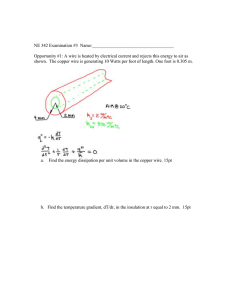
Homework week 5 (due February 17, 2008, 3AM PT)
advertisement
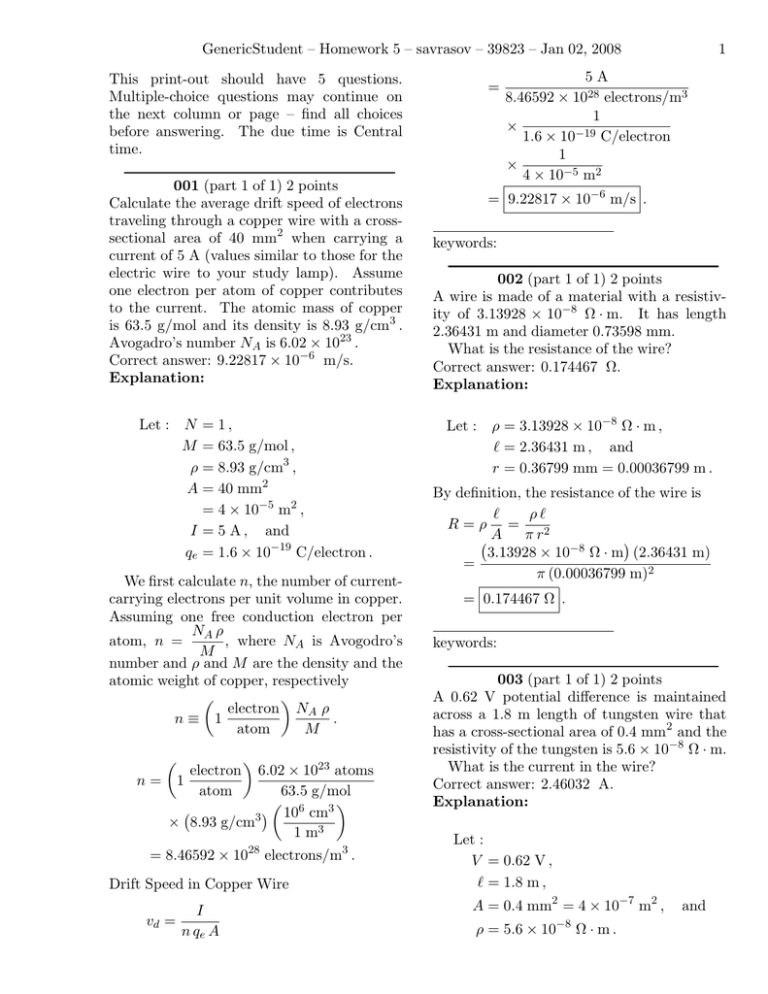
GenericStudent – Homework 5 – savrasov – 39823 – Jan 02, 2008 This print-out should have 5 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page – find all choices before answering. The due time is Central time. 001 (part 1 of 1) 2 points Calculate the average drift speed of electrons traveling through a copper wire with a crosssectional area of 40 mm2 when carrying a current of 5 A (values similar to those for the electric wire to your study lamp). Assume one electron per atom of copper contributes to the current. The atomic mass of copper is 63.5 g/mol and its density is 8.93 g/cm3 . Avogadro’s number NA is 6.02 × 1023 . Correct answer: 9.22817 × 10−6 m/s. Explanation: Let : N = 1 , M = 63.5 g/mol , ρ = 8.93 g/cm3 , A = 40 mm2 = 4 × 10−5 m2 , I = 5 A , and qe = 1.6 × 10−19 C/electron . We first calculate n, the number of currentcarrying electrons per unit volume in copper. Assuming one free conduction electron per NA ρ , where NA is Avogodro’s atom, n = M number and ρ and M are the density and the atomic weight of copper, respectively µ ¶ electron NA ρ n≡ 1 . atom M ¶ electron 6.02 × 1023 atoms n= 1 atom 63.5 g/mol µ 6 ¶ ¡ ¢ 10 cm3 3 × 8.93 g/cm 1 m3 = 8.46592 × 1028 electrons/m3 . µ Drift Speed in Copper Wire I vd = n qe A = 1 5A 8.46592 × 1028 electrons/m3 1 × −19 1.6 × 10 C/electron 1 × 4 × 10−5 m2 = 9.22817 × 10−6 m/s . keywords: 002 (part 1 of 1) 2 points A wire is made of a material with a resistivity of 3.13928 × 10−8 Ω · m. It has length 2.36431 m and diameter 0.73598 mm. What is the resistance of the wire? Correct answer: 0.174467 Ω. Explanation: Let : ρ = 3.13928 × 10−8 Ω · m , ` = 2.36431 m , and r = 0.36799 mm = 0.00036799 m . By definition, the resistance of the wire is ` ρ` R=ρ = π r2 ¡A ¢ 3.13928 × 10−8 Ω · m (2.36431 m) = π (0.00036799 m)2 = 0.174467 Ω . keywords: 003 (part 1 of 1) 2 points A 0.62 V potential difference is maintained across a 1.8 m length of tungsten wire that has a cross-sectional area of 0.4 mm2 and the resistivity of the tungsten is 5.6 × 10−8 Ω · m. What is the current in the wire? Correct answer: 2.46032 A. Explanation: Let : V = 0.62 V , ` = 1.8 m , A = 0.4 mm2 = 4 × 10−7 m2 , ρ = 5.6 × 10 −8 Ω · m. and GenericStudent – Homework 5 – savrasov – 39823 – Jan 02, 2008 2 The resistance is V ρ` R= = , I A so the current is VA ρ` (0.62 V) (4 × 10−7 m2 ) = (5.6 × 10−8 Ω · m) (1.8 m) I= = 2.46032 A . 005 (part 1 of 1) 2 points At 32 ◦ C the carbon resistor in an electric circuit, connected to a 4.3 V battery, has a resistance of 162 Ω. What is the current in the circuit when the temperature of the carbon rises to 71◦ C? Use a temperature coefficient of −0.0005 (◦ C)−1 . Correct answer: 27.0711 mA. Explanation: Let : keywords: 004 (part 1 of 1) 2 points One wire of a 13 m extension cord made of 16-gauge copper wire carrying a current of 3 A. What is the potential difference across the cord? Correct answer: 0.0947143 V. Explanation: T0 V R0 T1 = 32◦ C , = 4.3 V , = 162 Ω , = 71◦ C , and α = −0.0005 (◦ C)−1 . At 71◦ C the resistance has increased to R = R0 (1 + α ∆T ) = (162 Ω) © £ ¤ ª × 1 + −0.0005 (◦ C)−1 (39◦ C) = 158.841 Ω , so the current is Let : ρ = 1.7 × 10 ` = 13 m , −8 Ω · m, A = 7 mm2 = 7 × 10−6 m2 , I = 3 A. V 4.3 V 103 mA = · R 158.841 Ω 1A = 27.0711 mA . I= and keywords: The resistance is ρ` A (1.7 × 10−8 Ω · m) (13 m) = 7 × 10−6 m2 = 0.0315714 Ω . R= By Ohm’s Law, V = RI = (0.0315714 Ω) (3 A) = 0.0947143 V . keywords: