Diesel Electrical and Electrnoic Systems I
advertisement
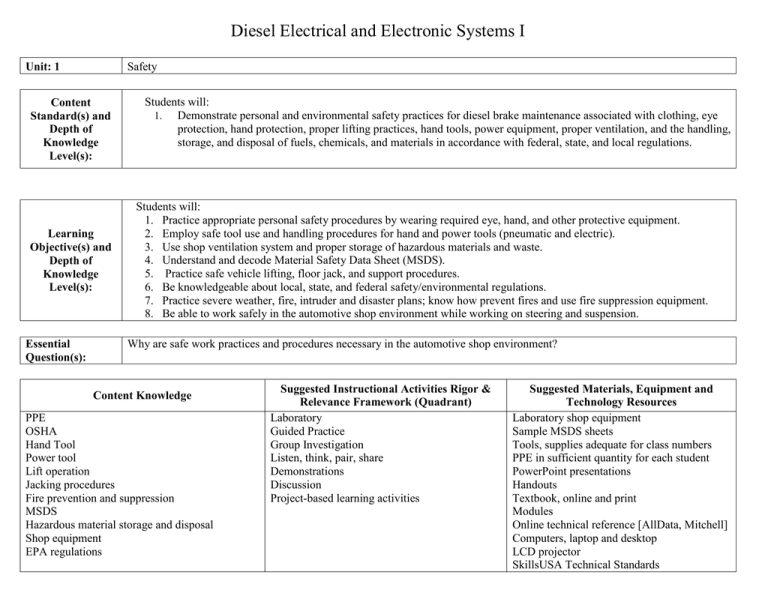
Diesel Electrical and Electronic Systems I Safety Unit: 1 Content Standard(s) and Depth of Knowledge Level(s): Learning Objective(s) and Depth of Knowledge Level(s): Essential Question(s): Students will: 1. Demonstrate personal and environmental safety practices for diesel brake maintenance associated with clothing, eye protection, hand protection, proper lifting practices, hand tools, power equipment, proper ventilation, and the handling, storage, and disposal of fuels, chemicals, and materials in accordance with federal, state, and local regulations. Students will: 1. Practice appropriate personal safety procedures by wearing required eye, hand, and other protective equipment. 2. Employ safe tool use and handling procedures for hand and power tools (pneumatic and electric). 3. Use shop ventilation system and proper storage of hazardous materials and waste. 4. Understand and decode Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS). 5. Practice safe vehicle lifting, floor jack, and support procedures. 6. Be knowledgeable about local, state, and federal safety/environmental regulations. 7. Practice severe weather, fire, intruder and disaster plans; know how prevent fires and use fire suppression equipment. 8. Be able to work safely in the automotive shop environment while working on steering and suspension. Why are safe work practices and procedures necessary in the automotive shop environment? Content Knowledge PPE OSHA Hand Tool Power tool Lift operation Jacking procedures Fire prevention and suppression MSDS Hazardous material storage and disposal Shop equipment EPA regulations Suggested Instructional Activities Rigor & Relevance Framework (Quadrant) Laboratory Guided Practice Group Investigation Listen, think, pair, share Demonstrations Discussion Project-based learning activities Suggested Materials, Equipment and Technology Resources Laboratory shop equipment Sample MSDS sheets Tools, supplies adequate for class numbers PPE in sufficient quantity for each student PowerPoint presentations Handouts Textbook, online and print Modules Online technical reference [AllData, Mitchell] Computers, laptop and desktop LCD projector SkillsUSA Technical Standards SkillsUSA PDP Unit Assessment: Unit/Course CTSO Activity: Unit/Course Culminating Product: Student will take and pass a safety exam with a score of 100%. The student will demonstrate safe shop practices, policies, and procedures on a daily basis. 1. Continue SkillsUSA Leadership Development Programs. 2. Establish documentation for students’ career portfolio. 3. Students review SkillsUSA Technical Standards and Contest Projects. Student will demonstrate knowledge of system being taught; provide accurate diagnosis of system and industry standard repairs. Removing, repairing and replacing components of a vehicle located in the laboratory Accomplishment of appropriate NATEF performance standards Course/Program Credential(s): Other: NATEF Standards Credential Certificate Postsecondary Degree University Degree Diesel Electrical and Electronic Systems I Unit: 2-4 Content Standard(s) and Depth of Knowledge Level(s): Learning Objective(s) and Depth of Knowledge Level(s): General Electrical System Diagnosis Students will: 2. Demonstrate diagnostic procedures in electrical and electronic systems. • Demonstrating proper work order procedures 3. Identify electrical and electronic system concerns. • Determining necessary action for electrical and electronic systems concerns 4. Research applicable vehicle and service information. Example: vehicle service history, technical service bulletins, interpretation of vehicle and major component identification numbers Students will: 1. Complete work order to include customer information, vehicle identifying information, customer concern, related service history, cause and correction. 2. Identify and interpret electrical/electronic system concern; determine necessary action. 3. Research applicable vehicle and service information, such as electrical/electronic system operation, vehicle service history, service precautions, and technical service bulletins. 4. Locate and interpret vehicle and major component identification numbers (VIN, vehicle certification labels, and calibration decals). 5. Diagnose electrical/electronic integrity of series, parallel and series-parallel circuits using principals of electricity Ohm’s Law). 