Selected Response Items
advertisement
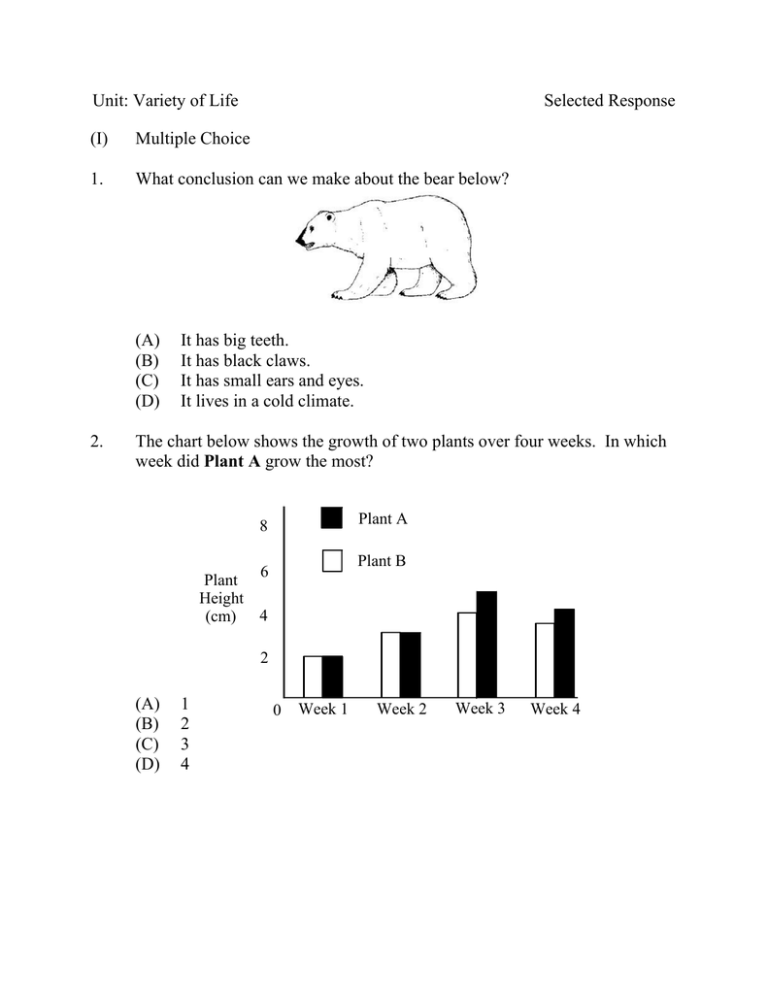
Unit: Variety of Life Selected Response (I) Multiple Choice 1. What conclusion can we make about the bear below? (A) (B) (C) (D) 2. It has big teeth. It has black claws. It has small ears and eyes. It lives in a cold climate. The chart below shows the growth of two plants over four weeks. In which week did Plant A grow the most? Plant A 8 Plant B 6 Plant Height (cm) 4 2 (A) (B) (C) (D) 1 2 3 4 0 Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Unit: Variety of Life 3. The diagram below shows the set up for a science experiment. What question can be answered from this experiment? (A) (B) (C) (D) 4. able to move from one place to another a hard exoskeleton makes its own food uses food to support its life functions Which characteristic would classify organisms as arthropods? (A) (B) (C) (D) 6. Can beans grow faster in groups of eight? Do beans need light in order to grow? Does seawater affect bean growth? How much water is needed for beans to grow? Which characterizes all living things? (A) (B) (C) (D) 5. Selected Response ability to make its own food backbone jointed legs seen only through a microscope Which is a kingdom in the classification of living things? (A) (B) (C) (D) Fish Fungi Mammals Reptiles 2 Unit: Variety of Life 7. Selected Response Which belongs to the kingdom Fungi? (A) (B) (C) (D) 8. Which organisms are able to make their own food? (A) (B) (C) (D) animals fungi micro-organisms plants 3 Unit: Variety of Life 9. Selected Response Which classification system would best suit the creatures below? Y X W (A) Z Shapes Angles Curves Antennae No antennae Antennae (B) No antenna Shapes Angles Curves One eye More than one eye One eye More than one eye Antennae (C) Two antennae Three antennae Angles Curves Curves Angles Antennae (D) Two antennae Three antennae 4 One eye More than one eye One eye More than one eye Unit: Variety of Life 10. What do fish, dogs, and birds have in common? (A) (B) (C) (D) 11. hair legs lungs spine Which kingdom contains organisms that were identified after the discovery of the microscope? (A) (B) (C) (D) 12. Selected Response Animals Fungi Plants Protists The classification system below groups trees based on leaf structure. Leaves of trees Needle-like Broad and flat Short, in bunches of three W Long, in Short, in bunches of bunches of five three Y X Long, in bunches of five Z What is the name of the tree that contains the leaf shown below? (A) (B) (C) (D) W X Y Z 5 Unit: Variety of Life 13. Selected Response Which animal would fit in the empty box? Animals with fur Animals without hooves Animals with hooves Animals with short tails Animals with Animals with long tails short tails (A) (B) (C) (D) 6 Animals with long tails Unit: Variety of Life 14. Selected Response Which animal belongs in group C below? Without feathers With feathers Group A With hair With scales Without scales Group B Group C Group D (A) (B) (C) (D) 7 Unit: Variety of Life 15. Which is found only in vertebrates? (A) (B) (C) (D) 16. backbone blood fur shells What is the difference between a reptile and an amphibian? (A) (B) (C) (D) 17. Selected Response An amphibian has a back bone and reptiles do not. An amphibian has adaptations for life on land and water and reptiles do not. A reptile has a back bone and amphibians do not. A reptile has adaptations for life on land and water and amphibians do not. Which is an arthropod? (A) (B) (C) (D) 8 Unit: Variety of Life 18. How do microorganisms benefit humans? (A) (B) (C) (D) 19. dry, cool, dark dry, warm, bright moist, cool, dark moist, warm, bright Which adaptation helps moose move through a thick wooded forest? (A) (B) (C) (D) 22. arm and base