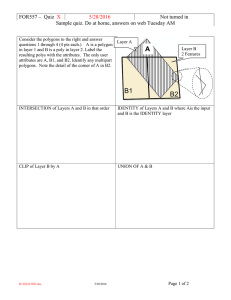
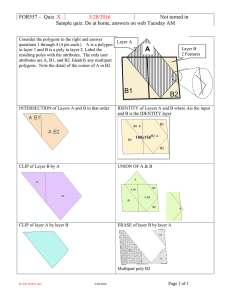
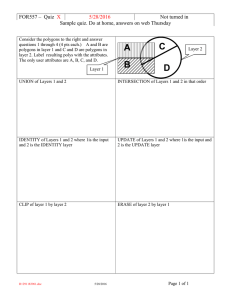
Geoprocessing of Vector Data Models
advertisement

Republic of the Philippines EASTERN VISAYAS STATE UNIVERSITY Tacloban City College of Engineering DEPARTMENT OF GEODETIC ENGINEERING GE 413 Geographic Information System Members: Alde, Ruby Angeline Fernandez, Lian Quitorio, Angel Joy B. Rivera, Mariel Group No. 5 Date Performed: August 28, 2018 Date Submitted: September 1, 2018 Rating: ___________ Exercise No. 2 Geoprocessing of Vector Data Models I. Introduction A GIS provides a spatial framework to support decisions to help manage the natural and man-made environment and resources of the earth. Geoprocessing allows the user to define, manage, and analyze the information used to form these decisions. Geoprocessing is a GIS operation used to manipulate spatial data. A typical geoprocessing operation takes an input dataset, performs an operation on that dataset, and returns the result of the operation as an output dataset. The purpose of this exercise is to learn the importance of geoprocessing tools and apply its function. In this exercise, some functions of geoprocessing tools and their differences will be explained. II. Objective Use and apply the functions in the geoprocessing tools of QGIS: a. Intersect b. Union c. Symmetrical Difference d. Clip e. Difference f. Dissolve III. Material QGIS Software Computer/Laptop IV. Procedure Open QGIS Software and create a new project. Add new shapefile layer by clicking the clicking on the menu bar Layer → New → New Shapefile Layer or the button at the Side Toolbar (or simply hold Ctrl+Sht+N) and locate the file (see figure 1). Figure 1. Adding New Shapefile Layer A new shapefile dialog will be displayed (see figure 2). Figure 2. New Shapefile Dialog Select Polygon and type ‘polygon1’ in the name field. Then click Add to attributes list (Add to field list). Click OK and a save dialog will appear. Navigate to a file directory and save the new layer as polygon1.shp. The new layer should appear in the Layer list. Navigate to and click on the Toogle Editing button on the toolbar and then click Add Feature button to start making polygons. Create 3 different polygons (Trapezoid, Triangle, Hexagon) as shown in figure 3. Figure 3. Three Different Polygons of polygon1 Layer Repeat the process on adding a polygon. This time, type ‘polygon2’ in the name field and save it as polygon2. Create 3 polygons (rectangle, triangle, small rectangle) over the polygon1 layers as shown in figure 4. Figure 4. Change the color of each polygon. For this exercise, use green for polygon1 and blue for polygon2) Navigate to and click on the menu bar Vector → Geoprocessing Tool → Intersection (see figure 5). Figure 5. Intersection Tool An Intersection dialog will appear. Choose polygon1 in the Input Layer and polygon 2 in the Intersect Layer (see figure 6). Figure 6. Intersection Dialog Click the browse button then save to file. A save file dialog will appear. Write a file name, save and click Run. Repeat the process and try the following geoprocessing tools: Union, Clip, Symmetrical Difference and Difference tool. Always choose polygon1 as the Input layer and polygon2 on the next required layer. Save each output shapefiles. For the Dissolve Tool, Add New Shapefile Layer and name it polygon3. Then add atleast 3 overlapping polygon features. Navigate to and click on the menu bar Vector → Geoprocessing Tool → Dissolve A Dissolve Dialog will appear. Choose polygn3 as the Input Layer, and add polygon3 by clicking the arrow-like button as shown in figure 7. Click the browse button and save the layer. Click run. Figure 7. Dissolve Dialog Results and Discussion A. Intersect Tool The purpose of the intersect tool is to overlay layers such that output contains areas where both layers intersect. To perform the function, two layers are required. The first one is the Input layer (polygon1) and the other one is the Intersect layer (polygon2) that is used for intersecting. The input layer can have any feature (points, line, polygon), while the intersect layer should have polygon feature. After performing/running the intersect tool, a new output layer (intersection layer) appeared on the layer panel. The new layer contains portion of features which overlap in all layers of feature classes. The features (polygon1 & polygon2) within the common area of both coverages are preserved. Figure 8. Output of Intersection Tool B. Clip Tool Clip tool cuts a layer based on the boundaries of another layer. This overlay function is performed to extract features in which the area of extraction is decided from the clip cover and the features to be extracted are from the input coverage. Input layers can be points, lines or polygons band the clip cover is always a polygon. After applying the Clip tool to