6. Use wiring diagrams during diagnosis of electrical circuit problems. 7. Demonstrate the proper use of a digital multi meter [DMM] during diagnosis of electrical circuit problems. 8. Check electrical circuits with a test light; determine necessary action. 9. Measure source voltage and perform voltage drop tests in electrical/electronic circuits using a volt meter; determine necessary action. 10. Measure current flow in electrical/electronic circuits using ammeter; determine necessary action. 11. Check continuity and measure resistance in electrical/electronic circuits and components using an ohmmeter; determine necessary action. 12. Check electrical circuits using fused jumper wires; determine necessary action. 13. Locate shorts, grounds, opens, and resistance problems in electrical/electronic circuits; determine necessary action. 14. Measure and diagnose the cause(s) of excessive key-off battery drain (parasitic draw); determine necessary action. 15. Inspect and test fusible links, circuit breakers, and fuses; determine necessary action. 16. Inspect and test switches, connectors, relays, solenoid solid state devices, and wires of electrical/electronic circuits; perform necessary action. 17. Remove and replace terminal end from connector. 18. Repair connectors and terminal ends. 19. Perform solder repair of electrical wiring. Essential Question(s): What is the primary function of the digital multi meter? How is resistance measured in an electrical circuit? Content Knowledge 1. Complete work order. A. Demonstrate knowledge of work order creation by either paper work order or computer based program. B. Document customer complaint or reason for visit to point where technician will have enough information to get started. C. Review related history for customer / vehicle. D. Present cause and correction on work order for customer. 2. Knowledge of common electrical system problems; poor ground loose connections, weak battery, failed diode etc. 3. Ability to use technical data base to research necessary testing and repair procedures 4. Knowledge of locations for important identifying numbers (VIN, calibration etc.) 5. Knowledge and understanding of parallel, series and parallel circuits and how to test them 6. Knowledge of how to use wiring diagrams, symbols and annotations 7. Demonstrated ability to accurately use Suggested Instructional Activities Rigor & Relevance Framework (Quadrant) Brainstorming/Discussion Case Studies/ Scenarios Collaborative Learning Cooperative learning Demonstration Experiments Field Trips Five Plus one (5+1) Games Group investigation Guest Speaker Guided Practice Instructional Technology Laboratory/ Shop Exercise Lecture, Lecture/Demonstration Note Taking PBL (Problem based Learning) Ten plus two (10+2) Work Based Learning Work Sheets Suggested Materials, Equipment and Technology Resources Laboratory shop equipment Sample MSDS sheets Tools, supplies adequate for class numbers PPE in sufficient quantity for each student. PowerPoint presentations Handouts Textbook, on line and print Modules Online technical reference [AllData, Mitchell] Computers, laptop and desktop LCD projector SkillsUSA Technical Standards SkillsUSA PDP DMM and other electrical test equipment 8. Appropriate use of 12v test light 9. Ability to set up and run voltage drop test using DMM 10. Ability to set up and run ammeter testing 11. Use of DMM to test continuity in circuits 12. Knowledge of circuit operation 13. Understanding of ground fault and power side testing of electrical circuits test same with jumper wires and other 14. Use of industry approved methods of determining excessive and parasitic drain 15. Knowledge of how and when fusible links are to be used 16. Knowledge of different types of switches, connectors etc including ability to test 17. Knowledge of proper wire stripping, insulating methods fro replacement of emergency terminal; ends 18. Knowledge of wire sizes terminal types for connecting wires of same and/or different sizes 19. Appropriate repair of can bus wires 20. Knowledge of how to prepare wire, use of solder gun 21. Use of technical reference material to locate hybrid disconnect Unit Assessment: Unit/Course CTSO Activity: Unit/Course Culminating Product: Written testing based on NATEF standards Performance evaluation based on NATEF standards The student will demonstrate safe shop practices, policies, and procedures on a daily basis. 