IFSTA CHAPTER 21 PPT FF1
advertisement

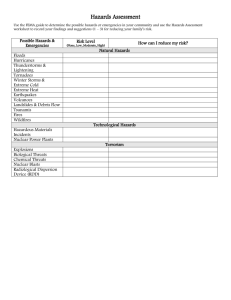
Essentials of Fire Fighting 6th Edition Firefighter I Chapter 21 — Fire and Life Safety Initiatives Learning Objective 1 Explain the steps taken during fire and life safety program development. 21–1 Firefighters need to understand the value of a life safety program. Help meet mission statements Encourage, empower citizens Emphasize firefighter safety Help firefighters 21–2 Raise awareness among department Development of a life safety program should be systematic. Model published by FEMA • Threat and Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment (THIRA) 21–3 FIVE STEPS 10–4 The first step in the THIRA is to identify threats and hazards. Natural Courtesy of Rich Mahaney Courtesy of Chris Mikal Technological Threats or humancaused 21–5 Step 1: Example Threats and Hazards of Concern 10–6 The second step in the THIRA is to give identified threats a context. Include Brief explanation of conditions • Possible time, location • Portion of population at greatest risk 21–7 The third step in the THIRA is to examine jurisdictional core capabilities. Based on list of descriptions Effects vary among communities 21–8 Combine effects with outcomes community wants to reach in reasonable time The fourth step in the THIRA is to set capability targets. Set once outcomes defined Should result in 21–9 The final step in the THIRA is to apply the assessment results. Develop action plans Coordinate activities with others Educate public Purchase materials 21–10 REVIEW QUESTION What steps should be taken when developing a fire and life safety program? 21–11 Learning Objective 2 Describe the components involved in fire and life safety program delivery. 21–12 Life safety program delivery is based on the five Es. 21–13 Answering questions not typically covered can be a part of education. Fire prevention presentations CPR training classes Fire prevention week activities annually in October Fire extinguisher training Home safety education Slip and fall prevention for older adults General health education for community or fire department 21–14 Practical bicycle safety for youths Enforcement activities are usually grouped into a few categories. • Building • Fire • Life safety • Enforce regulations internally 21–15 Economic incentives can also play a role in program delivery. Payment to participate • Tax deductions • Manufacturer’s rebates • Decreased insurance rates 21–16 Fire and life safety program delivery also requires engineering. Provide solutions • Prevent hazard • Reduce harm Primary responsibility • Manufacturers • Designers • Contractors Installation mandated Enforcement • Federal, state, local laws/ordinances • Fire department • Other agency 21–17 Emergency response is another aspect of program delivery. Not preventative measure • Fire • Extrication • Medical care • Structural collapse • Specialized rescue • Not same purpose as initiatives May include other emergencies 21–18 REVIEW QUESTION What components are involved in fire and life safety program delivery? 21–19 Learning Objective 3 Explain the impact of safety hazards, messages, and target audiences on creating fire and life safety education programs. 21–20 Learning Objective 4 Indicate ways to identify and prevent firesetter development. 21–21 Fire and life safety education is designed to reach two goals. Inform citizens about unsafe behaviors Provide information on how to change behaviors 21–22 Fire and life safety hazards are the two broad categories of hazards. Safety – Unsafe behaviors, conditions that result in Fire – Condition that would increase • Likelihood of fire starting • Extent or severity of fire • Injury • Death • Property damage not related to fire 21–23 Other hazards can also be the focus of provided safety messages. Hazardous processes Unsafe conditions Unsafe behaviors 21–24 Fire and life safety messages are chosen based on community assessment of risk and fall into four categories. Prevent Prepare 21–25 Protect Persuade Presentation materials are typically organized based on audience age range. Preschool children Elementary age children Middle school children High school students Adults Older adults 21–26 REVIEW QUESTION How does identifying a target audience impact the creation of a fire and life safety program? 21–27 Structure surveys can be part of fire and life safety education. Performed by fire companies • Become familiar with • Provide public service • Not required by law Company-level preincident survey • Generally on occupied structures • Include public areas • Others subject to survey 21–28 Firefighter I goals • Learn about community • Help distribute information • Learn about improving structure safety Juvenile firesetter programs take steps to reduce fires set by children. Identify at risk children Intervene in behavioral development Assess cause of obsession 21–29 The U.S. Fire Administration identifies the impact of juvenile firesetters. Arson arrests Property loss 21–30 2nd leading cause of fatalities Juvenile firesetters can be identified using information from several sources. Identify categories Steps to take Observational duties 21–31 Prevention of juvenile firesetters is accomplished through several messages. Should teach • Matches, lighters not toys • How to use – With supervision • Destructiveness Provide adults with • Categories, indicators • Importance of keeping matches, lighters out of reach • Supervise young children • Make children aware of dangers • Hire only properly trained babysitter Report • Trends to personnel or professionals • Follow department SOPs 21–32 REVIEW QUESTION What are some steps that can be taken to help prevent firesetter development? 21–33 Learning Objective 5 Describe the role of a Firefighter I in enforcing fire and life safety codes. 21–34 Fire and life safety codes are adopted using a specific process. Model code • Starting point • Developed by consensus organization • Agreed-upon requirements • Only enforceable when adopted by AJH • Know if current or not Steps 21–35 • Final draft received • Prepared for formal adoption • Date set for implementation; announcement made You should understand the two basic aspects of code enforcement. Inspections Investigation 21–36 REVIEW QUESTION What role does the Firefighter I perform when enforcing fire and life safety codes? 21–37 Summary • Fire and life safety initiative programs benefit both the community and the fire department. • When properly implemented the program can help provide an accurate assessment of hazards to which the community must respond. 21–38