midterm mc review packet with key last page
advertisement
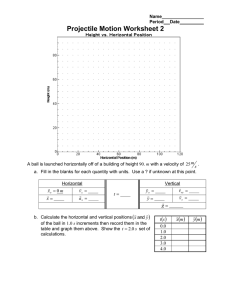
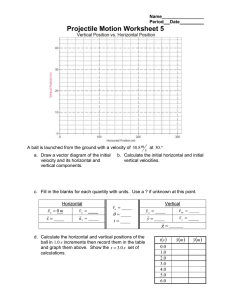
Name Regents Physics Physics Midterm Review - Multiple Choice Problems 1. A car traveling on a straight road at 15.0 meters per second accelerates uniformly to a speed of 21.0 meters per second in 12.0 seconds. The total distance traveled by the car in this 12.0-second time interval is A) 36.0 m C) 216 m B) 180. m D) 252 m 2. A baseball player runs 27.4 meters from the batter's box to first base, overruns first base by 3.0 meters, and then returns to first base. Compared to the total distance traveled by the player, the magnitude of the player's total displacement from the batter's box is A) 3.0 m shorter C) 3.0 m longer B) 6.0 m shorter D) 6.0 m longer 3. A blinking light of constant period is situated on a lab cart. Which diagram best represents a photograph of the light as the cart moves with constant velocity? A) B) C) 6. An object accelerates uniformly from rest to a speed of 50. meters per second in 5.0 seconds. The average speed of the object during the 5.0-second interval is A) 5.0 m/s C) 25 m/s B) 10. m/s D) 50. m/s 7. A child riding a bicycle at 15 meters per second decelerates at the rate of 3.0 meters per second2 for 4.0 seconds. What is the child's speed at the end of the 4.0 seconds? A) 12 m/s C) 3.0 m/s B) 27 m/s D) 7.0 m/s 8. A rock is dropped from a bridge. What happens to the magnitude of the acceleration and the speed of the rock as it falls? [Neglect friction.] A) Both acceleration and speed increase. B) Both acceleration and speed remain the same. C) Acceleration increases and speed decreases. D) Acceleration remains the same and speed increases. 9. Base your answer to the following question on the D) diagram below which shows a 1-kilogram mass and a 2-kilogram mass being dropped from a 4. Base your answer to the following question on the building 100 meters high. information below. A 1,000-kilogram car traveling with a velocity of +20. meters per second decelerates uniformly at –5.0 meters per second2 until it comes to rest. What is the total distance the car travels as it decelerates to rest? A) 10. m C) 40. m B) 20. m D) 80. m 5. Starting from rest, an object rolls freely down an incline that is 10 meters long in 2 seconds. The acceleration of the object is approximately A) 5 m/sec C) 10 m/sec B) 5 m/sec 2 D) 10 m/sec 2 Halfway down, the acceleration is A) greater for the 1-kilogram mass B) greater for the 2-kilogram mass C) the same for both masses 10. A ball is thrown vertically upward with an initial velocity of 29.4 meters per second. What is the maximum height reached by the ball? [Neglect friction.] A) 14.7 m C) 44.1 m 14. The graph below represents the displacement of an object moving in a straight line as a function of time. B) 29.4 m D) 88.1 m 11. A rock falls from rest a vertical distance of 0.72 meter to the surface of a planet in 0.63 second. The magnitude of the acceleration due to gravity on the planet is A) 1.l m/s2 C) 3.6 m/s 2 B) 2.3 m/s 2 D) 9.8 m/s 2 12. As shown in the diagram below, a student standing on the roof of a 50.0-meter-high building kicks a stone at a horizontal speed of 4.00 meters per second. What was the total displacement traveled by the object during the 10.0-second time interval? A) 0 m C) 16 m B) 8 m D) 24 m 15. Which graph best represents the motion of a block accelerating uniformly down an inclined plane? A) B) How much time is required for the stone to reach the level ground below? [Neglect friction.] A) 3.19 s C) 10.2 s B) 5.10 s D) 12.5 s 13. A ball is thrown horizontally at a speed of 24 meters per second from the top of a cliff. If the ball hits the ground 4.0 seconds later, approximately how high is the cliff? A) 6.0 m C) 78 m C) B) 39 m D) 96 m D) 16. The graph below represents the relationship between speed and time for an object moving along a straight line. What is the total distance traveled by the object during the first 4 seconds? A) 5 m C) 40 m B) 20 m D) 80 m 17. The graph below shows the relationship between speed and time for two objects, A and B. Compared with the acceleration of object B, the acceleration of object A is 19. A 5-newton ball and a 