1. Continue SkillsUSA Leadership Development Programs. 2. Establish documentation for students’ career portfolio. 3. Students review SkillsUSA Technical Standards and Contest Projects. Student will demonstrate knowledge of system being taught; provide accurate diagnosis of system and industry standard repairs. Removing repairing and replacing components of a vehicle located in the laboratory Accomplishment of appropriate NATEF performance standards Course/Program Credential(s): Other: NATEF Standards Credential Certificate Postsecondary Degree University Degree Diesel Electrical and Electronic Systems I Battery Diagnostics and Service Unit: 5 Content Standard(s) and Depth of Knowledge Level(s): 5. Demonstrate procedures for testing and servicing batteries. Example: performing battery state-of-charge test; inspecting and cleaning battery cables, connectors, clamps, and holddowns Learning Objective(s) and Depth of Knowledge Level(s): Students will: 1. Perform battery state-of-charge test: determine necessary action. 2. Perform battery capacity (or conductance test); confirm proper battery capacity for vehicle application; determine necessary action. 3. Maintain or restore electronic memory functions. 4. Inspect, clean, fill, and replace battery. 5. Perform slow/fast battery charge. 6. Inspect and clean battery cables, connectors, clamps, and hold downs; repair or replace as needed. 7. Start a vehicle using jumper cables and a battery or auxiliary power supply. 8. Identify electronic modules, security systems and/or radios that require re-initialization or code entry following battery disconnect. 9. Describe the different types of multi-battery systems. Essential Question(s): Students will: Why is it important to have strong knowledge and skills in electronics for diesel technology? Content Knowledge 1. Selection of appropriate equipment to test batteries and knowledge of battery construction to know when a battery has failed 2. Using appropriate test equipment, compare battery to rating for car using technical reference material 3. Use of memory battery or similar device, to hold functions normally deleted with battery Suggested Instructional Activities Rigor & Relevance Framework (Quadrant) Brainstorming/Discussion Case Studies/ Scenarios Collaborative Learning Cooperative learning Demonstration Experiments Five plus one (5+1) Games Group investigation Suggested Materials, Equipment and Technology Resources Laboratory shop equipment Sample MSDS sheets Tools, supplies adequate for class numbers PPE in sufficient quantity for each student PowerPoint presentations Handouts Textbook, online and print Modules Online technical reference [AllData, Mitchell] disconnect 4. Knowledge of chemical reactions caused by some cleaning agents, battery safety policies and procedures (remove negative cable 1st etc.) 5. Set up and select appropriate charging functions to properly charge battery. 6. Understand capabilities of corrosive materials as well as their invasive properties. 7. Knowledge of how to properly hook up cables or jump box to start disabled vehicle 8. Understanding of extremely high voltage nature of hybrid, location of isolation switches 9. Locate and program modules that require same when battery power is disconnected. 10. Use technical reference material to locate service batter on hybrid vehicles. 11. Series, parallel, series-parallel circuits 12. Wiring diagrams 13. Multimeter 14. Test light 15. Voltage 16. Current flow 17. Continuity and resistance 18. Fused jumper wires 19. Shorts, grounds, opens, and resistance 20. Key-off battery drain 21. Fusible links 22. Switches, connectors, relays, solid state devices, and wires 23. Wiring harnesses and connectors 24. Solder repair 25. Systems concerns 26. Vehicle and service information 27. Vehicle and major component identification numbers 28. State of charge 29. Battery capacity 30. Electronic memory functions 31. Inspect, clean, fill, and replace Guest Speaker Guided Practice Instructional Technology Laboratory/ Shop Exercise Lecture, Lecture/Demonstration Note Taking PBL (Problem Based Learning) Work Based Learning Work Sheets Computers, laptop and desktop LCD projector SkillsUSA Technical Standards SkillsUSA PDP 32. Battery charge 33. Battery cables, connectors, clamps, and holddowns 34. Jumper cables and power supplies Unit Assessment: Unit/Course CTSO Activity: Unit/Course Culminating Product: Written testing based on NATEF standards Performance evaluation based on NATEF standards The student will demonstrate safe shop practices, policies, and procedures on a daily basis. 