Cornell Notes and example
advertisement

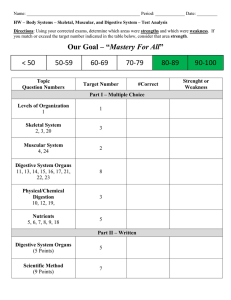
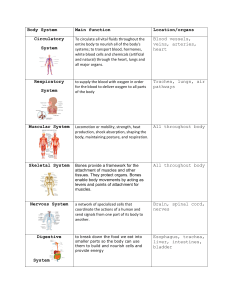
Cornell Notes Way of taking notes so that YOU understand the big ideas and can make connections Title Reread notes and reflect • • • • • • List main ideas Key points Drawings Connections Inference Questions you still have Take notes here • In short hand – abbreviate (text language) • Definitions • Important people • Repeated or stressed information • Diagrams or pictures Summary • In your OWN words, write a few complete sentences about what you learned.; and what you want to know more about. Interrelationship of the Body Systems (Video) - All cells can live, grow, get energy, get rid of waste, reproduce - Levels of organization: cells tissue organ organ system organism - Skeletal (bones) protect, support, make blood, move - Muscular (muscles) move - Circulatory (heart, blood, blood vessels) move nutrients, O2 & waste - Respiratory (lungs, alveoli) breathe - Digestive (stomach, intestines) break down food to absorb nutrients - Excretory all system that get rid of waste (respiratory – CO2, Skin – sweat, Urinary – urine, Digestive – feces) - Immune (new) protects against germs - Nervous (brain, spinal cord, nerves) sends messages, thinking, 5 senses - Endocrine uses hormones to send messages to grow, puberty - Reproductive (male/female) - needed for survival or species but not organism - All systems work together to maintain balance (homeostasis) - Integumentary ? (skin) Cells and organs work 2gether C are the foundation of a human (organism) All C carry out process for us to live and grow take in food & transform into energy gets rid of waste builds proteins that makes new cells Cells group to make up tissue tissue organs organs systems Skeletal (bones) Functions protect organs Store minerals Produce blood Help move joints - 2 bones meet cartilage – covers end of bone ligament – connect bones Muscular – F:move muscles team up contract/relax can be voluntary/involuntary (heart) Circulatory (heart, blood, blood vessels) delivers O2 (body uses to E out of food) picks up waste – CO2 blood vessels (veins, arties, capillaries – exchange Respiratory (lungs, alveoli – gas exchange)) breathe O2 (used by body to release E from food) get rid of CO2 waste Digestive (mouth, teeth, saliva, stomach, small intestine – absorb nutrients, large intestine, anus) need nutrients to grow & repair Excretory gets rid of CO2 (lungs), liquid urine, sweat (skin), solid (anus) Andreas Vesalius studied medical science through dissection & observation “Father of Anatomy” Immune (saliva, mucus, stomach juices, white blood cells) protects form germs by heating up Nervous (brain, nerves, spinal cord) think, balance sight, touch, hearing, smell Endocrine (F: grow, puberty) sends message by hormones Reproductive survival of species, but not organism All systems work together to make a fully functioning human (communication) Balance system work together Demo (5 kids spread out, but can touch, circle around feet, cannot get out of circle, must pass bucket of water, some has special features like no hands Riding bike needs muscular/skeletal to move respiratory/circulatory to breathe & deliver O2 Nervous to send messages Immune (hurt or sick) Digestive to break down food for energy Excretory to get rid of waste Cell Tissue organ Organ system Cells are the basic building blocks of life (cell theory). Cells are grouped to make up tissues, tissues make up organs, organs make up organ systems, and systems are group to make a whole organism. Systems of the human body include: skeletal, muscular, circulatory, respiratory, digestive, excretory, immune, nervous, endocrine, reproductive, and integumentary. All of these systems must work together as a team to keep the body in balance and functioning properly. Interrelationship of the Body Systems (Video)