Presentation1
advertisement

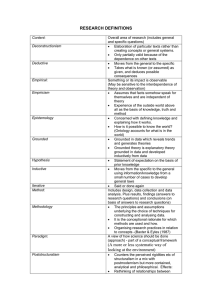
Presented By: Alishba Khan Aniqa Aurengzeb Aiman Sharukh Qualitative Research Qualitative Research is primarily exploratory research. It is used to gain an understanding of underlying reasons, opinions, and motivations. It provides insights into the problem or helps to develop ideas or hypotheses for potential quantitative research Method Technique Analysis Areas Processes of analysis Processes of analysis involved open coding, axial coding and selective coding. Open coding is based on the concept of data being “cracked open” as a means of identifying relevant categories. Axial coding is most often used when categories are in an advanced stage of development; and selective coding is used when the "core category", or central category that correlates all other categories in the theory, is identified and related to other categories. Advantages and Disadvantages Of Qualitative Research WHAT IS HISTORICAL RESEARCH ? HISTORICAL RESEARCH: A process of critical inquiry to past events systematically in order to provide an accurate description and interpretation of past events. It involves examining past events to draw conclusions and make predictions about the future. It may be a qualitative or quantitative research HR, finance and Marketing The important aims for conducting historical research are a. to reveal or uncover the unkown; b. to search and identity the relationship of past happenings and their links with the present; c. to record and assess past activities and achievements of individuals, agencies and institutions Field of study/ areas of historical study Cultural history: Combines approaches of anthropology and history Diplomatic history: Focuses on politics People history: Attempts to account for Historical events from the perspective of common people. Gender history: Looks at the past from the perspective of gender Historiography: Study of History and methodology of the discipline of history Asked Questions in historical research Analytical historical questions: All historical inquiry begins with a question that asks why and how things happened in the past. Descriptive historical questions: Who, what, where, when questions are important to establish context, but do not offer deep or interesting historical conclusions. Data Collection techniques Primary sources: first-person accounts that involve the oral or written testimony of eyewitnesses. (include documents, observational notes, photographs, recordings, diaries, journals, life histories, drawings) Secondary sources: descriptions of persons who are not eyewitnesses of the event or who did not personally know the person being studied (biographies, scholarly articles, reference books, textbooks, court records, newspaper articles etc Historical evidence is derived from the historical data by the process of criticism which is to types external and internal Steps in historical research Step 1: Developing a paperwork management system. Step 2: Selecting a Topic. Step 3: Background Reading for Historical Context. Step 4: Narrowing Your Topic. ... Step 5: Gathering and Recording Information. Step 6: Analyzing and Interpreting Sources and the Topic's Significance in History. ... Step 7: Developing a thesis. ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF HISTORICAL RESEARCH Disadvantages: Advantages: The main advantage of historical research is that is permits the investigation of topics that could be studied in no other way. It is the only research method that can study evidence from the past. The historical method is well suited for trend analysis. Cannot control for threats to internal vali dity Limitations are imposed due to the conte nt analysis Researchers cannot ensure representation of the sample. Bias in interpreting historical sources. Interpreting sources is very time consumin g. Sources of historical materials may be pro blematic Lack of control over external variables Grounded theory (GT) The grounded theory approach is a qualitative research method that uses a systematic set of procedures to develop an inductively derived grounded theory about a phenomenon”. It is a systematic methodology in the social sciences involving the construction of theories through methodical gathering and analysis of data. It focuses on building theory and create meaning from the collected data. [Note] Data coding forms theory as GT is not focused on testing theory. Grounded theory (GT) Grounded theory is a research methodology which operates inductively, in contrast to the hypothetico-deductive approach(hypothesis is developed and then tested. A study using grounded theory is likely to begin with a question, or even just with the collection of qualitative data. The, grounded theory is quite different from the traditional model of research, where the researcher chooses an existing theoretical framework, and only then collects data to show how the theory does or does not apply to the phenomenon under study. Steps As researchers review the data collected, repeated ideas, concepts or elements become apparent, and are tagged with codes, which have been extracted from the data. As more data is collected, and re-reviewed, codes can be grouped into concepts, and then into categories. These categories may become the basis for new theory. Advantages Grounded theory offers many advantages, however because it is such a painstakingly precise method of study, it requires high levels of both experience and acumen on the part of the researcher. For this reason, novice researchers should avoid this method of study until they have achieved the proper qualities needed to effectively implement the approach. Can use multiple types of data Provided in depth perspective new theories can emerge from coding the data into categories. Grounded theory can identify the situated nature of knowledge, as well as the contingent nature of practice. Grounded theory produces a 'thick description that acknowledges areas of conflict and contradiction. Grounded theory can respond and change as conditions that affect behavior change. Disadvantages Takes time to gather data : Grounded theory methods tend to produce large amounts of data, often difficult to manage. Researchers need to be skillful in using grounded theory methods. There are no standard rules to follow for the identification of categories Getting participants Next step can be unknown Researchers bias Case study To Data Analysis & Software https://www.predictiveanalyticstoday.com/top-qualitative-data-analysis-software/ Thank You