73.LP.Tides

Teacher : Friedlander
Assessment Question
Henderson Collegiate Science Lesson Plan
Unit : Astronomy Lesson #: 73 Lesson Date : 1/24/17
Exit Ticket Questions
Include exemplar answers
1. If the Sun, Earth, and Moon are lined up as follows, the Earth
2016-2017
Enduring Understanding/
Daily Question
Earth’s moon moves the tides.
How does a 90-degree alignment between Earth, the sun, and the moon impact the tides on Earth?
1.1.2
A) produces the greatest change in high and low tides.
B) It produces the least change in high and low tides.
C) It produces semidiurnal tides.
D) It produces no tides. would have__________. a. Spring Tides, which is when there are very high tides and very low tides. b. Spring Tides, which is when there are almost no tides. c. Neap Tides, which is when there are very high tides and very low tides. d. Neap Tides, which is when there are almost no tides.
2. Which of the following daily tidal patterns is most common along the east coast of the US? a. mixed semidiurnal b. semidiurnal c. diurnal d. nocturnal
Objective
Objective: Describe the cause and impact of tides as well as their cyclical nature
Conceptual Understanding:
The tides rise because the moon’s gravitational pull causes the water to move in its direction. As the moon gets further away, this pull weakens and the tide lower. The sun’s gravitational pull can both add to or subtract from this effect.
Criteria for Success/Procedural Understanding
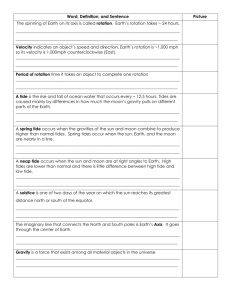
Define diurnal and semidiurnal tides
Define spring and neap tides
Connect the tides to the movement of planetary bodies in space
Notes/Reminders
Do Now (7 min)
- Spiral of previous skills
- Prime students for today’s lesson
Include written directions
EXEMPLAR ANSWERS and work habits
Above and beyond
Which
C
Instructional Goal
Address side conversations or students talking out at the wrong time by:
Resetting the expectation whole group
Using a tone change and executing a sideline or send out when a student then violates the expectation
Using an anonymous correction if you can't tell where the noise is coming from
D
D
C graph best represents the
duration of insolation during the year at the equator?
DON’T FORGET AN ABOVE AND BEYOND.
Oral Drill ( 2 min)
- Script the questions and correct responses
- Include vocabulary and spiraled content daily
Intro to New
Material
(15 min)
Include the conceptual and procedural understanding
Include the reading passage/chart/gr aph/map/etc. that you will be using to deliver information
Script CFU you will ask about the mini lesson
1. What is the shape of planetary orbits? Ellipse
2. The amount of solar radiation reflected by a surface albedo
3. List the universal hierarchy from smallest to biggest planet, solar system, galaxy, universe
4. What gases are responsible for producing acid rain? nitrous oxide and sulfur dioxide
5. Aquifer located underneath impermeable stone confined aquifer
6. What is the line of latitude marking the Equator? The North Pole? 0, 90N
7. Show me which way latitude goes? flat
8. Where is the barycenter located between two objects of equal mass? In the center
9. Fair, dry weather is associated with which type of pressure system?
High Pressure
10. How does the speed of the Earth change as it gets closer to the sun? Faster
11. Show me a hand sign for intensity of solar radiation. Fist pound
12. The model of our solar system with the sun in the center Heliocentric
Hook/Vegas
Script
TS: We’re about to look at an area of the world that experiences the most extreme tide on the planet.
Indicate when in the lesson it will be used
Framing the
Lesson
Must Include
Connection to
EU/DQ
Conceptual and https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=u3LtEF9WPt4
TS: Okay, that’s crazy, but what if the tides could go even higher? https://www.youtube.com/watch?annotation_id=annotation_88687&feature
=iv&hd=1&src_vid=u3LtEF9WPt4&v=hbzwzrZXUKA
TS: We’re going to try and answer two big questions today. First, what causes the tide? Second, what can cause the tide to grow even bigger, and smaller, than normal?
Procedural
Can include:
CFU’s of background info to understand today’s objectives
Independent Text
TS:
One thing you guys are going to notice with today’s text is that there are seven different types of tides, and we can see some of them on the board: diurnal, semidiurnal, neap, and spring. To keep these straight, you should redefine each term in your marginal notes. 3-5 words should be sufficient.