eyepiece and stage nosepiece and stage stage and base Which conditions most likely cause mold to grow on bread? (A) (B) (C) (D) 21. compost wastes increase food spoilage reproduce very quickly spread disease Which parts of a microscope should be held when carried? (A) (B) (C) (D) 20. Selected Response brown color large antlers long legs sense of smell Which structural adaptation do roses use for protection? (A) (B) (C) (D) flowers leaves roots thorns 9 Unit: Variety of Life 23. Selected Response Which part of the microscope is shown by X below? X (A) (B) (C) (D) 24. coarse adjustment knob eyepiece objective lens stage How much larger will the object appear through the microscope below? 10x 4x (A) (B) (C) (D) 10x 40x 100x 400x 10 40x 10x Object Unit: Variety of Life 25. What do palaeontologists study? (A) (B) (C) (D) 26. Selected Response climate fossils living things rocks Which organism is best adapted for a hot climate? (A) (B) (C) (D) 11 Unit: Variety of Life 27. Selected Response Euglena is a microorganism that contains a tapered whip-like tail. What is most likely the function of this tail? Euglena (A) (B) (C) (D) 28. feeding moving protection reproduction Which is best adapted for life in water? (A) (B) (C) (D) 12 Unit: Variety of Life 29. What adaptation makes the animal below best suited for movement in winter? (A) (B) (C) (D) 30. large ears large feet long arms long legs How do many northern birds prepare for cold winters? (A) (B) (C) (D) 31. Selected Response cover themselves fly south hibernate sit on their nests What protects the animal below from predators? (A) (B) (C) (D) hard shell long neck small mouth thick legs 13 Unit: Variety of Life 32. Selected Response Which beak below would be most helpful for a bird that eats nectar in flowers? (A) (B) (C) (D) 33. Raccoons living in cities are able to open garbage can lids. What does this ability best represent? (A) (B) (C) (D) adapting to its new environment becoming a plant eater being tamed by humans developing a strong sense of smell 14 Unit: Variety of Life 34. Which of these adaptations would best help animals survive in a very dry environment with hot daytime temperatures and cold night time temperatures? (A) (B) (C) (D) 35. Selected Response ability to climb tall trees ability to tunnel underground thick fur webbed feet Porcupines have sharp quills. For what purpose is this structure needed? Quills (A) (B) (C) (D) 36. Which would help a plant survive in an environment that is very hot in the day, cool at night, has little rain during the year and has strong wind storms? (A) (B) (C) (D) 37. camouflage movement protection warmth broad thick leaves small waxy leaves tall trunk with thick bark short trunk with thin bark What explains the presence of many different species of trout in Newfoundland and Labrador? (A) (B) (C) (D) artificial selection cross-breeding natural selection spread of disease 15 Unit: Variety of Life (II) Selected Response Completion 1. A(n) _____________ is the outer covering of an arthropod’s body. 2. ______________ are structural features and abilities that enable an organism to survive in its environment. 3. A(n) _______________ is a scientist that studies fossils. 4. A(n) _____________ is an animal with a backbone. 5. ________________ is a method of organizing and grouping things with like characteristics. 6. A(n) ________________ is any organism that is so small that you need a magnifier to view it. 7. A(n)__________ is the remains or traces of life from the past. 8. An invertebrate that has jointed legs and an exoskeleton is a(n) ____________ . 9. Each distinct kind of living thing is called a(n) _________. 