Substance Abuse
advertisement

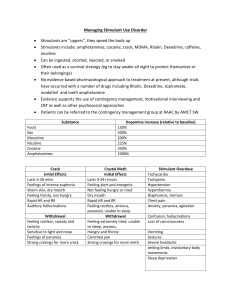
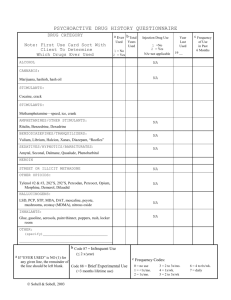
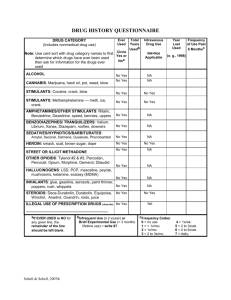
Substance Abuse Nurs 205 Important Terms Substance Abuse – The use of mood or behavior altering substances in a maladaptive manner Physical dependence – physiologic reliance on a substance Showing symptoms Psychologic dependence –strong desire to obtain and use a substance Important terms Addiction – strong physical and psychologic dependence on a drug or other psychoactive substance Withdrawal – A substance specific mental disorder that follows cessation or reduction of a substance Habituation Situation in which a patient becomes accustomed to a certain drug (devel) tolerance…. And may have mild psychological dependence, but will not show w.drawl symp -13:11 Commonly abused substances Major Categories Opioids Stimulants Depressants Commonly abused substances Specific drugs Alcohol Methamphetamine Nicotine MDMA Opioids Opioid analgesics – synthetic versions of pain relieving substances. FDA Aprroved High chance of addiction Morphine and Codeine Synthetic derivatives include: hydromorphone, hydrocodone, oxycodone, and meperidine Opioids Diacetylmorphine (heroin) Produces an intense euphoric state (rush) followed by a relaxed contented state that can last several hours. Schedule I drug- no currently accerpted medical use I US, lack of accepted safty, and high potential for abuse No FDA Opioids Mechanism of action – Blocks receptors in the central nervous system, thus blocking the perception of pain. Diff forms w/ age and reason Opioids Indications Relieve pain, reduce cough, relieve diarrhea, and induce anesthesia Contraindications Drug allergy, pregnancy, severe asthma Opioids Adverse effects – CNS related factors – nausea, vomiting, diuresis, respiratory depression Symp Decreased respiratory rate Opioids Management of withdrawal(opioids) Peak- 1-3 days Duration- 5-7 days Signs and symptoms- drug seeking, mydriasis, diaphoresis, rhinorrhea, lacrimtion, vim, diarrhea, insomnia, Higher BP & pulse rate Medications- Methadone, Buprenorphine(Subutex), clonidine, naltrexone(narcan) Stimulants Effect of stimulants include: Mood elevation, reduction of fatigue, and sense of increased alertness Drugs include: Amphetamines, Cocaine, Methylphenidate (Ritalin), methamphetamines and MDMA Stimulants Stimulants are often used in combination with alcohol and marijuana Restrictions on sales of pseudoephederine MDMA Stimulants Legal and illegal use of methylphenidate ADHD Study aide- used to prevent or reverse fatigue and sleep Amphetamine- stimulate respiratory center Stimulants used to decrese food intake & treat obesity Stimulants Mechanism of Action – Release of norepinephrine Increased BP, pulse, and potential for cardiac arrythmias Physical performance enhancements Stimulants Indications Contraindications ADD, ADHD, narcolepsy, respiratory stimulant Allergy, cardiovascular disorders Adverse effects Syncope, tremors, irritability Stimulants Withdrawal Peak and duration Signs and symptoms Treatment Depressants Drugs that relieve anxiety, irritability and tension Benzodiazepines Barbituates Marijuana Rohypnol GHB- gamma hydroxy butyric acid Depressants Mechanism of action – inhibits nerve transmission to the CNS by increasing the action of GABA.(Gamma Amino Butyric Acid- Amino Acid in brain that inhibit nerve transmission in the CNS). Causes relief of anxiety, sedation and muscle relaxation Also include amnesia, unconsciousness, and slight blood pressure decreases. Depressants Indications Contraindications Anxiety relief, sedation, sleep Allergy, dyspnea, glaucoma Adverse effects Drowsiness, loss of coordination, hallucinations Depressants Withdrawal Peak: 2-4 Days for short acting drugs, 4-7 days for long acting drugs Duration: 4-7 Days for short acting, 7-12 days for long acting Signs: Increased activity, agitation, hyperthermia, delirium, Higher BP Higher Pulse Symptoms: Anxiety, depression, tremors, suicidal thoughts Treatment: Benzodiazepines (Valium) Alcohol Widely available – not illegal (if you are over 21 Mechanisms of action – CNS depression by altering the lipid matrix in the brain. May decrease respirations Moderate doses cause vasodilation Alcohol Indications Drug solvent in medicinal mixtures Topical applications- ethanol is a coolant Cold and cough treatments Cardiovascular benefits- small lamt of ethonaol……………………. Alcohol Adverse Effects Long term effects: Neurologic and mental disorders Teratogenic effects: on fetus Nutritional and vitamin deficiencies Wernicke’s encephalopathy A neruo disorder charac by apathy, drowsy, ataxia, nystagmus, and opthalmoplegia Korsakoff’s psychosis A syndrome of amnesia with confabulation (making up stories) associated with c/c alcohol abuse, Alcohol Mild and Moderate withdrawal Elevated bp, temp, pulse, insomnia and agitation Severe withdrawal Delirium Tremens Alcohol Withdrawal treatment Cardiac monitoring Benzodiazepines Restraints B vitamin supplementation Alcohol Disulfiram – treatment for alcoholism Alters alcohol metabolism by causing an acetaldehyde syndrome(17-2) Signs and Symptoms effect Cardiovascular(Chest pain, hypotension), CNS(Head ache, sweat, confudion), GI(nausea, vom) and Respiratory systems(difficulty breathing) Nicotine Tobacco dependence Tolerance Need more to produce desired effect Chemicals and poisons in cigarettes 200 known poisons Nicotine Mechanisms of Action – Direct stimulation of autonomic ganglia Transient stimulation followed by more persistent depression Stimulates the CNS Increased heart rate and blood pressure Increased GI activity Nicotine Indications No known therapeutic effect May be used to reduce cravings Adverse effects Tremors, depression, nausea Nicotine Withdrawal management Symptoms – irritability, restlessness, and decrease in heart rate and blood pressure Therapies Transdermal nicotine Antidepressants Nicotine agonist Nursing process Assessment Relationship between substance abuse and other health issues Specific questions about substance use – how often and last time Lab work – Liver, renal function and HIV status Observation for withdrawal symptoms Nursing diagnosis Low self-esteem Deficient knowledge of abusive behaviors Risk of injury Planning and outcome criteria Patient regains control of ones own behavior Patient undergoes safe withdrawal Patient receives referral Implementation Interventions are based on the patient’s specific physical or emotional problems Monitor vital signs, neurological status and mental status Evaluation Patient safety Recovery and rehabilitation phases Family support