polygon1 and polygon2 layers, a new clipped output layer appeared on the layer panel. The attributes of the new clipped layer is mainly from polygon1 layer (input layer) and not from polygon2 layer (clipping layer). Figure 9. Output of Clip Tool Intersect Tool vs Clip Tool Upon looking at the outputs of the Intersect tool and Clip tool in figure 7 and 8, the user might get confused and might say that their functions are the same, but the difference is seen if the user look at the attributes of the result in the attribute table. When using Clip only the input feature’s attributes will be in the output (none from the clip feature), where if you used intersect the attributes form all features used will be in the output. The output of the clip tool (clip layer) contains the features’ attribute of the polygon1 that was used as the input layer, while the output of the intersect tool contains both polygon1 and polygon2 (see figure below). Figure 10. Attribute Table of Clip Layer (left) and Intersection Layer (right) C. Symmetrical Difference The Symmetrical Difference tool is used to perform overlay analysis on feature classes. This tool creates a feature class from those portions of features that are not common to any of the other inputs. After applying the symmetrical tool, a new output layer (symmetrical difference layer) appeared on the layer panel. The new symmetrical difference layer contains those areas of polygon1 and polygon2 that do not intersect or overlap. Figure 11. Output of Symmetrical Difference D. Difference The purpose of the Difference tool is to overlay layers such that output contains areas not intersecting the clip layer. It subtracts areas of one layer based on the overlap of another layer. Below is the result after applying difference tool to polygon1 and polygon2 layers. The left side shows the result when polygon1 was used as the input layer and polygon2 as the clip layer. The right side shows the result when polygon2 was used as the input layer and polygon1 as clip layer. Figure 12. Output of Difference Tool From the results, it can be stated that the difference tool creates a new feature based on the area of the input layer that is not overlapped by the clipping layer. Symmetrical Difference vs Difference ‘Symmetrical difference’ of two layers contains the portion of features of both layers except the portion or area of features of the two layers that overlapped, while the ‘difference’ of two layers contains the elements and features of the input layer except those belonging to the clip layer. Figure 13. Attribute Table of Different Tool (left) and Symmetrical Tool (right) E. Union The purpose of the Union tool is to overlay layers such that output contains intersecting and non-intersecting areas. It melds two layers together into one while preserving features and attributes of both. It also requires two input layers. After applying the Union tool on the two layers (polygon1 & polygon2), a union layer appeared on the layer panel. The layer contains geometric combination of the features of polygon1 and polygon2. Figure 14. Output of Union Tool The number of polygons in the union layer is more than in the polygon1 and polygon2. The Union layer contains both the attributes of the polygon1 and polygon2 (see figure below). Figure 15. Attributes of Union Layer F. Dissolve Tool Dissolve tool merge features based on input field. All features with identical input values are combined to form one single feature. In dissolve tool, new spatial geometry is formed and the number of polygons formed are reduced In the figure below, a new spatial geometry is formed from 3 overlapping polygons after applying the dissolve tool. Figure 16. Output of Dissolve Tool Union Tool vs Dissolve Tool The output of the Union tool and Dissolve tool is almost the same except that union tool overlay two layers, preserves the attribute of both features and a number of polygon is produced while in Dissolve tool new spatial geometry is formed and the number of polygons formed are reduced. The figure below shows the attributes of the Union and Dissolve tool: Figure 17. Attribute Table of Union Tool (left) and Dissolve Tool (right) On the left side, it can be seen that in Union attributes of polygon1 and polygon2 were preserved, while on the right side the features under polygon3 reduced into one. V. Conclusion Geoprocessing tools are helpful in managing spatial data. Using these tools, user can obtain additional information, extract subset from larger dataset, perform analyses, solves queries and many more. Its purpose is to automate GIS tasks and therefore makes lot of tasks in QGIS easier. VII. References QGIS User Guide. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://docs.qgis.org/2.18/en/docs/user_manual/ Geoprocessing in QGIS. (2013). Retrieved from https://www.slideshare.net/swethaashok28/geoprocessing-in-qgis