10. A(n) __________ is an arthropod with 3 pairs of jointed legs and 3 body parts. (III) True and False 1. It doesn’t matter how scientists classify organisms as long as they understand how they did it. ________ 2. Some bacteria are helpful to people. ________ 3. Animals that do not have a skeleton are arthropods. ________ 4. All invertebrates have an exoskeleton. ________ 5. Vertebrates are the most numerous organisms on Earth. ________ 16 Unit: Turn It On! Selected Response (I) Multiple Choice 1. Which safety precaution would best free a piece of toast stuck in a toaster? (A) (B) (C) (D) 2. What is the purpose of a fuse? (A) (B) (C) (D) 3. chemical energy current electricity mechanical energy static electricity Which is a good electrical conductor? (A) (B) (C) (D) 5. decrease bulb brightness distribute electricity through the house increase the power to an appliance prevent overheating of the circuit A person receives a shock when they touch a door handle. What kind of energy does the person feel? (A) (B) (C) (D) 4. make sure the toaster is plugged in remove the toast with a metal spoon unplug the toaster to prevent electric shock wet your hands so they don’t get burned glass metal plastic wood Which uses electricity? (A) (B) (C) (D) calculator candle skateboard tricycle 17 Unit: Turn It On! 6. Which is an example of wasting electricity? (A) (B) (C) (D) 7. The ground prong has been removed. The plug is coloured black. The plug wire is thin. The prongs have a hole in them. What is the best object to touch to remove a static electric charge? (A) (B) (C) (D) 9. adding insulation to homes taking baths instead of showers turning down a thermostat using lower watt light bulbs Which safety hazard is associated with this plug? (A) (B) (C) (D) 8. Selected Response concrete wall leather chair metal sink wooden door Which pair of objects could be separated using an electromagnet? (A) (B) (C) (D) aluminum and steel ceramic and plastic copper and aluminum glass and lead 18 Unit: Turn It On! 10. Which electrical device uses an electromagnet? (A) (B) (C) (D) 11. heating water in a 1000 Watt kettle for 15 minutes operating five 100 Watt light bulbs for 60 minutes using a 250 Watt computer for 120 minutes using a 3000 Watt heater for 30 minutes When two materials are rubbed together, which has the greatest effect on the production of static electricity? (A) (B) (C) (D) 14. holds the plug tighter to the wall makes it easier to hold in your hand provides a path to the ground increases power to the appliance Which uses the most electrical energy? (A) (B) (C) (D) 13. coffee pot drill kettle light bulb What is the function of the third prong on a plug? (A) (B) (C) (D) 12. Selected Response amount of time rubbed size of materials time of day type of materials In the circuit below, what happens to bulb A when bulb B is added? A (A) (B) (C) (D) blows out gets brighter gets duller stays the same Before 19 A After B Unit: Turn It On! 15. Selected Response Which circuit is complete? (A) (B) (C) (D) 20 Unit: Turn It On! 16. In the diagram below, what is needed to light the bulb? (A) (B) (C) (D) 17. 18. bigger wire filament longer wire more cells If a 3 volt battery contains two 1.5 volt cells, how many cells does a 9 volt battery contain? (A) 3.0 (B) 4.5 (C) 6.0 (D) 12.0 Which source of electricity is most environmentally friendly? (A) (B) (C) (D) 19. Selected Response hydro nuclear solar thermal Which sources of energy are renewable? (A) (B) (C) (D) nuclear, fossil fuels, solar nuclear, fossil fuels, wind water, solar, fossil fuels water, solar, wind 21 Unit: Turn It On! 20. Selected Response Which would be the strongest electromagnet? (A) (B) (C) (D) 22 Unit: Turn It On! (II) Selected Response Completion 1. A ____________ is a device with blades that are turned by the force of water, steam or gas to power a generator. 2. A _______________ is a path along which electricity flows. 3. In a _______________ circuit, each bulb shares its power source with other bulbs. 4. _______________ electricity is produced by rubbing certain materials together. 5. A(n) __________________ is made by wrapping an iron rod with a coil of copper wire and running electric current through it. 6. A ________________ is a device that changes mechanical energy into electrical energy. 7. A ______________ is a device that allows you to control the flow of electricity through a circuit. 8. A __________________ is a substance that allows electricity to flow through it easily. 9. ____________________ is a form of energy produced when a current of electrons flow through a circuit. 10. As a safety precaution, if a circuit has too much electricity flowing through it, the wire in a ____________ will melt and cause a break in the circuit. 23 Unit: Turn It On! Selected Response (III) Matching 1. wind turbine ______ a. when two electrically charged objects pull together 2. repulsion ______ b. a substance that does not allow electricity to flow 3. energy _____ d. the path along which electricity flows 4. insulator _____ e. electricity that uses water as its source 5. electrons _____ f. tiny particles found in atoms 6. hydroelectricity _____ 7. attraction 8. circuit g. when two electrically charged objects push away from each other _____ _____ h. a machine with blades that are turned by the force of moving gases i. a force that makes things change 24 Unit: The Sky’s the Limit (I) Multiple Choice 1. Which force slows a flying object? (A) (B) (C) (D) 2. Selected Response drag inertia lift thrust Which glider will fly straight and level? (A) (B) (C) (D) 25 Unit: The Sky’s the Limit 3. Selected Response Which position of the parts on the airplane produces the most drag? aileron rudder flap flap aileron 4. ailerons flaps rudder (A) down down right (B) level level straight (C) level down right (D) up level left Which shape will create the most drag? (A) (B) (C) (D) 26 Unit: The Sky’s the Limit 5. Which are opposing forces? (A) (B) (C) (D) 6. 7. Thrust Wing Surface (A) less less (B) less more (C) more less (D) more more What part of an airplane pulls it through the air? airfoil jet engine propeller wing Which Canadian made a significant contribution to flight? (A) (B) (C) (D) 9. drag and gravity drag and resistance lift and gravity lift and resistance Which combination of thrust and wing surface would provide the most lift? (A) (B) (C) (D) 8. Selected Response Charles Lindburg John McCurdy Orville Wright William Alcock Which demonstrates Bernoulli’s Principle? (A) (B) (C) (D) air blowing through a window hot air balloon rising shower curtain moving toward the stream of water running through a swimming pool of water 27 Unit: The Sky’s the Limit 10. Selected Response Which combination of forces enables an aircraft to climb to a higher altitude? (A) Thrust Drag Lift Gravity Thrust Drag Lift Gravity Thrust Drag Lift Gravity Thrust Drag Lift Gravity (B) (C) (D) 28 Unit: The Sky’s the Limit 11. Selected Response Which wing profile demonstrates the proper terms and forces? low pressure (A) trailing edge leading edge high pressure high pressure (B) trailing edge leading edge low pressure low pressure (C) trailing edge leading edge high pressure high pressure (D) trailing edge leading edge low pressure 12. What is the best way to test a new wing design? (A) (B) (C) (D) attach the wing to a plane and fly it drag the wing through water observe the wing test wing in a wind tunnel 29 Unit: The Sky’s the Limit 13. What could happen to the tent below if the front and back doors were opened