Procedural Lap Lens: (annotations checklist)
Circle new vocabulary
Underline key ideas
Write marginal notes to summarize paragraphs
There are few things in nature as predictable as the tides, which are the periodic rise and fall of ocean waters. Tides are so reliable because their movements are based on the positioning of the moon and sun in relation to the earth. These celestial bodies do not change their patterns, so it's easy for us to predict when the tides will rise and fall today, tomorrow and even next year and beyond. In this lesson, you will learn more about how the moon and sun cause the tides and the effects tides have on coastal regions.
High Tide and Low Tide
Because the moon is closer to the earth than the sun, it has the most influence on the tides. In fact, it's fair to say that tides would not occur if the earth and the moon were not attracted to each other. Of course, I'm not referring to a love/hate type of attraction but rather the gravitational attraction between the two bodies. The gravitational pull of the moon causes the oceans and other major water bodies to bulge out toward the moon.
When the gravitational pull is at its highest point, the result is high tide, which is the highest level of the tide. When the pull is at its lowest point, we see low tide, or the lowest level of the tide. The earth itself is also pulled toward the moon but with less strength. This pulls the earth away from the water on the opposite side of the earth, making the water on that side bulge as well. Therefore, high tide occurs on both sides of the planet at the same time. Meanwhile the earth is rotating. So, we experience tides throughout the day.
Semidiurnal and Diurnal Tides
Now, if the earth were perfectly round with no big land masses, all bodies of water in the world would experience two nearly equal high tides and two low tides each day. This tidal pattern is known as semidiurnal tides, as seen in the graphs above. However, the continents of earth disrupt water bodies, and so this can produce different tidal patterns. For example, some bodies of water, such as the Gulf of Mexico, have diurnal tides, which means only one high tide and one low tide each day. The rest of the East Coast experiences semidiurnal tides.
You can recall these terms by remembering that the word 'diurnal' means 'happening daily.'
Therefore, we see that diurnal tides happen once a day. And if we add the prefix 'semi,' which means 'half,' we can understand that semidiurnal tides happen every half a day.
Spring Tides and Neap Tides
The earth and moon are constantly in motion around the sun, and all have their own gravitational pull. So, when the alignment between the three bodies changes, it changes the strength of the overall gravitational pull and therefore the size of the tides.
Spring tides are tides that occur when the earth, moon and sun are aligned, and the
tidal range between high and low tide is at its maximum. This happens basically twice a month, during the full and new moon phases. At these times, the three bodies are in line and their gravitational pulls reinforce each other. When the spring tide is happening, we see higher than average high tides and lower than average low tides.
It's important to point out that 'spring' does not refer to the season. Instead, you can recall the meaning of 'spring tides' by thinking of them as the tides that 'spring' out and then
'spring' back with the most intensity. A few weeks after the spring tides, we see the neap tides. These are tides that occur when the moon and sun are at right angles to the earth's orbit, and the tidal range between high and low tide is at its minimum. The neap tides occur when the moon is in its first and last quarter phase. Because of the position of the moon and sun, their gravitational pulls on the waters of earth partially cancel each other out, resulting in smaller differences between the high and low tides.
Reading Check: What phenomenon do we see in Earth’s oceans when the Moon’s gravitational pull is at its strongest point? a. Semidiurnal tide b. Diurnal tide c. High tide d. Low tide
Tides Affect Coastal Regions
Tides affect coastal regions in different ways. High tides push large amounts of water far up onto beaches and leave the sand and sediment mixed with the water behind when the tide goes out. Therefore, tides transport sand and sediment and shape shorelines.
Tides feed estuaries. Estuaries are coastal areas where freshwater mixes with ocean water that is delivered by the tides. High tides bring nourishing sediment and sea life into estuaries. Estuaries are home to biologically diverse and unique plant and animal communities because their waters contain a mix of freshwater and salty ocean water.
Tides can present challenges to coastal regions, especially during storms. Storms that form out in the ocean intensify waves. If the storm waves come ashore at high tide, tides can worsen damage and erosion caused by storm waves.
Tides can also be a source of energy. Tides provide tidal power. Tidal power is energy obtained from the rise and fall of tides. Tides move massive amounts of water toward and then away from shore. The energy of the moving water can be harnessed by placing turbines in the path of the moving water. These turbines can be connected to generators that create a renewable source of electricity.
Lesson Summary
Tides are the periodic rise and fall of ocean waters. The gravitational pull of the moon and sun creates the tides. When the gravitational pull is at its highest point, the result is high tide, which is the highest level of the tide. When the pull is at its lowest point, we see low tide, or the lowest level of the tide.