10-newton ball are released simultaneously from a point 50 meters above the surface of the Earth. Neglecting air resistance, which statement is true? A) The 5-N ball will have a greater acceleration than the 10-N ball. B) The 10-N ball will have a greater acceleration than the 5-N ball. C) At the end of 3 seconds of free-fall, the 10-N ball will have a greater momentum than the 5-N ball. D) At the end of 3 seconds of free-fall, the 5-N ball will have a greater momentum than the 10-N ball. 20. A force of 6.0 newtons changes the momentum of a moving object by 3.0 kilogram•meters per second. How long did the force act on the mass? A) 1.0 s C) 0.25 s 21. A 5.0-kilogram cart moving with a velocity of 4.0 meters per second is brought to a stop in 2.0 seconds. The magnitude of the average force used to stop the cart is A) 20. N C) 10. N A) B) C) D) one-third as great twice as great three times as great the same B) 2.0 s D) 0.50 s B) 2.0 N D) 4.0 N 22. When a 1.0-kilogram cart moving with a speed of 0.50 meter per second on a horizontal surface collides with a second 1.0-kilogram cart initially at rest, the carts lock together. What is the speed of the combined carts after the collision? [Neglect friction.] A) 1.0 m/s C) 0.25 m/s B) 0.50 m/s D) 0 m/s 23. A 750-newton person stands in an elevator that 18. In the diagram below, a 10-kilogram ball is fired is accelerating upward. The upward force of the with a velocity of 500 meters per second from a elevator floor on the person must be 1,000-kilogram cannon. What is the recoil A) equal to 0 N velocity of the cannon? B) less than 750 N C) equal to 750 N D) greater than 750 N A) 5 m/s C) 10 m/s B) 2 m/s D) 500 m/s 24. On a small planet, an astronaut uses a vertical force of 175 newtons to lift an 87.5-kilogram boulder at constant velocity to a height of 0.350 meter above the planet's surface. What is the magnitude of the acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the planet? A) 0.500 N/kg C) 9.81 N/kg B) 2.00 N/kg D) 61.3 N/kg 25. Four forces act concurrently on a block on a horizontal surface as shown in the diagram below. 28. What is the magnitude of the gravitational force between two 5.0-kilogram masses separated by a distance of 5.0 meters? A) 5.0 × 10 0 N C) 6.7 × 10 –11 N B) 3.3 × 10 D) 1.3 × 10 –10 –11 N N 29. As a meteor moves from a distance of 16 Earth radii to a distance of 2 Earth radii from the center of Earth, the magnitude of the gravitational force between the meteor and Earth becomes A) B) 8 times as great as great C) 64 times as great D) 4 times as great 30. The diagram below shows a 2.0-kilogram object accelerating at 5.0 meters per second 2 on a rough horizontal surface. As a result of these forces, the block A) B) C) D) moves at constant speed to the right moves at constant speed to the left accelerate to the right accelerate to the left 26. Two forces, F 1 and F 2, are applied to a block on a frictionless, horizontal surface as shown below. What is the magnitude of the frictional force Ff acting on the object? A) 5.0 N C) 20. N 31. An 8.0-newton wooden block slides across a horizontal wooden floor at constant velocity. What is the magnitude of the force of kinetic friction between the block and the floor? A) 2.4 N C) 8.0 N If the magnitude of the block's acceleration is 2.0 meters per second 2, what is the mass of the block? A) 1 kg B) 5 kg C) 6 kg D) 7 kg 27. A student pulls a 60.-newton sled with a force having a magnitude of 20. newtons. What is the magnitude of the force that the sled exerts on the student? A) 20. N C) 60. N B) 40. N D) 80. N B) 10. N D) 40. N B) 3.4 N D) 27 N 32. Two forces act concurrently on an object on a horizontal, frictionless surface, as shown in the diagram below. What additional force, when applied to the object, will establish equilibrium? A) 16 N toward the right C) 4 N toward the right B) 16 N toward the left D) 4 N toward the left 33. Which term identifies a scalar quantity? A) displacement C) velocity B) momentum D) time 34. Which is a vector quantity? A) distance C) power B) speed D) force 35. The vector diagram below represents the horizontal component, FH, and the vertical component, FV, of a 24-newton force acting at 35° above the horizontal. 