Abraham Maslow
advertisement

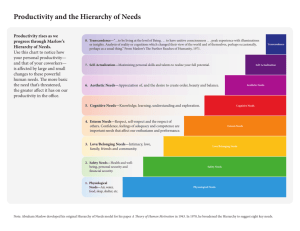
Abraham Maslow The Hierarchy of Needs Linda Zimmerman Professor of Student Development Oakton Community College ABRAHAM MASLOW • was a leading humanistic psychologist (Third Force) • developed the Hierarchy of Needs • promoted the concept of self-actualization • was born in 1908, Brooklyn, New York Maslow’s Early Life • was the eldest of seven siblings • was a poor student as an adolescent • was pressured by dad to become an attorney • took one law class, dropped out of college for one year • entered U of WI one year later to study scientific psychology Maslow’s Professional Life • studied dominance in monkeys • received Ph.D. in experimental psychology in 1934 • was on the Brooklyn College faculty, 1937-1951 • was on the Brandeis U faculty, 1952-1969 • became a fellow of Laughlin Foundation in CA • died in 1970, age 62 Hierarchy of Needs growth emotional physical Hierarchy of Needs Physiological Needs Physiological Needs • food • water • air • sleep Food: A Most Powerful Need • South American Rugby team crashed in 1970 • Food was the most pressing problem. • They ate human flesh for survival. • Even the strongest taboo was broken to fill the basic need for food. Food: A Most Powerful Need • Ik tribe in Uganda forced to give up hunting and live on unfertile land • long standing social mores dissolve - people became psychopathic • “ngag”, word for food, also becomes word for good • parents steal food from children, children from other children Hierarchy of Needs Safety Needs Physiological Needs Safety Needs • from physical attack • from emotional attack • from fatal disease • from invasion • from extreme losses (job, family members, home, friends) Safety: A Most Powerful Need • when frightened, our thoughts and energies are diverted • threat of, or actual attack creates “fight or flight” reaction • threats to safety can be physical or emotional Hierarchy of Needs Love & Belonging Needs Safety Needs Physiological Needs Love and Belonging (social/emotional) • Inclusion - part of a group: colleagues, peers, family, clubs • Affection - love and be loved • Control - influence over others and self Love and Belonging: A Most Powerful Need Hierarchy of Needs Esteem Needs Love & Belonging Needs Safety Needs Physiological Needs Esteem Needs emotional (ego) • respect from others through: awards honors status • respect for self through: mastery achievement competence Esteem from Self and Others: A Most Powerful Need Congratulations Hierarchy of Needs Self-Actualization Needs B- Needs (being) Higher needs Esteem Needs D- Needs Deficit Survival Love & Belonging Needs Safety Needs Physiological Needs Some Self-Actualizing People from History • • • • • • • Abraham Lincoln Thomas Jefferson Mahatma Gandhi Albert Einstein Eleanor Roosevelt William James Benedict Spinoza Self-Actualization Needs • stop cruelty and exploitation • encourage talent in others • try to be a good human being • do work one considers worthwhile • enjoy taking on responsibilities • prefer intrinsic satisfaction • seek truth • give unselfish love • be just B-Needs of the Self-Actualized • • • • • • • Truth Goodness Beauty Unity Aliveness Uniqueness Perfection and Necessity • • • • • • • • Completion Justice and order Simplicity Richness Effortlessness Playfulness Self-sufficiency Meaningfulness Qualities of the Self-Actualized • • • • • • • • An non-hostile sense of humor Intimate personal relationships Acceptance of self and others Spontaneity and simplicity Freshness of appreciation More peak experiences Democratic values Independence Peak Experiences Moments of Pure Bliss


![Abraham Maslow [Autosaved]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/025194284_1-d4cda09130dfc06314210c770d18f8c4-300x300.png)