on a windy day? (A) (B) (C) (D) 14. air gravity light water What is the best means of propulsion for a trip to the moon? (A) (B) (C) (D) 16. Only the roof would push up. The doors would close. The floor and roof would push up. The roof and the sides would push in. What is needed in order for a propeller driven plane to fly? (A) (B) (C) (D) 15. Selected Response flappable wings jet engines propellers rocket boosters Which was first used to fly? (A) (B) (C) (D) bi-plane balloon shuttle jet 30 Unit: The Sky’s the Limit 17. Which activity became popular with fast air travel? (A) (B) (C) (D) 18. Selected Response computer use home construction oil exploration tropical vacations Different shaped objects were placed between the candle and the wind tunnel. Which setup would most likely blow out the candle first? (A) wind direction wind tunnel candle (B) wind direction wind tunnel candle (C) wind direction wind tunnel candle (D) wind direction wind tunnel candle 31 Unit: The Sky’s the Limit Selected Response (II) Completion 1. An upward force called __________ enables planes to fly. 2. __________ is a force that acts against a moving object. 3. Jet engines produce __________ to push it forward. 4. An airplane wing provides __________ and the propeller provides __________. 5. __________ allows airplanes to move with as little resistance as possible. (III) Matching 1. Propulsion _____ a. height above Earth’s surface 2. Ailerons _____ b. the ability to move an object 3. Rudder _____ c. hinged sections of a plane that control its balance from side to side 4. Manoeuvrable _____ d. driving force that pushes a boat forward 5. Altitude _____ e. enables an aircraft to move left or right (IV) True and False 1. Air helps keep balloons and parachutes in the air. ________ 2. Air is much lighter than most solids. ________ 3. Balloons are able to fly because the air on the inside is heavier than the air outside. ________ 4. The movement of an object is the result of unequal forces. ________ 5. Compressed air has less force than air that is not compressed. ________ 32 Unit: Out of This World Selected Response (I) Multiple Choice 1. What is the most important thing to consider when designing clothing for astronauts? (A) (B) (C) (D) 2. Which two countries have contributed the most to space exploration? (A) (B) (C) (D) 3. Edwin (Buzz) Aldrin Marc Garneau Neil Armstrong Yuri Gagarin How do satellite images help people on Earth? (A) (B) (C) (D) 5. Canada and Brazil Germany and Great Britain Mexico and Australia Russia and United States Which astronaut is Canadian? (A) (B) (C) (D) 4. comfort fashion pockets for storage protection from heat highlight constellation formations indicate connections in food webs track weather systems show political boundaries During a recent space mission to Mars, scientists found water a few feet underground. What conclusion could be made about Mars from this discovery? (A) (B) (C) (D) It is the closest planet to Earth. It is the farthest planet from Earth. Life could have existed there. Life never existed there. 33 Unit: Out of This World 6. What effect does the moon have on Earth? (A) (B) (C) (D) 7. rises in the east and sets in the west rises in the north and sets in the south rises in the south and sets in the north rises in the west and sets in the east What period of time is equal to one complete revolution of a planet around the sun? (A) (B) (C) (D) 10. one day one month twelve days twelve months What is the general path the sun takes as it appears to move across the sky? (A) (B) (C) (D) 9. daylight global warming seasons tidal changes How much time does it take Earth to make one complete revolution around the sun? (A) (B) (C) (D) 8. Selected Response day month