1. Continue SkillsUSA Leadership Development Programs. 2. Establish documentation for students’ career portfolio. 3. Students review SkillsUSA Technical Standards and Contest Projects. Student will demonstrate knowledge of system being taught; provide accurate diagnosis of system and industry standard repairs. Removing repairing and replacing components of a vehicle located in the laboratory Accomplishment of appropriate NATEF performance standards Course/Program Credential(s): Other: NATEF Standards Credential Certificate Postsecondary Degree University Degree Diesel Electrical and Electronic Systems I Unit: 6 Content Standard(s) and Depth of Knowledge Level(s): Learning Objective(s) and Depth of Knowledge Level(s): Starting System Diagnosis and Repair Students will: 6. Explain starting system components and operations. • Performing test procedures for starting systems Students will: 1. Diagnose and repair starting system malfunctions. 2. Perform starter current draw tests; determine necessary action. 3. Perform starter circuit voltage drop tests; determine necessary action. 4. Inspect and test starter relays and solenoids; determine necessary action. 5. Remove and install starter in a vehicle. 6. Inspect and test switches, connectors, and wires of starter control circuits; perform necessary action. • Differentiate between electrical and engine mechanical problems that cause a slow-crank or no-crank condition. 7. List the equipment needed to perform a starter current draw test. • Explaining the process of performing starter current draw tests • Identifying proper course of action based on the test results 8. List the equipment needed to perform a starter circuit drop test. • Explaining the process of performing starter circuit drop tests • Identifying proper course of action based on the test results 9. List the equipment needed to test starter relays and solenoids. • Explaining the process of inspecting and testing starter relays and solenoids • Identifying proper course of action based on the test results • List tools need to remove and install a starter in a vehicle. 10. Explain the process in removing and installing a starter in a vehicle. 11. Identify switches, connectors, and wires of starter control circuits. 12. Identify the location of switches, connectors, and wires of starter control circuits. 13. Identify equipment used to test switches, connectors, and wires of starter control circuits. 14. Identify inspection and test criteria for switches, connectors, and wires of starter control circuits. 15. Explain the process of inspecting and testing switches, connectors and wires of starter control circuits. 16. Define slow crank. 17. Define no-crank condition. What equipment is needed to perform a starter circuit drop test? What operation must be performed to correct slow crank? Essential Question(s): Content Knowledge Current draw Current drop Circuit voltage drop Relays and solenoids Switches, connectors, and wires Starters and starter controls Electrical and engine mechanical problems Unit Assessment: Unit/Course CTSO Activity: Unit/Course Culminating Product: Suggested Instructional Activities Rigor & Relevance Framework (Quadrant) Brainstorming/Discussion Case Studies/ Scenarios Collaborative Learning Cooperative learning Demonstration Experiments Five plus one (5+1) Games Group investigation Guest Speaker Guided Practice Instructional Technology Laboratory/ Shop Exercise Lecture, Lecture/Demonstration Note Taking PBL (Problem Based Learning) Work Based Learning Work Sheets Suggested Materials, Equipment and Technology Resources Laboratory shop equipment Sample MSDS sheets Tools, supplies adequate for class numbers PPE in sufficient quantity for each student PowerPoint presentations Handouts Textbook, online and print Modules Online technical reference [AllData, Mitchell] Computers, laptop and desktop LCD projector SkillsUSA Technical Standards SkillsUSA PDP Written testing based on NATEF standards Performance evaluation based on NATEF standards The student will demonstrate safe shop practices, policies, and procedures on a daily basis. 1. Continue SkillsUSA Leadership Development Programs. 2. Establish documentation for students’ career portfolio. 