EE221L Good Prelab Example - University of Nevada, Las Vegas
advertisement

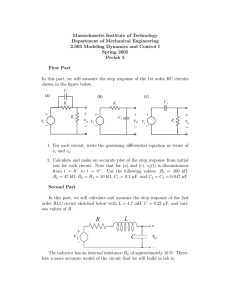
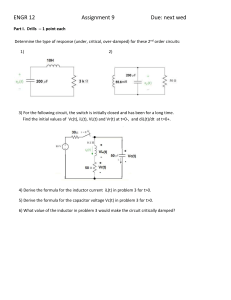
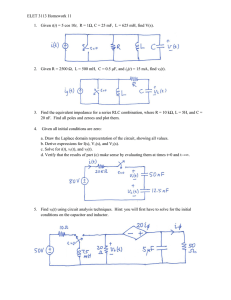
UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA L AS VEGAS . DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING LABORATORIES . Class: EE221 Circuits II - 1002 Points Semester: Fall 2015 Document author: Author's email: Prelab 5 Document topic: Instructor's comments: Introduction / Theory of operation An RC circuit is a circuit composed of resistors, capacitors and a voltage source. The charge and discharge time of the capacitor is dependent on both the series resistance and the capacitance. The charge rate is given by V = Vmax * (1 – e-t/(RC)) where R is the resistance and C is the capacitance. The discharge rate is given by V = Vmax * e-5/(RC). The capacitor is approximately entirely discharge in 5 time constants (5 * RC). An RL circuit consists of a resistor, an inductor and a voltage source. The charge time for an inductor is dependent on the resistance and the inductance. The charge rate is given by I(t) = Vin/R * (1 – e-tR/L). An RLC circuit consists of a resistance, inductance and capacitance. The response of the circuit depends on all three elements. The circuit can have either an underdamped response, overdamped response, or a critical response. An underdamped response will resonate naturally. A critically damped response is just on the edge of oscillation. An overdamped response will not oscillate at all. Prelab main content Analysis 1: τ = RC = (200KΩ)(220μF) = 44s 5τ = 5 ∗ 44s = 220s Therefore, it takes 220 seconds to charge the capacitor. −𝑡 (𝜏) ) = 0 ( ) 𝑒 44𝑠 ) = −𝑡 (44𝑠) 𝑉𝑜𝑢𝑡 (𝑡) = 𝑉𝑖𝑛 (1 – 𝑒 𝑉𝑖𝑛 (1 – 𝑒 𝑉𝑜𝑢𝑡 (0) = 𝑉𝑖𝑛 (1 – 𝑉𝑖𝑛 (0) = 0 𝑉𝑜𝑢𝑡 (∞) = 𝑉𝑖𝑛 (1 – 𝑒 −∞ (44𝑠) ) = 𝑉𝑖𝑛 (1) = 𝑉𝑖𝑛 ) Figure 1: Analysis 1 LTSpice circuit (Left), and The simulation of the circuit (Right) Analysis 2: τ = RC = (200KΩ)(220μF) = 44s 5τ = 5 ∗ 44s = 220s Therefore, it takes 220 seconds to discharge the capacitor. −𝑡 (𝜏) = 𝑉𝑖𝑛 0 ( 𝜏) 𝑉𝑖𝑛 ∗ 𝑒 = 𝑉𝑖𝑛 −∞ ( ) 