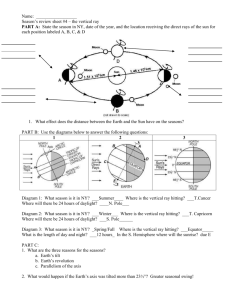
Vertical Rays WS Key
advertisement
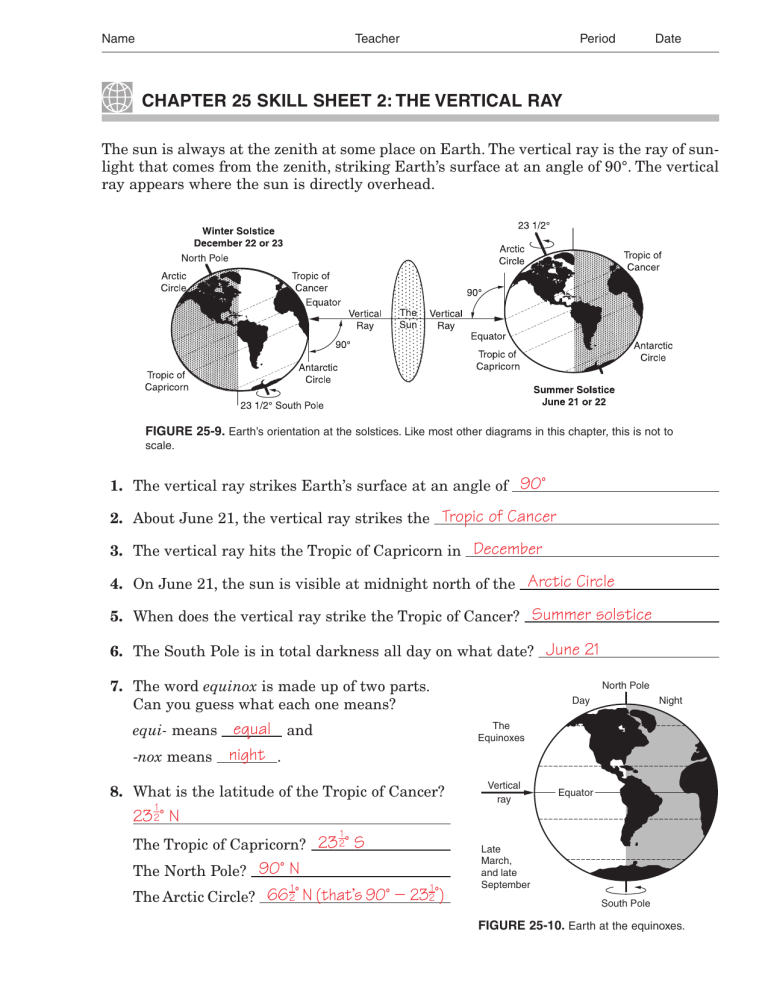
Name Teacher Period Date CHAPTER 25 SKILL SHEET 2: THE VERTICAL RAY The sun is always at the zenith at some place on Earth. The vertical ray is the ray of sunlight that comes from the zenith, striking Earth’s surface at an angle of 90°. The vertical ray appears where the sun is directly overhead. FIGURE 25-9. Earth’s orientation at the solstices. Like most other diagrams in this chapter, this is not to scale. 1. The vertical ray strikes Earth’s surface at an angle of 90° 2. About June 21, the vertical ray strikes the Tropic of Cancer 3. The vertical ray hits the Tropic of Capricorn in December 4. On June 21, the sun is visible at midnight north of the Arctic Circle 5. When does the vertical ray strike the Tropic of Cancer? Summer solstice 6. The South Pole is in total darkness all day on what date? June 21 7. The word equinox is made up of two parts. Can you guess what each one means? North Pole Day Night The Equinoxes equal and -nox means night . equi- means 8. What is the latitude of the Tropic of Cancer? 1 2 Vertical ray Equator 23 ° N C 1 The Tropic of Capricorn? 23 2° S The North Pole? 90° N The Arctic Circle? 66 2° N (that’s 90° 232°) 1 1 Late March, and late September South Pole FIGURE 25-10. Earth at the equinoxes. SKILL SHEET 2: THE VERTICAL RAY 293 Name Teacher Period Date 9. How could you determine the exact position of the Tropic of Cancer without using a map or any previous knowledge of its position? Observe the latitude beyond which the noon sun is never overhead. 10. How would the seasons be affected if Earth’s tilt were to increase to an angle 1 significantly greater than 23 2°? The seasons would become more extreme (hotter summers and colder winters). It has been suggested that this might cause an ice age due to the reflection from long-lasting snow cover.) 11. Albert Einstein postulated that gravity makes light rays seem to bend. This has been confirmed by scientific observations. Einstein explained that gravity causes the “warping of space.” How can this be observed? C. This effect can be observed only when the gravitational field is extreme. Gravity in this part of the Milky Way is not strong enough to make this effect visible to us. A phenomenon called lensing occurs when a star behind an extremely massive star becomes visible due to the bending of light. 294 CHAPTER 25 EARTH, SUN, AND SEASONS LABORATORY MANUAL