3. Students review SkillsUSA Technical Standards and Contest Projects. Student will demonstrate knowledge of system being taught; provide accurate diagnosis of system and industry standard repairs. Removing repairing and replacing components of a vehicle located in the laboratory Accomplishment of appropriate NATEF performance standards Course/Program Credential(s): Other: NATEF Standards Credential Certificate Postsecondary Degree University Degree Diesel Electrical and Electronic Systems I Charging System Diagnosis and Repair Unit: 7 Content Standard(s) and Depth of Knowledge Level(s): Learning Objective(s) and Depth of Knowledge Level(s): Essential Question(s): Students will: 7. Explain charging system components and operations. Students will: 1. Diagnose instrument panel mounted volt meters and/or indicator lamps that show a no charge, low charge, or overcharge condition; determine needed action. 2. Diagnose the cause of a no charge, low charge, or overcharge condition, determine needed action. 3. Inspect, adjust, and replace alternator drive belts, pulleys, fans, tensioners, and mounting brackets. 4. Perform charging system voltage and amperage output test; determine needed action. 5. Perform charging circuit voltage drop tests; determine needed action. 6. Remove and replace alternator. 7. Inspect, repair, or replace connectors and wires I the charging circuit. 8. Diagnose AC voltage leakage (failed rectifier) at alternator output; determine needed action. How is a charging output test performed? What are the test criteria for switches? Content Knowledge Current draw Current drop Circuit voltage drop Relays and solenoids Switches, connectors, and wires Starters and starter controls Electrical and engine mechanical problems Suggested Instructional Activities Rigor & Relevance Framework (Quadrant) Brainstorming/Discussion Case Studies/ Scenarios Collaborative Learning Cooperative learning Demonstration Experiments Five plus one (5+1) Games Group investigation Guest Speaker Guided Practice Suggested Materials, Equipment and Technology Resources Laboratory shop equipment Sample MSDS sheets Tools, supplies adequate for class numbers PPE in sufficient quantity for each student PowerPoint presentations Handouts Textbook, online and print Modules Online technical reference [AllData, Mitchell] Computers, laptop and desktop LCD projector Instructional Technology Laboratory/ Shop Exercise Lecture, Lecture/Demonstration Note Taking PBL (Problem based Learning) Work Based Learning Work Sheets SkillsUSA Technical Standards SkillsUSA PDP Unit Assessment: Written testing based on NATEF standards Performance evaluation based on NATEF standards The student will demonstrate safe shop practices, policies, and procedures on a daily basis. Unit/Course CTSO Activity: Skills USA activity centered on appropriate industry practices and procedures including interschool competitions where practical. (Youth detention programs follow appropriate facility policies.) Students begin or continue their SkillsUSA Professional Development Program. Students review SkillsUSA Technical Standards. Unit/Course Culminating Product: Student will demonstrate knowledge of system being taught; provide accurate diagnosis of system and industry standard repairs. Removing repairing and replacing components of a vehicle located in the laboratory Accomplishment of appropriate NATEF performance standards Course/Program Credential(s): Other: NATEF Standards Credential Certificate Postsecondary Degree University Degree Diesel Electrical and Electronic Systems I Lighting System Diagnosis and Repair Unit: 8 Content Standard(s) and Depth of Knowledge Level(s): Learning Objective(s) and Depth of Knowledge Level(s): Essential Question(s): Students will: 8. Analyze lighting systems to determine necessary action. Students will: 1. Diagnose and repair lighting system malfunctions. 2. Diagnose the cause of brighter than normal, intermittent, dim, or no light operation; determine necessary action. 3. Inspect, replace, and aim headlights and bulbs. 4. Inspect and diagnose incorrect turn signal or hazard light operation; perform necessary action. 5. Define brighter than normal, intermittent, dim, or no light operation. 6. Describe inspection criteria for headlights and bulbs. 7. Identify incorrect turn signal. 8. Describe inspection criteria for turn signals and headlights. 