week year Which planet has the longest year in Earth time? (A) (B) (C) (D) Earth Mars Mercury Venus 34 Unit: Out of This World 11. Selected Response The diagram below represents a lunar eclipse. What does each letter indicate? X Y Z X Y Z (A) Earth moon sun (B) Earth sun moon (C) sun Earth moon (D) sun moon Earth 12. The diagram below represents a view of Earth from above the North Pole. What does each letter indicate? Z North Pole Y W X W X Y Z (A) noon sunrise midnight sunset (B) noon sunset midnight sunrise (C) sunrise midnight noon sunset (D) sunrise midnight sunset noon 35 Unit: Out of This World 13. Which planet is closest to the sun? (A) (B) (C) (D) 14. ball of gas that gives off light ball of rock that orbits Earth small chunk of ice that orbits the sun small chunk of rock that orbits the sun What best describes a comet? (A) (B) (C) (D) 17. body that orbits planets body that reflects light planet in our solar system star in our solar system What is a meteoroid? (A) (B) (C) (D) 16. Earth Mars Mercury Venus Which best describes the sun? (A) (B) (C) (D) 15. Selected Response ice, gas and dust which orbits Earth ice, gas and dust which orbits the sun rock, water, and waste which orbits Earth rock, water, and waste which orbits the sun Which group of planets have rocky surfaces? (A) (B) (C) (D) Earth, Mercury, Jupiter Jupiter, Saturn, Neptune Mercury, Venus, Earth Venus, Neptune, Pluto 36 Unit: Out of This World 18. If all the planets started together on their orbits around the sun, which one would finish last? (A) (B) (C) (D) 19. Jupiter Mercury Pluto Saturn Which planet is closest to Earth? (A) (B) (C) (D) 20. Selected Response Jupiter Mercury Saturn Venus Which letter in the diagram below represents Mars? Sun W (A) (B) (C) (D) 21. X Earth Y W X Y Z What is a star? (A) (B) (C) (D) A large ball of gas that gives off light and heat. A large, icy object that orbits the Sun. A small ball of gas that gives off light and heat. A small, icy object that orbits the Sun. 37 Z Unit: Out of This World 22. Which is true about constellations? (A) (B) (C) (D) 23. to guide them during space travel to guide them during explorations to provide energy for space stations to provide energy for their homes What is a constellation? (A) (B) (C) (D) (II) They are always visible in the night sky. They are found within our solar system. They are named after characters from stories. They are visible because they reflect the sun’s light. In what way did people use stars in the past? (A) (B) (C) (D) 24. Selected Response collection of stars and the moon group of stars which form a pattern reflection from the sun star which has burnt out Completion 1. The ____________ is the center of our Solar System. 2. ____________ is debris which looks like dirty snowballs in space. 3. ____________ is rocky, metallic objects that orbit the Sun. 4. Ursa Major and Ursa Minor are _____________. 5. ____________ helps us to observe the sky. 38 Unit: Out of This World Selected Response (III) Matching 1. Jupiter _____ a. closest to the sun 2. Venus _____ b. has a large ring system 3. Uranus _____ c. largest planet 4. Neptune _____ d. looks red and is mostly desert 5. Mercury _____ e. close to Earth and similar in size 6. Earth _____ f. spins on its side 7. Saturn _____ g. furthest from the sun 8. Mars _____ h. first planet to be identified 9. Pluto _____ i. able to support living things (IV) True and False 1. During a lunar eclipse, a person cannot see the moon. _____ 2. The sun only shines on Earth during the daytime. _____ 3. During a solar eclipse, the moon blocks the sun’s light from Earth. _____ 4. The sun is the closest star to Earth. _____ 5. A person’s body weight on Earth is less than on the moon. _____ 39