5254421
advertisement

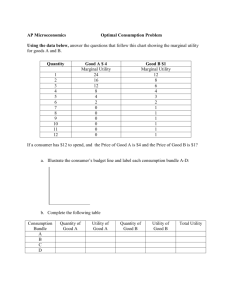
Module Micro: 15 Econ: 51 Utility Maximization KRUGMAN'S MICROECONOMICS for AP* Margaret Ray and David Anderson What you will learn in this Module: • How consumers make choices about the purchase of goods and services • How does our satisfaction change as we consume greater quantities of a product? Or, when should we stop? • How do we choose how much of each different product to consume? • How do we find the optimal consumption bundle? Do Now • Graph Sherry’s utility from berry consumption. #1 in the worksheet. Maximizing utility In the Theory of Consumer Choice, consumers’ goal is to maximize their utility. Utility • Utility: a measure of the satisfaction the consumer derives from consumption of goods and services. • Total utility: utility of total quantity consumed. • Marginal utility – utility of the last item consumed. Figure 51.1 Cassie’s Total Utility and Marginal Utility Ray and Anderson: Krugman’s Economics for AP, First Edition Copyright © 2011 by Worth Publishers Marginal vs. Total Utility How does marginal utility relate to total utility? How does it help us make consumption decisions? Question If you had two consumption choices, how would you decide the amount of each that you would consume? Let’s get real • Consumption is limited by income – which is scarce. • The budget line: shows combinations of products that we can afford assuming we spend all of our income. • These combinations are called consumption bundles. • The budget line shows consumption possibilities. Figure 51.2 The Budget Line Ray and Anderson: Krugman’s Economics for AP, First Edition Copyright © 2011 by Worth Publishers Practice Step 1 • Krugman, page 527, Problem #17 • Do A. Find the affordable consumption bundles, and • Graph. Figure 51.3 Optimal Consumption Bundle Ray and Anderson: Krugman’s Economics for AP, First Edition Copyright © 2011 by Worth Publishers Utility Race Step 2 • If you graphed the total utility of each bundle, which one would you pick?. Spending the Marginal Dollar • Marginal utility per dollar. • MU= 10, cost = $5, MU / $1 = 2 • Optimal consumption rule: consumption is optimal when the marginal utility per dollar of each product is equal. [And we’ve spent all of our money.] Table 51.3 Sammy’s Marginal Utility per Dollar Ray and Anderson: Krugman’s Economics for AP, First Edition Copyright © 2011 by Worth Publishers Figure 51.4 Marginal Utility per Dollar Ray and Anderson: Krugman’s Economics for AP, First Edition Copyright © 2011 by Worth Publishers Spending the Marginal Dollar Problem #17 b Also, solve for optimal bundle using zig zag method. Summary Utility • Total utility • Maximized when MU = 0 • Budget constraint Budget • Consumption possibilities • Marginal utility per $ Optimal • Optimal consumption rule