Titration
advertisement

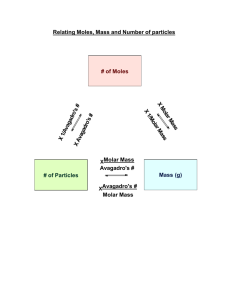
Acid base Titration What is the colour change of the methyl orange during the A student is given a sample of a carbonate, M2CO3, where M is titration? a metal. The colour changes from ......................... to ......................... [1] He is asked to determine the relative atomic mass of M. The student does three titrations. The diagrams below show (a) A sample of the carbonate is added to a previously weighed parts of the burette with the liquid levels at the beginning and beaker which is then reweighed. end of each titration. mass of beaker + M2CO3 = 7.69 g mass of beaker = 5.99 g Calculate the mass of M2CO3. ........................................................ g [1] (b) The student transfers the sample of M2CO3 to a beaker and adds 50.0 cm3 of 1.00 mol / dm3 hydrochloric acid (an excess). A gas is produced. Name the gas and describe a test for this gas. gas ..................................................................... test.......................................................................................[2] (c) When the reaction has finished, the solution in the beaker is (d) Use the diagrams to complete the following table. transferred to a volumetric flask and made up to 250 cm3 with distilled water. This is solution G. Using a pipette, 25.0 cm3 of G is transferred to a conical flask and a few drops of methyl orange indicator are added. A burette is filled with 0.100 mol / dm 3 sodium hydroxide. Aqueous sodium hydroxide is run into the conical flask until an Summary end-point is reached. Tick (✓) the best titration results. 1 Using these results, the average volume of 0.100 mol / dm3 sodium hydroxide is .................................................moles [1] (h) Calculate the number of moles of hydrochloric acid contained in the original 50.0 cm3 of 1.00 mol / dm3 hydrochloric acid. ................................................... cm3. [4] (e) Calculate the number of moles of sodium hydroxide in the average volume of 0.100 mol / dm3 sodium hydroxide in (d). .................................................moles [1] (i) By subtracting your answer in (g) from your answer in (h), calculate the number of moles of hydrochloric acid that reacts with the sample of M2CO3. .................................................moles [1] .................................................moles [1] (j) Using the equation, calculate the number of moles of M 2CO3 (f) Using the equation, calculate the number of moles of that reacts with the number of moles of hydrochloric acid in hydrochloric acid in 25.0 cm3 of G. your answer in (i). M2CO3 + 2HCl → 2MCl + CO2 + H2O .................................................moles [1] .................................................moles [1] (g) Calculate the number of moles of hydrochloric acid in 250cm3 of G. (k) Using your answers in (a) and (j) calculate the relative formula mass of M2CO3 and hence the relative atomic mass of M. [Ar: C, 12; O, 16] 2 relative formula mass of M2CO3 .................................................. burette and added to the solution in the conical flask until an relative atomic mass of M ...................................................... [2] end-point is reached. [Total: 16] Phenolphthalein is colourless in acidic solution and pink in alkaline solution. 8 A student is given a sample of an organic acid, G, and asked What is the colour of the solution in the conical flask to (i) before the acid is added • determine its relative molecular mass ........................................................................................... • suggest its formula. (ii) at the end-point? (a) A sample of the acid is placed in a previously weighed ................................................................................................ [1] container and reweighed. (c) The student does three titrations. The diagrams below show parts of the burette with the liquid levels at the beginning and end of each titration. Calculate the mass of G used in the experiment. .............................................. g [1] (b) The student transfers the sample to a beaker and adds 50.0 cm3 of 1.00 mol / dm3 sodium hydroxide, an excess. The contents of the beaker are allowed to react and then transferred to a volumetric flask. The solution is made up to 250 cm 3 with distilled water. This is solution H. 25.0 cm3 of H is transferred into a conical flask. Use the diagrams to complete the following table. A few drops of phenolphthalein indicator are added to the conical flask. 0.100 mol / dm3 hydrochloric acid is put into a 3 (g) Using your answer from (f) calculate the number of moles of sodium hydroxide in 250 cm3 of H. ...................................... moles [1] (h) Calculate the number of moles of sodium hydroxide in 50.0 cm3 of 1.00 mol / dm3 sodium hydroxide. Summary Tick (✓) the best titration results. Using these results, the average volume of 0.100 mol / dm3 hydrochloric acid is ...................................... moles [1] (i) By subtracting your answer in (g) from your answer in (h), .......................................... cm3 [4] (d) Calculate the number of moles of hydrochloric acid in the calculate the number of moles of sodium hydroxide that reacts with the original sample of the organic acid, G. average volume of 0.100 mol / dm3 hydrochloric acid from (c). ...................................... moles [1] (e) Construct the equation for the reaction between hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide. ...................................... moles [1] ................................................................................................ [1] (j) One mole of G reacts with two moles of sodium hydroxide. (f) Using your equation and the answer from (d), deduce the Deduce the number of moles of G in the sample. number of moles of sodium hydroxide present in 25.0 cm3 of H. ...................................... moles [1] 4 ...................................... moles [1] [Total: 16] (k) Using your answers from (a) and (j) calculate the relative molecular mass of the acid G. .................................................. [1] (l) The acid G contains two carboxylic acid groups and has the formula HO2CCxHyCO2H where x and y are whole numbers. Deduce the values of x and y in the formula. [Ar: H, 1; C, 12; O, 16] x ................................................. y ................................................. [2] 5