36. A shopping cart slows as it moves along a level floor. Which statement describes the energies of the cart? A) The kinetic energy increases and the gravitational potential energy remains the same. B) The kinetic energy increases and the gravitational potential energy decreases. C) The kinetic energy decreases and the gravitational potential energy remains the same. D) The kinetic energy decreases and the gravitational potential energy increases. 37. If the speed of a moving object is doubled, the kinetic energy of the object is A) halved C) unchanged What are the magnitudes of the horizontal and vertical components? A) B) C) D) FH = 3.5 N and FV = 4.9 N FH = 4.9 N and FV = 3.5 N FH = 14 N and FV = 20. N FH = 20. N and FV = 14 N B) doubled D) quadrupled 38. A 1.00-kilogram ball is dropped from the top of a building. Just before striking the ground, the ball’s speed is 12.0 meters per second. What was the ball’s gravitational potential energy, relative to the ground, at the instant it was dropped? [Neglect friction.] A) 6.00 J C) 72.0 J B) 24.0 J D) 144 J 39. Which statement describes the kinetic energy and total mechanical energy of a block as it is pulled at constant speed up an incline? A) Kinetic energy decreases and total mechanical energy increases. B) Kinetic energy decreases and total mechanical energy remains the same. C) Kinetic energy remains the same and total mechanical energy increases. D) Kinetic energy remains the same and total mechanical energy remains the same. 40. A spring gains 2.34 joules of elastic potential energy as it is compressed 0.250 meter from its equilibrium position. What is the spring constant of this spring? A) 9.36 N/m C) 37.4 N/m B) 18.7 N/m D) 74.9 N/m 41. A student performed a laboratory investigation to determine the spring constant of a spring. The force applied to the spring was varied and the resulting elongation of the spring was measured. The student graphed the data collected, as shown below. 43. The diagram below shows a 50.-kilogram crate on a frictionless plane at angle to the horizontal. The crate is pushed at constant speed up the incline from point A to point B by force F. If angle were increased, what would be the effect on the magnitude of force F and the total work W done on the crate as it is moved from A to B? A) W would remain the same and the magnitude of F would decrease. B) W would remain the same and the magnitude of F would increase. C) W would increase and the magnitude of F would decrease. D) W would increase and the magnitude of F would increase. 44. A 500.-newton girl lifts a 10.-newton box vertically upward a distance of 0.50 meter. The work done on the box is A) 5.0 J C) 250 J According to the student's graph, what is the spring constant for this spring? A) 0.050 m/N C) 13 N• m B) 9.8 N/kg D) 20. N/m 42. How much work is required to lift a 10.-newton weight from 4.0 meters to 40. meters above the surface of Earth? A) 2.5 J C) 3.6 ×10 2 J B) 3.6 J D) 4.0 ×10 2 J B) 50. J D) 2500 J 45. A student pulls a box across a horizontal floor at a constant speed of 4.0 meters per second by exerting a constant horizontal force of 45 Newtons. Approximately how much work does the student do against friction in moving the box 5.5 meters across the floor? A) 45 J C) 250 J B) 180 J D) 740 J 46. If a motor lifts a 400.-kilogram mass a vertical distance of 10. meters in 8.0 seconds, the minimum power generated by the motor is A) 3.2 10 2 W C) 4.9 10 3 W B) 5.0 10 2 W D) 3.2 10 4 W 47. A baseball bat strikes a ball with an average force of Newtons. If the bat stays in contact with the ball for a distance of meter, what kinetic energy will the ball acquire from the bat? A) C) B) D) 48. A pendulum is made from a 7.50-kilogram mass attached to a rope connected to the ceiling of a gymnasium. The mass is pushed to the side until it is at position A, 1.5 meters higher than its equilibrium position. After it is released from rest at position A, the pendulum moves freely back and forth between positions A and B, as shown in the diagram below. What is the total amount of kinetic energy that the mass has as it swings freely through its equilibrium position? [Neglect friction.] A) 11 J C) 110 J B) 94 J D) 920 J 49. As a block slides across a table, its speed decreases while its temperature increases. Which two changes occur in the block’s energy as it slides? A) a decrease in kinetic energy and an increase in internal energy B) an increase in kinetic energy and a decrease in internal energy C) a decrease in both kinetic energy and internal energy D) an increase in both kinetic energy and internal energy 50. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below. The diagram represents a 1.00 kilogram object being held at rest on a frictionless incline. As the object slides down the incline, the sum of the gravitational potential energy and kinetic energy of the object will A) decrease C) remain the same B) increase 51. Base your answer to the following question on the information and diagram below. A ball is thrown horizontally with an initial velocity of 20.0 meters per second from the top of a tower 60.0 meters high. 52. A red ball and a green ball are simultaneously thrown horizontally from the same height. The red ball has an initial speed of 40. meters per second and the green ball has an initial speed of 20. meters per second. Compared to the time it takes the red ball to reach the ground, the time it takes the green ball to reach the ground will be A) B) C) D) What is the horizontal velocity of the ball just before it reaches the ground? [Neglect air resistance.] A) 9.81 m/s C) 34.3 m/s B) 20.0 m/s D) 68.6 m/s the same twice as much half as much four times as much 53. Base your answer to the following question on the information and diagram below A golf ball leaves a golf club with an initial velocity of 40.0 meters per second at an angle of 40º with the horizontal. What is the total horizontal distance traveled by the golf ball during the first 2.10 seconds of its flight? A) 100. m B) 76.6 m C) 64.3 m 54. An archer uses a bow to fire two similar arrows with the same string force. One arrow is fired at an angle of 60.° with the horizontal, and the other is fired at an angle of 45° with the horizontal. Compared to the arrow fired at 60.°, the arrow fired at 45° has a A) longer flight time and longer horizontal range B) longer flight time and shorter horizontal range C) shorter flight time and longer horizontal range D) shorter flight time and shorter horizontal range 55. A basketball player jumped straight up to grab a rebound. If she was in the air for 0.80 second, how high did she jump? A) 0.50 m C) 1.2 m B) 0.78 m D) 3.1 m D) 40.0 m 56. A projectile is fired from a gun near the surface of Earth. The initial velocity of the projectile has a vertical component of 98 meters per second and a horizontal component of 49 meters per second. How long will it take the projectile to reach the highest point in its path? A) 5.0 s C) 20. s B) 10. s D) 100. s 57. An unbalanced force of 40. newtons keeps a 5.0-kilogram object traveling in a circle of radius 2.0 meters. What is the speed of the object? A) 8.0 m/s C) 16 m/s B) 2.0 m/s D) 4.0 m/s 58. A ball of mass M at the end of a string is swinging in a horizontal circular path of radius R at constant speed V. Which combination of changes would require the greatest increase in the centripetal force acting on the ball? A) B) C) D) doubling V and doubling R doubling V and halving R halving V and doubling R halving V and halving R 59. A 1.0 × 103-kilogram car travels at a constant speed of 20. meters per second around a horizontal circular track. Which diagram correctly represents the direction of the car’s velocity (v) and the direction of the centripetal force (Fc) acting on the car at one particular moment? A) B) C) D) 60. A student on her way to school walks four blocks east, three blocks north, and another four blocks east, as shown in the diagram. Compared to the distance she walks, the magnitude of her displacement from home to school is A) less C) the same B) greater Answer Key Midterm Review (2015) 1. C 36. C 2. B 37. D 3. C 38. C 4. C 39. C 5. B 40. D 6. C 41. D 7. C 42. C 8. D 43. D 9. C 44. A 10. C 45. C 11. C 46. C 12. A 47. A 13. C 48. C 14. B 49. A 15. D 50. C 16. C 51. B 17. C 52. A 18. A 53. C 19. C 54. C 20. D 55. B 21. C 56. B 22. C 57. D 23. D 58. B 24. B 59. A 25. D 60. A 26. B 27. A 28. C 29. C 30. D 31. A 32. D 33. D 34. D 35. D