Tides are predictable, and there are different tidal patterns in different areas of the world.
Some areas experience semidiurnal tides, which are two nearly equal high tides and two low tides each day. Other areas may experience diurnal tides, which are only one high tide and one low tide each day.
Spring tides are tides that occur when the earth, moon and sun are aligned and the tidal range between high and low tide is at its maximum. This happens during the full and new moon phases. Neap tides are tides that occur when the moon and sun are at right angles to the earth's orbit, and the tidal range between high and low tide is at its minimum. The neap tides occur when the moon is in its first and last quarter phases.
Tides affect coastal regions in different ways. For example, they transport sand and
sediment and shape shorelines. They also feed estuaries, which are coastal areas where freshwater mixes with ocean water that is delivered by the tides. Tides can worsen damage and erosion caused by storm waves, but they can also provide tidal power, which is energy obtained from the rise and fall of tides.
GP Work Habits TS: Turn to your Guided Practice #73 and track me for some quick instructions that are going to help you guys crush some tough questions.
Procedural Lap Lens:
TS: When you get to #4, use your work habits to show the gravitational pull, this will help you identify the correct multiple choice answer.
Conceptual Lap Lens:
TS: Once you’ve selected the correct answer, make sure your written response defends that answer in full, based on the gravitational pulls that you showed.
Highest Leverage
GP problem
*If this is a section of the MI, please indicate
Problem and Exemplar
Answer
Anticipated
Misconception
*for MC, name the misconception for each answer choice
Response to Data
1. If the Sun, Earth, and
Moon are lined up as follows, the Earth would have a. Spring Tides, which is when there are very high tides and very low tides. b. Spring Tides, which is when there are almost no tides. c. Neap Tides, which is when there are very high tides and very low tides. d. Neap Tides, which is when there are almost no tides.
Explain this phenomenon:
*for main idea, write what you will look for to see if they are taking shortcuts or misunderstand the text
Students will probably get this question correct but have difficulty explaining it.
Explaining the first part is easy, tide is very high because the gravitational pull of the sun and moon work together. The reason the tide is also very low at this point is trickier to figure out from the diagram. It’s because the
Earth is rotating, so when a body of water is facing 90 degrees away from the moon, it’s ALSO facing 90 degrees away from the sun, so no object has a major gravitational pull.
If on track:
Proceed directly to IP.
If 50% or less are off track:
Class discussion. Why are the tides at their lowest point during a spring tide? Project the diagram on the board that includes rotation of the Earth, but don’t immediately point it out unless the conversation struggles.
If more than 50% are off track:
Have students turn to the diagram in their text showing the spring and neap tides. On the diagram itself, have students annotate the gravitational pull exerted by each object with arrows.
TS: Show me, are the arrows representing gravitational pull surrounding the Earth?
“NO”
TS: What’s going to happen then when a body of water rotates to this point?
“Tides will be low”
Guided Practice
(10 min)
Script questions
How will you
Written/Discussion Questions indicate if the question will be written (W) slates (S) discussion (D) cold call (CC) Turn and Talk (TT)
Partner Problems (PP)
Can include “stretch it” questions as a reward for the
Exemplar Answers
(script what you want from kids)
stamp the conceptual understanding? correct answer or the prompts you will use in a discussion
1. Roberto went to Myrtle Beach with his family and on their evening beach walk under the bright, full moon, they noticed the water level was much higher than it was during the day. How could Roberto explain this to his family? a. We’ve got to get out of here ASAP, there’s going to be a tidal wave!” b. “We’re experiencing high tide, because of the gravitational pull of the moon on Earth.” c.
“We’re experiencing low tide, because there is an equal and opposite reaction to the sun’s gravitational pull on Earth on the other side of the world.” d. “The water is so high because the sun isn’t out and water expands when it gets cold.”
2. The sun and moon have a large influence on tides. What situation would cause the lowest tides? a. When the Sun, Moon and Earth are in alignment. b. When the Sun, North Star and Earth are in alignment c. When the Sun, Moon and Earth are at 90 degree angles. d. When the Sun is experiencing a solar flair.
3. What has the greatest effect on the tides on Earth? a. The Moon b. The Sun c. The North Star d. Jupiter
Defend your Answer:
The moon has a greater effect because it is so close to the Earth, even the other objects are much more massive.
IP Work Habits
- Checklists
4. If the Sun, Earth, and Moon are lined up as follows, the Earth would have a. Spring Tides, which is when there are very high tides and very low tides. b. Spring Tides, which is when there are almost no tides. c. Neap Tides, which is when there are very high tides and very low tides. d. Neap Tides, which is when there are almost no tides.
