Nasal oxygenation (SuperNova Mask)]. Nicholas Burjek, MD Nothing to disclose Carin A Hagberg, MD Grant/Research/Clinical Support: Ambu [Airway management (Ambu aScope 3, Ambu AuraFlex, Ambu AuraGain, Ambu Aura-I, Ambu AuraOnce, Ambu AuraStraight, Ambu Aura40, King Vision Video Laryngoscope, King Vision Video Laryngoscope aBlade System, King LT, King LT-D, King LTS, King LTS-D)]. Consultant/Advisory Boards: Ambu [Airway management (Ambu aScope 3, Ambu AuraFlex, Ambu AuraGain, Ambu Aura-I, Ambu AuraOnce, Ambu AuraStraight, Ambu Aura40, King Vision Video Laryngoscope, King Vision Video Laryngoscope aBlade System, King LT, King LT-D, King LTS, King LTS-D)]. Lena S Sun, MD Consultant/Advisory boards: Merck [Anesthesia care (Sugammadex)]; Neuorprorexeon. Employment: Partial salary support to be the Medical Director of SmartTots, a public-private partnership between FDA and International Anesthesia Research Society. Marianna Crowley, MD Nothing to disclose Contributor disclosures are reviewed for conflicts of interest by the editorial group. When found, these are addressed by vetting through a multi-level review process, and through requirements for references to be provided to support the content. Appropriately referenced content is required of all authors and must conform to UpToDate standards of evidence. Conflict of interest policy https://www.uptodate.com/contents/complications-of-pediatric-airway-management-for-anesthesia/print?search=pulmonary%20aspiration%20anesthesia&sourc… 9/9