9. Explain the process for inspecting and diagnosing incorrect turn signal or hazard light operation. What tools, equipment, and skills are required when properly troubleshooting lighting system malfunctions? Content Knowledge Light operation Light and lamp conditions Headlights and bulbs Turn signal and hazard light operation Wire sizes Suggested Instructional Activities Rigor & Relevance Framework (Quadrant) Laboratory demonstrations and experiments Guided practice Group investigation Listen, think, pair, share Demonstrations Discussion Individual and group practice Problem solving exercises Math application exercises Math application worksheets Suggested Materials, Equipment and Technology Resources Laboratory shop equipment Sample MSDS sheets Tools, supplies adequate for class numbers PPE in sufficient quantity for each student PowerPoint presentations Handouts Textbook, online and print Modules Online technical reference [AllData, Mitchell] Computers, laptop and desktop LCD projector SkillsUSA Technical Standards SkillsUSA PDP Unit Assessment: Unit/Course CTSO Activity: Unit/Course Culminating Product: Written testing based on NATEF standards Performance evaluation based on NATEF standards The student will demonstrate safe shop practices, policies, and procedures on a daily basis. 1. Continue SkillsUSA Leadership Development Programs. 2. Establish documentation for students’ career portfolio. 3. Students review SkillsUSA Technical Standards and Contest Projects. Student will demonstrate knowledge of system being taught; provide accurate diagnosis of system and industry standard repairs. Removing repairing and replacing components of a vehicle located in the laboratory Accomplishment of appropriate NATEF performance standards Course/Program Credential(s): Other: NATEF Standards Credential Certificate Postsecondary Degree University Degree Diesel Electrical and Electronic Systems I Gauge, Warning Device, and Driver Information System Diagnosis and Repair Unit: 9 Content Standard(s) and Depth of Knowledge Level(s): Learning Objective(s) and Depth of Knowledge Level(s): Essential Question(s): Students will: 9. Describe diesel electronic system gauges, warning devices, and driver information system operations. • Demonstrating component operations tests for diesel electronic systems Students will: 1. Diagnose and repair gauge and warning device system malfunctions. 2. Diagnose the cause of brighter than normal, intermittent, dim, or no light operation; determine necessary action. 3. Inspect and replace components as determined necessary. 4. Explain the process of inspecting and replacing components. What are potential dangers if the warning devices do not operate properly? Content Knowledge Gauges Warning devices Device inspection Electrical/electronic components Device replacement Suggested Instructional Activities Rigor & Relevance Framework (Quadrant) Laboratory demonstrations and experiments Guided practice Group investigation Listen, think, pair, share Demonstrations Discussion Individual and group practice Problem solving exercises Math application exercises Math application worksheets Suggested Materials, Equipment and Technology Resources Laboratory shop equipment Sample MSDS sheets Tools, supplies adequate for class numbers PPE in sufficient quantity for each student PowerPoint presentations Handouts Textbook, online and print Modules Online technical reference [AllData, Mitchell] Computers, laptop and desktop LCD projector SkillsUSA Technical Standards SkillsUSA PDP Unit Assessment: Unit/Course CTSO Activity: Unit/Course Culminating Product: Written testing based on NATEF standards Performance evaluation based on NATEF standards The student will demonstrate safe shop practices, policies, and procedures on a daily basis. 1. Continue SkillsUSA Leadership Development Programs. 2. Establish documentation for students’ career portfolio. 3. Students review SkillsUSA Technical Standards and Contest Projects. Student will demonstrate knowledge of system being taught; provide accurate diagnosis of system and industry standard repairs. Removing repairing and replacing components of a vehicle located in the laboratory Accomplishment of appropriate NATEF performance standards Course/Program Credential(s): Other: NATEF Standards Credential Certificate Postsecondary Degree University Degree Diesel Electrical and Electronic Systems I Horn, Wiper, and Washer Diagnosis and Repair Unit: 10 Content Standard(s) and Depth of Knowledge Level(s): Learning Objective(s) and Depth of Knowledge Level(s): Students will: 10. Demonstrate accuracy in diagnostic procedures for horn, wiper, and washer controls. Students will: 1. Diagnose and repair horn, wiper, and washer control problems. 