01 Faraday`s Law and Linear DC Machine
advertisement

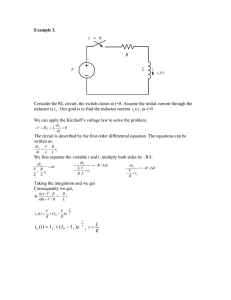
Faraday’s Law and Linear DC machine Faraday’s Law (I) d d C E dl dt S B dS dt B dl C n E S Electromotive Force (emf) ------ V emf E dl C Total Magnetic Flux ------ Wb B dS S Faraday’s Law (II) d d C E dl dt S B dS dt B dl C n E S • The emf generated around a closed contour C is related to the time rate of change of the total magnetic flux through the open surface S bounded by that contour. Faraday’s Law (III) d d C E dl dt S B dS dt • Lenz’s Law: The emf induced in the contour is of a polarity that tends to generate an induced current whose magnetic flux tends to oppose any change in the original magnetic flux. i E B --Vind +++ B Vind d dt Faraday’s Law (IV) Top view B B --Vind N turns +++ Vind d N dt + Vind - Inductor Operation 1 (Like Generator) R i Bext --Vind i +++ R i + Vind - B dS B S Vind N i Bfrom i N turns Note: B is total magnetic flux density. B Bexternal Bfrom i Bext S ext dS Bfrom i dS ext from i Bfrom i S d d ext d from i d ext d from i d ext di N N N N L dt dt dt dt dt dt dt i is induced current: Vind i R Dynamical equation: di R N d ext (t ) i dt L L dt Inductor Operation 2 (Like Motor) R + ~ V (t ) s - i R --Vindd +++ B B i + + i - ~ V (t ) V ind s - i N turns Note: i is total current or actual current in operation Vs (t ) Vind Vs (t ) Vind i Magnetic flux density B comes from i. R R R d d di Vind N Dynamical equation: dt dt V (t ) di R i s dt L L L dt Induced Voltage from a Moving Bar B B + + Vind - Vind l v v - 0 BA Blx Vind x d dx Bl Blv dt dt Magnetic Force – Biot-Savart’s Law dF idl B B dF idl B l i F F=Bli Linear Machine – Case 1 (Motor, No Load) i t=0 VB B + R Vind 0 1. t 0, close the switch, it 0 Find VB , Find Blit 0 R l x dv Find M , M : mass of bar, v : velocity of bar. The bar will accelerate. dt VB Vind 2. v , Vind Blv , i , Find Bli R 3. When Vind VB , i 0, Find 0, no force is on the bar. The machine reaches steady state with constant velocity v. V V From Vind Blv, we have v ind B . Bl Bl Linear Machine – Case 2 (Motor, with Load) i t=0 B + R VB Vind - Fload Find l x 0 1. t 0, close the switch, it 0 VB , Find Blit 0 , R Fnet Find Fload The bar will accelerate if Fnet 0. Fnet M dv dt VB Vind , Find Bli R 3. When Find Fload or Fnet 0, motor reaches steady state with constant velocity v. Find Vind From Find Fload Bli, we get i . Vind VB -iR Blv, we have v . Bl Bl 2. v , Vind Blv , i Linear Machine – Case 3 (Generator) i B + R Find Vind - l Fapply x 0 1. t 0, apply Fapply, the bar will accelerate. Fapply M dv dt Vind , Find Bli , opposite to Fapply or against th e motion. R 3. When Fnet Fapply Find 0, reaches steady state with constant velocity v. 2. v , Vind Blv , i From Find Fapply Bli, i Fapply Bl . From Vind iR Blv, v Vind . Bl Linear Machine – Case 4 (Mixed - 1) i (t=∞) t=0 VB R i(t=0) + Vind - F ind B Fload Fapply l (t=∞) Find (t=0) x 0 Assume Fext Fapply Fload 0 VB , Find Bli in the direction of Fapply R dv Fnet Fapply Find Fload. The bar will accelerate if Fnet 0. Fnet M dt V V 2. v , Vind Blv , i B ind , Find Bli . R WhenVind VB , i 0, Find 0. Since Fext Fapply Fload 0, the bar will still accelerate. 1. t 0, close the switch and apply Fapply, it 0 Linear Machine – Case 4 (Mixed - 2) B t=0 VB R i(t=0) + Vind - F ind Fload Fapply l (t=∞) Find (t=0) x 0 3. Vind , Vind VB , directions of i and Find Bli changed, device becomes generator. 4. When Find Fext or Fnet 0, bar reaches steady state with constant velocity v From Find Fapply Fload Bli, we get it Vind Vind VB it R Blv, we have v . Bl Find . Bl Example B t=0 R Fload VB Fapply l 0 B = 0.1 T l = 10 m VB=120 V R = 0.3 W x Find steady state current and speed of the bar if (1) No external force; (2) Fload 30N; also plot vsteady for Fload from 0 to 50N (3) Fapply 30N; also plot vsteady for Fapply from 0 to 50N. (1) – Case 1, (2) – Case 2, (3) – Case 4 Linear Machine – Transient Analysis (1) B t=0 VB R + i Vind 0 Fload Fapply l Find x dv Fnet Fapply Find Fload , Fnet M dt VB Vind Vind Blv, i , Find Bli. R dv V V M Fapply Find Fload Fapply Bli Fload Fapply Bl B ind Fload dt R VB Blv ( Bl )2 BlVB Fapply Fload Bl v Fapply Fload R R R dv ( Bl )2 1 BlVB Dynamical Equation : v Fapply Fload dt MR M R Linear Machine – Transient Analysis (2) B t=0 VB R i + Vind - 0 Fload Fapply l Find x dv ( Bl )2 1 BlVB Dynamical Equation : v Fapply Fload dt MR M R dv For steady state : 0, we have : dt Fapply Fload VB vsteady R ( Bl )2 Bl Linear Machine – Transient Analysis (3) Velocity (m/s) 150 B = 0.1 T l = 10 m VB=120 V R = 0.3 W 100 50 0 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2 Time (s) 1.4 1 1.2 Time (s) 1.4 1.6 1.8 2 M = 1 kg Fapply = 40 N Fload = 20 N 400 Current (A) 300 200 100 0 -100 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.6 1.8 2 EMF Constant and Force Constant Vind Blv Vind Bl EMF Constant: k E v F Bli F Bl Force Constant: k F i kE kF How to Solve a Dynamic Equation Using SimuLink? dx dt z dy p dt dz 2 1 2x 2 1 a sin y 1 2 2 2 dt 1 x ( 1 x ) 2 dp 1 2 1 1 a sin y a sin( 2 y ) 2 dt 1 x Solve Assume x(0) 0; y (0) 0; z(0) 2sin ; p(0) 2cos a 0.01 30o dynamic.mdl Another Example R B i + + ~ V (t ) V ind s - Dynamical equation: i Vs (t ) di R i dt L L R 1W, L 2 H , Vs (t ) 5cos(2 t ) i (0) 0