Plate Tectonics Quiz: Earth Science Questions
advertisement

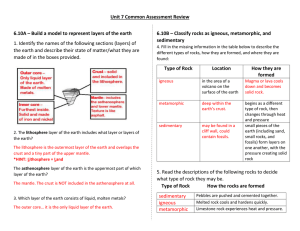
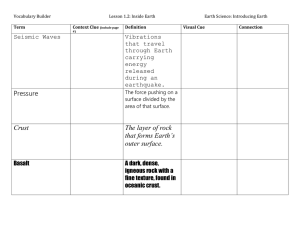
Name Date Plate Tectonics Quiz 1. The Ring of Fire is found: a. In a volcano b. Around the border of the North American Plate c. Around the border of the Pacific Plate d. On the San Andreas Fault 2. The core is made up of ____ layers. a. 3 b. 4 c. 1 d. 2 3. The mantle is found: a. Under the crust b. Below the crust c. Beneath the core d. On the surface of the Earth 4. At the mid-Atlantic ridge, tectonic plates are moving apart. This is an example of a ___________ boundary. a. transform b. divergent c. convergent d. separating 5. What causes Tectonic Plates to move? a. ocean currents b. tectonic motion c. wind patterns in the atmosphere d. convection currents in the mantle 6. Where is the crust the thickest? a. mountain ranges b. ocean floor c. at sea level d. at the boundry of a tectonic plate 7. The crust is the ___________ layer of the Earth. a. innermost b. outermost c. under the mantle d. thickest 8. The two types of crust are: a. oceanic and tectonic b. oceanic and mantle c. continental and volcanic d. continental and oceanic 9. The mantle is made up of solid rock. a. true b. false 10. Tectonic plates remain in one position and do not move. a. true b. false 11. The scientist that proposed the theory of Continental Drift is: a. Albert Einstein b. Albert Schweitzer c. Prince Albert of Monaco d. Albert Wegener 12. The name of the land mass containing all of the continents millions of years ago is: a. Panacopita b. Pancreatica c. Panacea d. Pangea 13. Subduction occurs when an oceanic plate is driven underneath a continental plate. This is an example of a ______________ boundry. a. convergent b. divergent c. transform d. continental 14. What kind of boundary occurs when two continents collide? a. divergent b. transform c. thermal vent d. convergent 15. The crust is made up of magma. a. true b. false 16. What kind of boundary is found at most mountain ranges, volcanoes, and sites of earthquakes? a. convergent b. divergent c. tectonic d. transform 17. Continental Drift is the theory that the Earth’s surface is constantly changing due to the movement of the plates. a. true b. false 18. True or False: The inner core is solid. a. True b. False 19. Which two elements are found in both the inner and outer core of the earth? a. Gold and mercury b. Lithium and Silicon c. Copper and Zinc d. Nickel and Iron 20. Rocks that are formed from melted or liquid material are ____________ rocks. a. Igneous b. Metamorphic c. Sedimentary 21. Hot melted rock below the surface of the earth is called ___________. a. Lava b. Magma c. Metamorphic d. Corona 22. A type of rock that is formed from fragments of rocks that have hardened together by pressure and cementing is _______________. a. Igneous b. Metamorphic c. Sedimentary 23. A type of rock that is changed by heat and/or pressure is called a ________________ rock. a. Igneous b. Metamorphic c. Sedimentary 24. Wind, glaciers and moving water are all ways that _____________. a. Change the crystal size in igneous rocks b. Move rock fragments of different sizes to places where sedimentary rocks are formed c. Create heat and pressure to metamorphose existing rocks. 25. Which of the following is the most useful in assessing the possibility of an earthquake occurring in a particular area? A. Local soil or rock type. B. Distance from a shoreline. C. Local magnetic field strength. D. Distance from a plate boundary. 26. The earthquakes which occur the most frequently also A. cause damage to cities. B. have small magnitudes. C. generate large tsunamis. D. occur in the middle of plates. Use the following sketch map of California to answer this question. 27. The region which has stored the most elastic energy, due to deformation of the crust, is A. W B. X C. Y D. Z . 28. An earthquake has occurred at X. Compared to city 2, city 1 would experience A. Lower magnitude seismic waves B. Higer magnitude seismic waves 29. In order to design an earthquake-resistant structure for an earthquake-prone region, one should take into account A. the magnitude of the largest earthquake expected B. the expected length (duration) of the earthquake shocks C. the nature of the rock or soil upon which the structure is built D. all of the above 30. Which of the following is LEAST likely to be a serious potential danger of earthquakes? A. Fires. B. Tsunamis. C. Severe weather D. Broken sewage lines; 31. A body wave that vibrates parallel to the direction of wave travel is A. P-wave. B. S-wave. C. L-wave. D. it-wave. 32. The first waves to arrive at a seismograph station are the A. tsunami waves. B. S-waves. C. L-waves. D. P-waves. 33. The minimum number of seismograph stations required to determine the location for an epicentre is A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 34. P-waves can best be distinguished from S-waves by the difference in their A. speeds. B. epicentres. C. magnitudes. D. points of origin. Use the map to answer the next two questions. 35. On the map are shown an earthquake epicentre and four seismometers. Which of the sites on the map above will have the shortest P-S wave interval? A. W B. X C. Y D. Z Use the sketch of a seismograph to answer the next question. The four seismographs illustrated below all have a mass with an attached pen. The white cylinder is a slowly turning paper drum that records any relative movement between the pen and the paper. 36. Which seismograph would BEST record the amplitude of vertical earthquake motions? A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 Use the diagram of seismograms at four stations to answer the next question. 37. The seismograms above were recorded for one earthquake by using similar seismographs at four different stations. The correct order, from closest to farthest, in terms of distance from the epicenter to each station is A. 2, 1, 3, 4 B. 2, 3, 4, 1 C. 3, 4, 1, 2 D. 3, 2, 1, 4 Short Answer 1. Label the layers of the earth. (4) 2. Use the following words to label the missing parts of the Rock Cycle in the diagram below. (4) Igneous (from lava – above ground) Igneous (from magma – underground) Sedimentary Metamorphic