𝑉𝑖𝑛 ∗ 𝑒 𝜏 = 0 𝑉𝑜𝑢𝑡 (𝑡 ) = 𝑉𝑖𝑛 ∗ 𝑒 𝑉𝑜𝑢𝑡 (0) = 𝑉𝑜𝑢𝑡 (∞) = ∗𝑒 −𝑡 (44𝑠) Figure 2: Analysis 2 circuit (Left) and the simulation (Right) Analysis 3: τ= 𝐿 1.2mH = = 12μs 𝑅 100 −𝑡 −𝑡 𝑉𝑖𝑛 𝑉𝑖𝑛 (1 − 𝑒 τ ) = (1 − 𝑒 12μs) 𝑅 𝑅 0 𝑉𝑖𝑛 𝐼 (0) = (1 − 𝑒 12μs) = 0 𝑅 ∞ 𝑉𝑖𝑛 𝑉𝑖𝑛 (1 − 𝑒 12μs ) = 𝐼 (∞) = 𝑅 𝑅 𝐼 (𝑡 ) = Analysis 4: 𝛼 𝑅 1 𝐿𝑒𝑡 𝜉 = , 𝑤ℎ𝑒𝑟𝑒 𝛼 = , 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝜔0 = , 𝑡ℎ𝑒𝑛 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑟𝑒𝑠𝑝𝑜𝑛𝑠𝑒𝑠 𝑎𝑟𝑒: ω0 2𝐿 √𝐿𝐶 𝐶𝑟𝑖𝑡𝑖𝑐𝑎𝑙𝑙𝑦 𝑑𝑎𝑚𝑝𝑒𝑑 𝑤ℎ𝑒𝑛 𝜉 = 1 𝑂𝑣𝑒𝑟𝑑𝑎𝑚𝑝𝑒𝑑 𝑤ℎ𝑒𝑛 𝜉 > 1 𝑈𝑛𝑑𝑒𝑟𝑑𝑎𝑚𝑝𝑒𝑑 𝑤ℎ𝑒𝑛 𝜉 < 1 For this circuit, 𝛼 𝑅 100 𝜉= = ∗ √𝐿𝐶 = >1 ω0 2𝐿 4.32 ∗ 10−8 So, the circuit is overdamped 𝑅 2𝐿 2(1.2 ∗ 10−3 ) ̅̅Ω 𝜉= = ∗ √𝐿𝐶 = 1 → 𝑅 = = = 133. ̅̅ 33 ω0 2𝐿 √𝐿𝐶 √1.2 ∗ 10−3 ∗ 0.27 ∗ 10−6 𝛼 This circuit will be ̅̅̅̅Ω 𝑂𝑣𝑒𝑟𝑑𝑎𝑚𝑝𝑒𝑑 𝑤ℎ𝑒𝑛 𝑅 > 133. 33 ̅̅Ω 𝐶𝑟𝑖𝑡𝑖𝑐𝑎𝑙𝑙𝑦 𝑑𝑎𝑚𝑝𝑒𝑑 𝑤ℎ𝑒𝑛 = 133. ̅̅ 33 ̅̅ ̅̅ 𝑈𝑛𝑑𝑒𝑟𝑑𝑎𝑚𝑝𝑒𝑑 𝑤ℎ𝑒𝑛 𝑅 < 133. 33Ω Overdamped circuit Critically damped circuit Underdamped circuit Analysis 5: 𝛼 𝐿𝑒𝑡 𝜉 = , 𝑤ℎ𝑒𝑟𝑒 𝛼 = 1 1 , 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝜔0 = , 𝑡ℎ𝑒𝑛 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑟𝑒𝑠𝑝𝑜𝑛𝑠𝑒𝑠 𝑎𝑟𝑒: ω0 2𝑅𝐶 √𝐿𝐶 𝐶𝑟𝑖𝑡𝑖𝑐𝑎𝑙𝑙𝑦 𝑑𝑎𝑚𝑝𝑒𝑑 𝑤ℎ𝑒𝑛 𝜉 = 1 𝑂𝑣𝑒𝑟𝑑𝑎𝑚𝑝𝑒𝑑 𝑤ℎ𝑒𝑛 𝜉 > 1 𝑈𝑛𝑑𝑒𝑟𝑑𝑎𝑚𝑝𝑒𝑑 𝑤ℎ𝑒𝑛 𝜉 < 1 For this circuit, 1 𝐿 √ = 0.333 < 1 ω0 2𝑅 𝐶 So, the circuit is underdamped 𝜉= 𝜉= 𝛼 𝛼 ω0 = = 1 𝐿 1 𝐿 ̅̅ √ = 1 → 𝑅 = √ = 33. ̅̅ 33 2𝑅 𝐶 2 𝐶 This circuit will be ̅̅Ω 𝑂𝑣𝑒𝑟𝑑𝑎𝑚𝑝𝑒𝑑 𝑤ℎ𝑒𝑛 𝑅 < 33. ̅̅ 33 ̅̅̅̅Ω 𝐶𝑟𝑖𝑡𝑖𝑐𝑎𝑙𝑙𝑦 𝑑𝑎𝑚𝑝𝑒𝑑 𝑤ℎ𝑒𝑛 = 33. 33 ̅̅̅̅Ω 𝑈𝑛𝑑𝑒𝑟𝑑𝑎𝑚𝑝𝑒𝑑 𝑤ℎ𝑒𝑛 𝑅 > 33. 33 Overdamped circuit: Critically damped circuit: Underdamped circuit: Altium: Fig 4-1: [ ] [ ] [ Vin HDR1X2 Header 2 R1 AXIAL-0.3 Res1 C1 RAD-0.3 Cap ] Fig 4-2: [ ] [ Vin HDR1X2 Header 2 C1 RAD-0.3 Cap ] [ R1 AXIAL-0.3 Res1 ] Fig 4-3: [ ] [ ] [ ] Vin HDR1X2 Header 2 R1 AXIAL-0.3 Res1 L1 0402-A Inductor Fig 4-4: [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ Vin HDR1X2 Header 2 S1 SPST-2 SW-PB R2 AXIAL-0.3 Res1 R1 AXIAL-0.3 Res1 L1 0402-A Inductor c2 RAD-0.3 Cap ] Fig 4-5: [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] s1 SPST-2 SW-PB r1 AXIAL-0.3 Res1 l1 0402-A Inductor Iin HDR1X2 Header 2 c1 RAD-0.3 Cap