Chapter 2 BiochemOfTheBody
advertisement

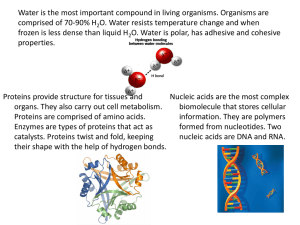
CHEMISTRY BACKGROUND INFORMATION FOR BIOCHEM MATTER • All the “stuff” on Earth • Solid, liquid, gas, or plasma • Change physically or chemically ENERGY • Effects all matter • Kinetic Energy – energy that does work • Potential Energy – stored energy that is inactive ENERGY • Chemical Energy • Stored in bonds of chemicals • Electrical Energy • Movement of charged particles • Mechanical Energy • Directly involved in movement • Radiant Energy • Travels in waves COMPOSITION OF MATTER • All matter is made of elements • Elements – unique substances that can’t be made simpler • Periodic Table COMPOSITION OF MATTER • Each element is made of atoms • Atomic symbols • Nucleus • Protons and neutrons • Outer “shell” • Electrons IDENTIFYING ELEMENTS • Atomic Number • Number of protons • Atomic Mass • Number of protons and neutrons • Isotopes • Differing numbers of neutrons • Some are radioactive COMBINATIONS OF ATOMS • Two or more atoms combined makes a molecule • Two or more different atoms combined makes a compound CHEMICAL BONDS • Use electrons from outer valence shell to bond • 2 or 8 maximum • Ionic bonds and covalent bonds IONIC BONDS • When an atom loses or gains an electron it becomes a charged ion • Ions can steal or give electrons to opposite ions and bond COVALENT BONDS • Some bonds equally share valence electrons • Works to get maximum valence electrons for each HYDROGEN BONDS • Extremely weak covalent bonds • Commonly found in water CHEMICAL REACTIONS • Synthesis Reactions • Combining reactants to make a product • Decomposition Reactions • Breaking a reactant down into products • Exchange Reactions • Substances change or trade parts BIOCHEMISTRY • Two main biological molecules • Inorganic • Usually lack Carbon • Organic • Include Carbon INORGANIC COMPOUNDS • Water • Salts • Many acids and bases WATER • • • • • Most abundant inorganic compound Can absorb and release a lot of heat Universal solvent Important in chemical reactions of the body Part of body protection SALTS • Ionic compounds • Vital to body function • Electrolytes • Substances that conduct electrical current in solution ACIDS • Release H+ ions • Called proton donors BASES • Release OH- ions • Called proton acceptors ACIDS AND BASES • Neutralize each other • pH scale • Concentration of ions • Human body has many buffers to combat excessive pH values ORGANIC MOLECULES • Have functional groups for reactions • Four main macromolecules or polymers • • • • Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic acids CARBOHYDRATES • Sugars and starches • Monosaccharides • Simple sugars • Example, glucose • Disaccharides • Double sugars • Example, sucrose CARBOHYDRATES • Polysaccharides • Many sugars • Example, starch • Carbohydrates are great energy storage molecules LIPIDS • Fats, oils, and waxes • Triglycerides • Made of three fatty acids and glycerol • Saturated • Only have single bonds between carbons • Unsaturated • May have double or triple bonds LIPIDS • Phospholipids • Two fatty acids and a phosphorous group • Make cell boundaries • Steroids • Rings of lipid material • Cholesterol • Energy storage and cell structure PROTEINS • Many roles • Mostly related to cell and body function • Made of amino acids in a chain PROTEINS • Four levels of structure • • • • Primary Secondary Tertiary Quaternary PROTEINS • Three main proteins of the body • Fibrous • Providing strength to body tissue • Globular • Functional proteins • Enzymes • Start chemical reactions in the body NUCLEIC ACIDS • Make up your genes and send info through the cell • DNA and RNA • Made of nucleotides NUCLEIC ACIDS • Nucleotides • Nitrogen base • Adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine, or uracil • 5 carbon sugar • Phosphate group ATP • Adenosine triphosphate provides valuable energy to the cell • Uses energy from glucose by storing it and converting it