Explain this phenomenon:
The Sun’s gravitational pull aligns with the moon’s pull, so this causes the tide to reach higher than normal levels. It is also when the tide is lowest, because when the
Earth rotates away from the moon it is also rotating away from the Sun, so no planetary body has a major gravitational pull.
TS: You will have 15 minutes to tackle the Solo Climb. Flip to it and track me.
- Feedback Codes
Highest Leverage
IP problem
Independent
Practice
(15 min)
Define the assignment and how long
students will work
Procedural Lap Lens:
TS: For my first lap, I will be looking for work habits only. You will not receive feedback until these are shown, but I only need to see one prove and one disprove.
Conceptual Lap Lens:
TS: Some of these answers aren’t going to be in the text, so be ready to base answers on what you DO know about tides. The moon causes tides, and the moon orbits around the
Earth.
Problem and Exemplar Anticipated
Misconceptions
Response to Data
Answer
#3 (doesn’t fit because of the graphs)
The misconception would be for students to focus on the times the tides are occurring or the length of time between tides (which are all the same). High tide is ALL about positioning of the moon,
Earth, and Sun. These positions can actually happen at many different times of day and in the year.
If on track:
Proceed directly to ET
If 50% or less are off track:
Turn and Talk discussion, find the homerun answer.
TS: Every object in space has a gravitational pull, and these pulls can either reinforce each other or work against each other. Which of the diagrams below would have a set of gravitational forces that increase the tide?
If more than 50% are off track:
TS:
1. What is the question asking us to find? 15 seconds to read and mark up the question.
(Position that will cause the highest tides)
2. Build on it, what creates the tides?
(Gravitational pull of the moon)
3. How could the objects in space be arranged to make that pull even stronger?
What will students be doing to practice the skill independently to synthesize information and demonstrate higher-level mastery? (Copy and paste from classwork)
Include Exemplar Answers
1. How does a straight alignment between Earth, the sun, and the moon impact the tides on Earth? a. It produces the greatest change in high and low tides. b. It produces the least change in high and low tides c. It produces semidiurnal tides. d. It produces diurnal tides.
2.
3.
Explain the difference between diurnal and semidiurnal tides. Which type of tide do we experience on the NC coast?
Diurnal = one high tide and one low tide per day
Semidiurnal = 2 high tides and 2 low tides per day
NC coast has semidiurnal tides.
The Bay of Fundy, located on the east coast of Canada, has the highest ocean tides in the world. The St. John River enters the Bay of Fundy at the city of St. John, where the river actually reverses direction twice a day at high tides. Data for the famous Reversing Falls of the St. John River are given below for high and low tides on June 26 through 28, 1994.
Which model of the Sun, Earth (E), and Moon (M) best represents a position that would cause the highest ocean tides in the Bay of Fundy?
(Sizes and distances are not drawn to scale).
C
4. Spring tides occur approximately a. once each year b. twice each year c. once each month d. twice each month
Defend your Answer:
They occur when the moon is aligned with the Sun. The moon orbits the Earth once per month, and spring tides occur both when then Earth is in between the two and when they’re on the same side.
5. Draw a graphic representation (picture/diagram) that shows spring and neap tides.
Spring – Sun and Moon aligned
Neap – Sun and Moon at 90 degrees
6. Which of the following tidal patterns exhibit only one high and low tide each day?
a. mixed semidiurnal b. semidiurnal c. diurnal d. nocturnal
Extra Exploration
A. If it is LOW tide at a harbor with a semi-diurnal tide patter at 9:00 am, at about what time would you expect it to be HIGH tide in the afternoon? 3:00 pm
B. If it is HIGH tide at 8:00 pm, when would you expect the next HIGH tide to be? 8am
Closing/ Summary
(5 min)
Include what students will do or say to internalize the before students begin an exit ticket
How will you have students summarize the lesson? What will you do/ask to “make it stick”?
1. If the Sun, Earth, and Moon are lined up as follows, the Earth would have__________. a. Spring Tides, which is when there are very high tides and very low tides. b. Spring Tides, which is when there are almost no tides. c. Neap Tides, which is when there are very high tides and very low tides. d. Neap Tides, which is when there are almost no tides.
2. Which of the following daily tidal patterns is most common along the east coast of the US? a. mixed semidiurnal b. semidiurnal c. diurnal d. nocturnal
Exit Ticket – Method of Data Collection:
Open Response Exemplar Answer:
Tallies (if applicable)