2. Diagnose the cause of horn, wiper, and washer control problems. 3. Inspect and replace horn, wiper, washer, and control components. Where the sensor is typically located for automatic wipers? Essential Question(s): Content Knowledge Horn components Horn controls Wiper components Wiper blades Wiper controls Washer components Washer systems Washer controls Suggested Instructional Activities Rigor & Relevance Framework (Quadrant) Laboratory demonstrations and experiments Guided practice Group investigation Listen, think, pair, share Demonstrations Discussion Individual and group practice Problem solving exercises Math application exercises Math application worksheets Suggested Materials, Equipment and Technology Resources Laboratory shop equipment Sample MSDS sheets Tools, supplies adequate for class numbers PPE in sufficient quantity for each student PowerPoint presentations Handouts Textbook, online and print Modules Online technical reference [AllData, Mitchell] Computers, laptop and desktop LCD projector SkillsUSA Technical Standards SkillsUSA PDP Unit Assessment: Unit/Course CTSO Activity: Unit/Course Culminating Product: Written testing based on NATEF standards Performance evaluation based on NATEF standards The student will demonstrate safe shop practices, policies, and procedures on a daily basis. 1. Continue SkillsUSA Leadership Development Programs. 2. Establish documentation for students’ career portfolio. 3. Students review SkillsUSA Technical Standards and Contest Projects. Student will demonstrate knowledge of system being taught; provide accurate diagnosis of system and industry standard repairs. Removing repairing and replacing components of a vehicle located in the laboratory Accomplishment of appropriate NATEF performance standards Course/Program Credential(s): Other: NATEF Standards Credential Certificate Postsecondary Degree University Degree Diesel Electrical and Electronic Systems I Accessory Diagnosis and Repair Unit: 11 Content Standard(s) and Depth of Knowledge Level(s): Learning Objective(s) and Depth of Knowledge Level(s): Essential Question(s): Students will: 11. Utilize proper diagnostic procedures for accessories to determine necessary action. Students will: 1. Diagnose and repair accessory system problems. 2. Diagnose the cause of accessory system problems. 3. Inspect and replace accessory system components. 4. Explain the process of inspecting and diagnosing incorrect turn signal or hazard light operation. Why is a good understanding of electronics important in the diagnostics and repairs of accessories? Content Knowledge Accessory system components Accessory controls Accessory system inspection Accessory system component replacement Turn signals Hazard lights Suggested Instructional Activities Rigor & Relevance Framework (Quadrant) Laboratory demonstrations and experiments Guided practice Group investigation Listen, think, pair, share Demonstrations Discussion Individual and group practice Problem solving exercises Math application exercises Math application worksheets Suggested Materials, Equipment and Technology Resources Laboratory shop equipment Sample MSDS sheets Tools, supplies adequate for class numbers PPE in sufficient quantity for each student PowerPoint presentations Handouts Textbook, online and print Modules Online technical reference [AllData, Mitchell] Computers, laptop and desktop LCD projector SkillsUSA Technical Standards SkillsUSA PDP Unit Assessment: Unit/Course CTSO Activity: Unit/Course Culminating Product: Written testing based on NATEF standards Performance evaluation based on NATEF standards The student will demonstrate safe shop practices, policies, and procedures on a daily basis. 1. Continue SkillsUSA Leadership Development Programs. 2. Establish documentation for students’ career portfolio. 3. Students review SkillsUSA Technical Standards and Contest Projects. Student will demonstrate knowledge of system being taught; provide accurate diagnosis of system and industry standard repairs. Removing repairing and replacing components of a vehicle located in the laboratory Accomplishment of appropriate NATEF performance standards Course/Program Credential(s): Other: NATEF Standards Credential Certificate Postsecondary Degree University Degree